本文已被:浏览 682次 下载 2697次
投稿时间:2021-06-27 修订日期:2022-03-30
投稿时间:2021-06-27 修订日期:2022-03-30
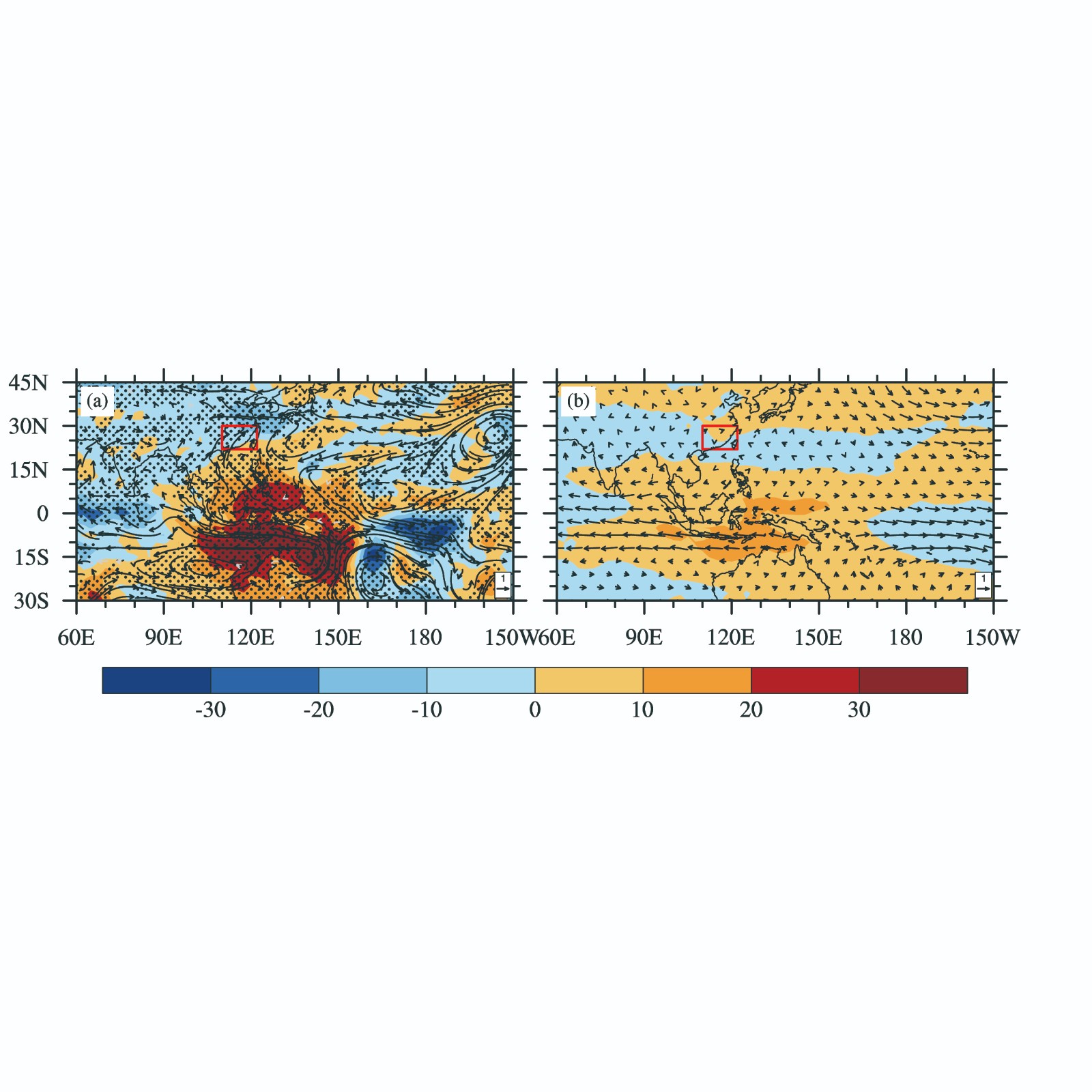
中文摘要: 基于再分析资料揭示了2019年2—3月中国南方持续性降水事件的成因及其与Madden-Julian Oscillation(MJO)的关系。此次持续性降水事件可以分为两个阶段:第一阶段降水覆盖了整个南方地区,第二阶段降水主要出现在华南地区,且降水强度比第一阶段更强。大尺度环流分析表明,此次降水事件中,中国南方和西太平洋的位势高度异常呈现出西低东高的形势,有利于南方地区出现偏南气流和水汽辐合。在第一阶段,整个南方地区都出现明显的水汽辐合和上升运动;而第二阶段,仅在华南地区出现显著的水汽辐合和上升运动。水汽收支诊断分析发现两个阶段中的水汽通量散度异常主要是经向水汽辐合所导致,它对水汽通量散度的贡献率达到70%以上。通过对比分析降水和MJO活动演变,发现降水的变化与MJO位相和振幅的演变有着紧密的联系。当MJO振幅明显增强(减弱)时,南方地区的降水异常显著增加(减少)。经向水汽辐合的尺度分析表明,低频尺度(大于90 d)和季节内尺度(30~90 d)的水汽和环流的相互作用对经向水汽辐合起到决定性作用,尤其是季节内经向风对大于90 d低频水汽的辐合。因此,热带地区MJO的活动可通过调节季节内经向风对低频水汽的输送,从而对此次南方地区的持续性降水事件产生重要影响。
Abstract:Based on the reanalysis data, the causes of persistent precipitation over southern China during February-March 2019 and the relationship with Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) are studied. This persistent precipitation can be divided into two episodes. During the first episode, the precipitation covered the whole southern China, during the second episode it mainly occurred in South China, with intensity stronger than the first. The large-scale circulation analyses show that during this precipitation event, the abnormal geopotential height over southern China and western Pacific was low in the west and high in the east, which was conducive to the occurrence of abnormal southerlies and moisture transport. During the first episode, moisture convergence and upward movement appeared obviously over the whole southern China; during the second episode, stronger moisture convergence and upward movement occurred only in South China. The diagnostic analyses of moisture budget show that the anomalous moisture flux divergence during the two episodes was primarily caused by the meridional moisture convergence, which contributed more than 70% to moisture flux divergence. By comparing the evolution of precipitation and MJO activity, we find that the variation of precipitation was closely related to the phase and amplitude of MJO. When the amplitude of MJO enhanced (weakened) obviously, the anomalous precipitation over southern China increased (decreased). The scale analyses of meridional moisture convergence suggest that the interaction between moisture and circulation at the low-frequency scale (longer than 90 days) and the intraseasonal scale (30-90 days) plays a decisive role in the meridional moisture convergence, especially low-frequency moisture convergence by intraseasonal meridional wind. Therefore, the MJO activity over the tropical region can play a significant role in the persistent precipitation over southern China through regulating the low-frequency moisture transport by the intraseasonal meridional wind.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1505901)和国家自然科学基金项目(41520104008、41475070、41575062)共同资助
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 李力锋' target='_blank'>LI Lifeng | College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073 |
| 陈雄' target='_blank'>CHEN Xiong | College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073 |
| 李崇银' target='_blank'>LI Chongyin | College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG),Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029 |
| 黎鑫' target='_blank'>LI Xin | College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073 |
| 林毅鑫' target='_blank'>LIN Yixin | Unit No.94755 of PLA, Fujian, Zhangzhou 363000 |
| 杨明浩' target='_blank'>YANG Minghao | College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073 |
引用文本:
李力锋,陈雄,李崇银,黎鑫,林毅鑫,杨明浩,2022.2019年2—3月中国南方持续性降水成因及其与MJO的关系[J].气象,48(9):1090-1100.
LI Lifeng,CHEN Xiong,LI Chongyin,LI Xin,LIN Yixin,YANG Minghao,2022.Causes of Persistent Precipitation over Southern China During February-March 2019 and the Relationship with MJO[J].Meteor Mon,48(9):1090-1100.
李力锋,陈雄,李崇银,黎鑫,林毅鑫,杨明浩,2022.2019年2—3月中国南方持续性降水成因及其与MJO的关系[J].气象,48(9):1090-1100.
LI Lifeng,CHEN Xiong,LI Chongyin,LI Xin,LIN Yixin,YANG Minghao,2022.Causes of Persistent Precipitation over Southern China During February-March 2019 and the Relationship with MJO[J].Meteor Mon,48(9):1090-1100.