本文已被:浏览 369次 下载 1963次
投稿时间:2023-05-08 修订日期:2024-09-10
投稿时间:2023-05-08 修订日期:2024-09-10
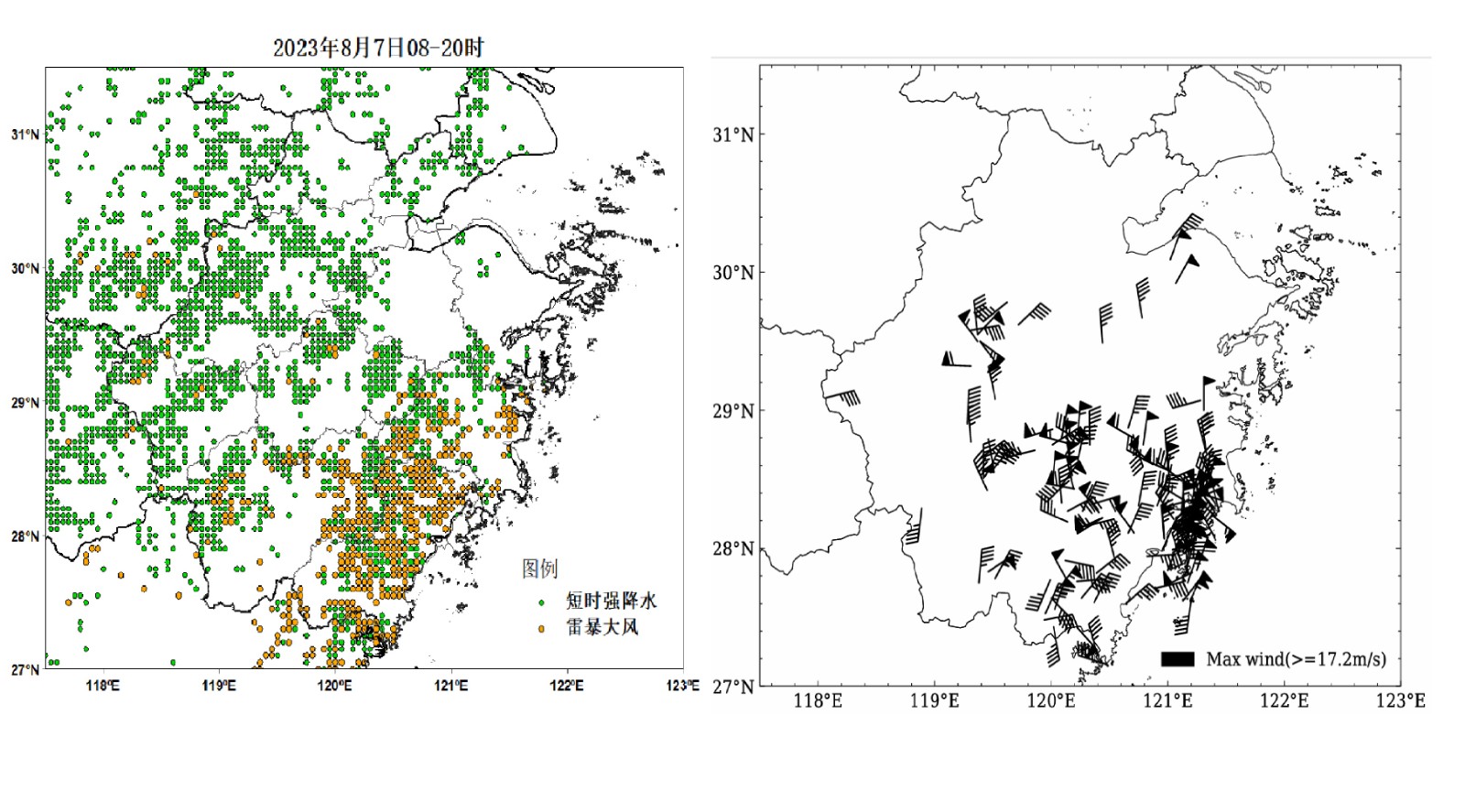
中文摘要: 如何提高强对流天气的客观分类和时空预报的准确性一直是天气预报中的难点。文章将机器学习分类算法融合中尺度模式,实现了雷暴大风和短时强降水的逐小时预报。具体算法为:首先利用XGBoost分类算法和10年以上历史数据建立强对流分类潜势预报模型;其次通过统计CMA-SH9模式要素的最佳空间邻域半径和概率密度分布特征,基于组合最优评分提取要素阈值,建立要素空间邻域“配料”模型;最后通过联合判别将机器学习分类方法和要素空间邻域“配料法”融合,建立雷暴大风和短时强降水的逐小时预报模型。检验表明:该融合方法显著优于数值模式预报结果和国家下发指导产品,2021—2022年短时强降水24小时逐小时预报的平均命中率为0.51,TS为0.15,相比模式的改进率分别为82%和36%;雷暴大风24小时逐小时预报的平均命中率达到0.37,TS为0.07,相比模式(反射率因子≥45 dBz)的改进率分别为68%和133%,显著提高了雷暴大风的预报准确性。
Abstract:Improving the accuracy of objective classification and spatio-temporal forecast of severe convective weather has always been a challenge in meteorological forecasting. This paper integrates mesoscale models with machine learning classification algorithms, achieving hourly forecasting of classified severe convection. The specific algorithm is as follows. First, the XGBoost classification algorithm and historical data over 10 years are used to establish a classification potential forecast model for severe convection. Secondly, by statistically analyzing the optimal spatial neighborhood radius and probability density distribution characteristics of CMA-SH9 model elements, and extracting element thresholds based on the combination of optimal scores, a spatial neighborhood graded element ingredient model is established. Finally, through joint discrimination, the machine learning classification method and the spatial neighborhood element “ingredient method” are integrated to establish hourly forecast models for thunderstorm gales and short-time heavy rainfall. The validation results show that this fusion algorithm significantly outperforms numerical model forecast results and national guidance products. For short-time heavy rainfall forecasts on an hourly basis over 24 h during 2021-2022, the average hit rate is 0.51 and the TS (threat score) is 0.15, which reflects the improvements of 82% and 36% respectively compared to the model. For thunderstorm gale forecasts on an hourly basis over 24 h, the average hit rate reaches 0.37 and the TS is 0.07, representing improvements of 68% and 133% respectively relative to the model (reflectivity factor ≥45 dBz). Thus, the forecast accuracy of thunderstorm gale is significantly improved.
文章编号: 中图分类号:P456 文献标志码:
基金项目:浙江省自然科学联合基金项目 (LZJMD23D050001、LZJMZ23D050006)、浙江省科技厅科技项目(2022C03150)和中国气象局重点创新团队(CMA2022ZD07)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 李文娟 | 浙江省气象台,杭州 310051 |
| 郦敏杰 | 杭州市气象局,杭州 310057 |
| 马昊 | 浙江省气象台,杭州 310051 |
| 黄旋旋 | 浙江省气象台,杭州 310051 |
| 张智察 | 浙江省气象台,杭州 310051 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 李文娟' target='_blank'>LI Wenjuan | Zhejiang Meteorological Observatory, Hangzhou 310051 |
| 郦敏杰' target='_blank'>LI Minjie | Hangzhou Meteorological Bureau, Hangzhou 310057 |
| 马昊' target='_blank'>MA Hao | Zhejiang Meteorological Observatory, Hangzhou 310051 |
| 黄旋旋' target='_blank'>HUANG Xuanxuan | Zhejiang Meteorological Observatory, Hangzhou 310051 |
| 张智察' target='_blank'>ZHANG Zhicha | Zhejiang Meteorological Observatory, Hangzhou 310051 |
引用文本:
李文娟,郦敏杰,马昊,黄旋旋,张智察,2024.基于XGBoost分类和数值模式“配料”的浙江强对流预报方法[J].气象,50(11):1343-1358.
LI Wenjuan,LI Minjie,MA Hao,HUANG Xuanxuan,ZHANG Zhicha,2024.Severe Convection Prediction Method Based on XGBoost Classified Algorithm and Numerical Model Ingredients[J].Meteor Mon,50(11):1343-1358.
李文娟,郦敏杰,马昊,黄旋旋,张智察,2024.基于XGBoost分类和数值模式“配料”的浙江强对流预报方法[J].气象,50(11):1343-1358.
LI Wenjuan,LI Minjie,MA Hao,HUANG Xuanxuan,ZHANG Zhicha,2024.Severe Convection Prediction Method Based on XGBoost Classified Algorithm and Numerical Model Ingredients[J].Meteor Mon,50(11):1343-1358.