本文已被:浏览 334次 下载 2058次
投稿时间:2022-10-15 修订日期:2023-05-08
投稿时间:2022-10-15 修订日期:2023-05-08
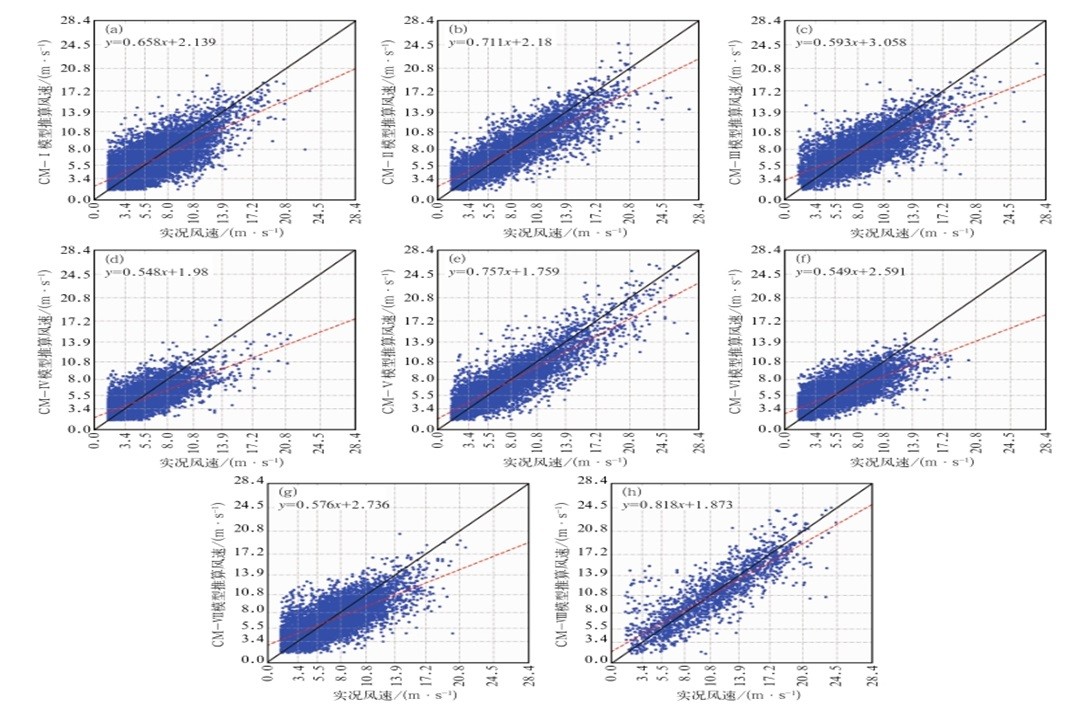
中文摘要: 为了弥补海上风场监测数据不足,提高对黄渤海海上风场监测能力,针对不同大气环流形势,基于较为稳定的74个沿海和海岛站等陆基站2017—2020年风场观测资料,以及同时段具有一定连续性的21个浮标站和船舶站等海基站观测数据,采用多元线性回归方法,建立由陆基站推算海区风速的模型。利用2021年实况资料对推算结果进行检验评估。结果表明:分别针对全部风力等级和6级及以上大风建立的风速推算模型(以下分别简称CM模型和HM模型)均具有较高的可靠性,其中HM模型对大风推算的准确率更高;8种天气类型中共5种类型发生大风的概率高于60%,其中对西北高东南低类型的推算效果最好,对西高东低型、西南高东北低型和西北低东南高型的6~7级大风推算效果较好,对8级及以上大风的推算效果略差;不同海区大风的推算结果中,对黄渤海大部分海区推算的风速略偏小,仅对渤海西南部海区的部分站点推算的风速略偏大;对黄海北部海区风速推算的平均绝对误差最小(0.95 m·s-1),对其他海区风速推算的平均绝对误差在1.32~1.70 m·s-1;在海区观测不连续、不稳定的情况下,推算的风速能够对海上风场资料进行有效的补充。该推算方法易于业务化应用,可随不同海区观测资料的增加而进一步优化,对海洋观测布局设计也有一定的参考作用。
中文关键词: 黄渤海,大风实况,天气分型,推算,检验
Abstract:To deal with the lack of marine observation data and enhance the monitoring ability of strong wind event in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, a calculation method of wind speed in sea area under different atmospheric circulation patterns is developed, on the basis of multiple linear regression method and observation data from 74 coastal and island stations as well as 21 sea-based stations of buoy and ship stations from 2017 to 2020. The calculated results are tested by the observation data in 2021. The results show that the wind speed prediction models (CM model and HM model, respectively) established for all wind scales and winds stronger than scale 6 have higher reliability, and especially the HM model has higher accuracy for wind prediction. The probability of strong winds exceeds 60% for five out of the eight weather types. Among the five weather types with high frequency of gale, the calculation effect for the northwest high-southeast low type is the best, the calculation effects for winds at scales 6-7 of the west high-east low type, the southwest high-northeast low type and the northwest low-southeast high type are better, but the calculation effects for the three types of strong winds at scale 8 and above are slightly worse. In the calculation results of gale in different sea areas, the wind speed calculated for most sea areas of the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea is smaller than observation data, and the wind speed calculated for some stations in the southwest sea area of the Bohai Sea is larger than observation data. The minimum mean absolute error in the northern Yellow Sea is 0.95 m·s-1, and the mean absolute error in other sea areas is 1.32-1.70 m·s-1. The calculated wind speed can effectively supplement the marine wind observation in the case of discontinuous and unstable observation in the sea area. The calculating method is easy to be applied in operational work, and can be further optimized with increasing number of observation data in different sea areas. It also has a certain reference value in designating the layout of marine observation systems.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2022MD040)、环渤海区域科技协同创新基金项目(QYXM202202、QYXM202007)、中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022P012)、公益性行业(气象)科研专项(GYHY201206001)和山东省气象局面上课题(2020sdqxm7)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 曲巧娜 | 山东省气象防灾减灾重点实验室,济南 250031 山东省气象科学研究所,济南 250031 |
| 吴炜 | 山东省气象防灾减灾重点实验室,济南 250031 山东省气象科学研究所,济南 250031 |
引用文本:
曲巧娜,吴炜,2024.黄渤海海区风速推算方法及效果评估[J].气象,50(2):234-245.
QU Qiaona,WU Wei,2024.Calculation Method for Wind Field in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea Area Based on Coastal Actual Condition and Effect Evaluation[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):234-245.
曲巧娜,吴炜,2024.黄渤海海区风速推算方法及效果评估[J].气象,50(2):234-245.
QU Qiaona,WU Wei,2024.Calculation Method for Wind Field in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea Area Based on Coastal Actual Condition and Effect Evaluation[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):234-245.