本文已被:浏览 411次 下载 2502次
投稿时间:2022-09-20 修订日期:2023-03-10
投稿时间:2022-09-20 修订日期:2023-03-10
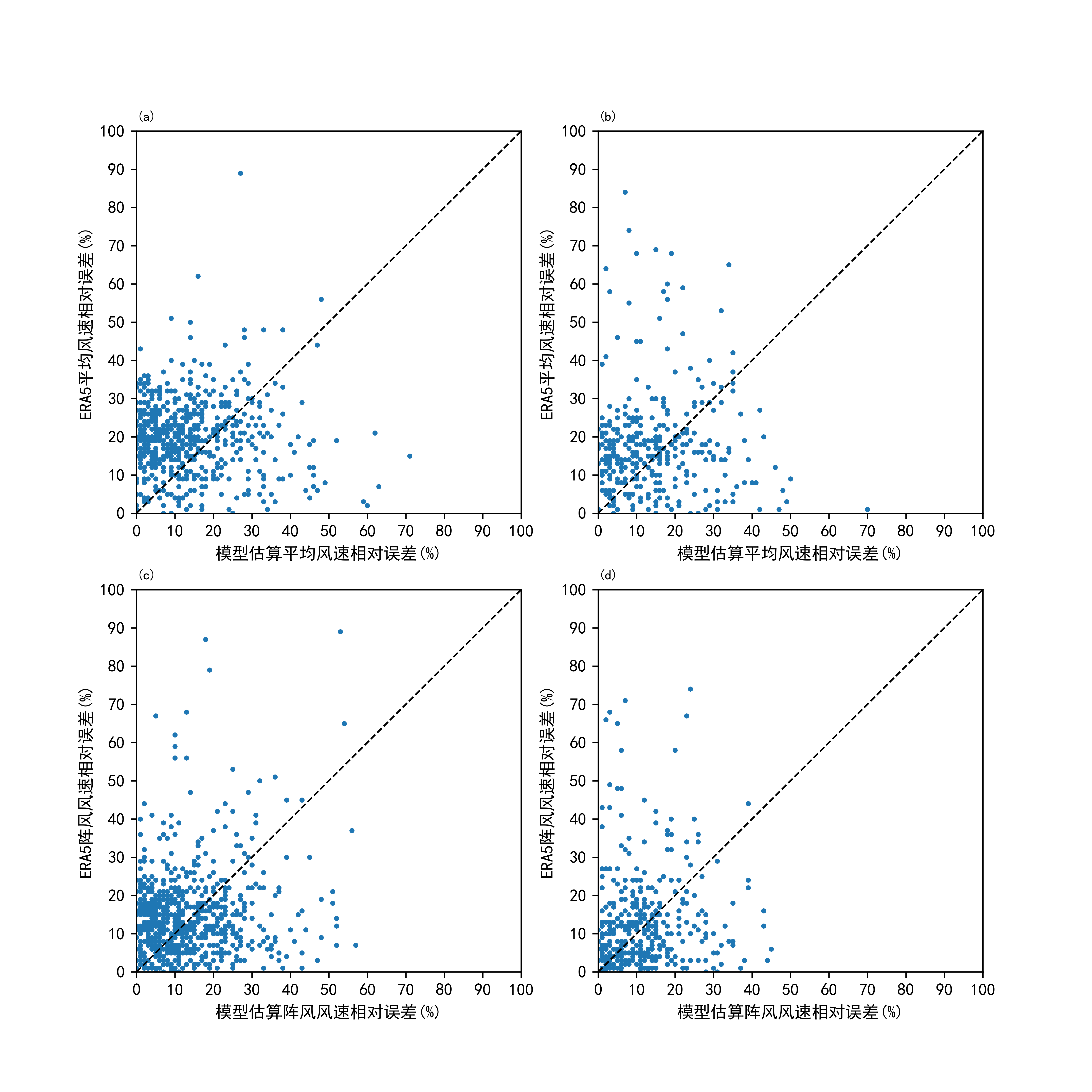
中文摘要: 沿岸海上观测站点稀少,而沿岸陆地观测站点相对密集,开展海陆分布导致的海陆风速差异特征研究,实现由陆地观测风速估算海上风速,有助于提高海上大风预报服务能力。利用我国北方地区两组浮标及其邻近陆地观测站点的2016—2020年逐小时平均风速和阵风风速数据,统计分析海陆风速差异特征及规律,采用支持向量机方法,构建了基于陆地平均风速、陆地阵风风速、海陆站点距离、月份及观测时次的海上风速估算模型。利用另外两组海陆观测站2021年观测数据对估算模型进行检验,结果表明:对于6级及以上的平均风速和7级及以上的阵风风速,模型具有较高的估算准确率,模型估算的两个检验组的海上站点平均风速(阵风风速)RMSE分别为2.40m·s-1(3.20m·s-1)和2.35m·s-1(2.57m·s-1),较ERA5分别减少了24%(14%)和23%(20%)。在一次温带气旋和冷空气共同影响的大风过程中,模型估算的两个检验组的海上平均风速(阵风风速)平均绝对误差分别为1.6m·s-1(2.3 m·s-1)和1.1m·s-1(1.5m·s-1),在极值时刻的平均风速(阵风风速)误差分别为-1.3m·s-1(-0.6m·s-1)和-1.2 m·s-1(-3.1 m·s-1),均优于ERA5计算结果。基于支持向量机的海上风速估算模型能够利用陆地观测风速估算出较为准确的海上大风,可降低海上观测资料不足的影响,具有一定的应用前景。
中文关键词: 海陆风速差异,海上平均风,海上阵风,支持向量机
Abstract:Coastal offshore observation stations are rare, but coastal land observation stations are relatively dense. Carrying out research on the characteristics of land-sea wind speed difference caused by land-sea distribution and realizing the estimation of sea surface wind speed from land observation wind speed is helpful to improve the service ability of sea surface wind forecast. In this paper, the hourly mean wind speed and gust speed data of two groups of buoys and their adjacent land observation stations in the north coast of China from 2016 to 2020 are used to statistically analyze the characteristics and regularity of the difference between sea surface wind speed and land wind speed. And the support vector machine method is used to build the sea surface wind speed estimation model based on the land mean wind speed, land gust speed, distance between land-sea stations, month and hour. The estimation model is tested by using the observation data of the other two groups of land-sea observation stations in 2021. The results show that for the mean wind speed ≥ scale 6 and gust wind speed ≥ scale 7, the model has a high estimation accuracy. The root mean square errors of the mean wind speed (gust speed) of the two groups estimated by the model are 2.40 m·s-1 (3.20 m·s-1) and 2.35 m·s-1 (2.57 m·s-1), respectively. Compared with ERA5, the errors decreased by 24% (14%) and 23% (20%) respectively. In a strong wind process jointly affected by an extratropical cyclone and cold air, the mean absolute errors of the mean wind speed (gust speed) estimated by the model for the two test groups are 1.6 m·s-1 (2.3 m·s-1) and 1.1 m·s-1 (1.5 m·s-1) respectively, and the mean wind speed (gust speed) errors at the extreme moment are -1.3 m·s-1 (-0.6 m·s-1) and -1.2 m·s-1 (-3.1 m·s-1) respectively, which are better than those from ERA5. The sea surface wind speed estimation model based on support vector machine can estimate accurate heavy sea surface wind speed using the land observation wind speed, which can reduce the impact of insufficient sea observation data, and has a certain application prospect.
keywords: land-sea wind speed difference, sea surface mean wind, sea surface gust, support vector machine
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC3000905)资助
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 渠鸿宇' target='_blank'>QU Hongyu | National Meteorological Centre, Beijing 100081 |
| 胡海川' target='_blank'>HU Haichuan | National Meteorological Centre, Beijing 100081 |
| 黄彬' target='_blank'>HUANG Bin | National Meteorological Centre, Beijing 100081 |
引用文本:
渠鸿宇,胡海川,黄彬,2024.基于SVM的我国北部沿岸海上风速估算方法研究[J].气象,50(2):221-233.
QU Hongyu,HU Haichuan,HUANG Bin,2024.Research on the Estimation Method of Sea Surface Wind Speed Along the North Coast of China Based on SVM[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):221-233.
渠鸿宇,胡海川,黄彬,2024.基于SVM的我国北部沿岸海上风速估算方法研究[J].气象,50(2):221-233.
QU Hongyu,HU Haichuan,HUANG Bin,2024.Research on the Estimation Method of Sea Surface Wind Speed Along the North Coast of China Based on SVM[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):221-233.