本文已被:浏览 779次 下载 3782次
投稿时间:2021-01-07 修订日期:2021-08-03
投稿时间:2021-01-07 修订日期:2021-08-03
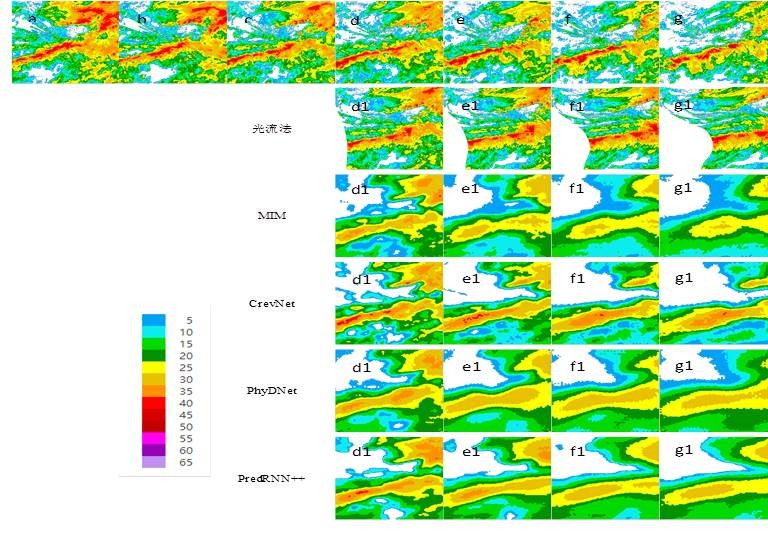
中文摘要: 基于PredRNN++、MIM、CrevNet和PhyDNet四种机器深度学习算法,利用武汉地区2012—2019年的雷达和降水资料,开展了人工智能技术在武汉地区临近预报中的应用研究,根据均方误差(MSE)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)、命中率(POD)、虚警率(FAR)和临界成功指数(CSI)等指标检验评估了四种机器学习算法对武汉地区雷达回波临近预报的预报性能,并以半拉格朗日光流法进行了对比,得到以下主要结论:MIM算法的MSE和FAR最低,SSIM最高;PredRNN++算法的POD和CSI最高。机器深度学习算法的POD、CSI和SSIM均高于光流法,FAR和MSE则更低,其中SSIM、POD、CSI三种指标的提升幅度在3.2%~24.7%,MSE和FAR两种指标的降幅在13.1%~43.3%。30 min以内,除CrevNet外,其余三种机器学习算法和光流法的预报能力较为接近;30 min以后,深度学习算法和光流法都随着预报时效的延长,预报能力均显著下降,但机器学习算法下降得更缓慢,尤其是60 min以后光流法的降幅进一步增加,显示出机器学习长预报时效的优势。此外,机器学习算法之间针对不同评分指标在不同预报时效的下降速度并不一致。PredRNN++算法在所有强度上CSI均表现最佳,MIM和PhyDNet两种算法对≥40 dBz的回波预报、CrevNet算法对≥50 dBz的回波预报均好于光流法。机器学习算法和光流法都随着回波强度的增加,CSI和POD迅速降低,FAR快速上升,但机器学习算法的FAR上升得更慢。四个不同回波形态、不同发展趋势个例的分析结果表明,机器学习算法不仅具备对一定回波强度变化的预报能力,而且对回波强度和面积变化趋势的时间节点预报也与实况基本一致。此外,机器学习算法对回波运动的预报能力明显强于光流法,显示出机器学习算法良好的应用前景。
中文关键词: 机器深度学习,雷达回波,临近预报,检验评估
Abstract:Based on four machine deep learning algorithms (PredRNN++, MIM, CrevNet and PhyDNet), radar data and precipitation data in Wuhan from 2012 to 2019, this study investigates the possibility of application of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the nowcasting of Wuhan Region. The forecasting skills of radar echo nowcasting are examined in terms of mean square error (MSE), structural similarity index (SSIM), probability of detection (POD), false alarm rate (FAR) and critical success index (CSI), then compared with the semi-Lagrangian optical flow method. The results are summarized as follows. The MSE and FAR are the lowest and SSIM is the highest in the MIM algorithm. The POD and CSI of PredRNN++ are the highest. The POD, CSI and SSIM of machine learning are higher than semi-Lagrangian optical flow, while the FAR and MSE of machine learning are much lower, of which the SSIM, POD and CSI of machine algorithms are improved by 3.2%-24.7% than semi-Lagrangian optical flow, but the MSE and FAR are reduced by 13.1%-43.3%. Within 30 minutes, except the CrevNet algorithm, the skills of other algorithms are similar to that of semi-Lagrangian optical flow. 30 minutes later, the skills of both machine algorithm and semi-Lagrangian optical flow decline significantly with the increase of forecast lead time. However, the skill of machine algorithms declines much more slowly. Especially after 60 minutes, the skill of semi-Lagrangian optical flow descends more quickly indicating the advantage of machine learning algorithms for long-term prediction. In addition, the descending rates at different forecast lead times for different score indexes are different among the machine algorithms. The CIS of PredRNN++ is the highest in any intensity, MIM and PhyDNet performance is better than semi-Lagrangian optical flow for radar echo intensity exceeding 40 dBz, but CrevNet shows better skill for radar echo intensity exceeding 50 dBz. The POD and CSI of machine algorithms and semi-Lagrangian optical flow decline significantly with the increase of forecast intensity of radar echo, while the FAR increases quickly, but the increase of FAR rate of machine learning algorithm is much slower. To sum up, the analysis of four different echo patterns and different development trends shows that the machine learning algorithm has the ability not only to predict the change of radar echo intensity in a certain content, but also to predict the time node of the evolution tendency of intensity and acreage, which are basically consistent with the observation. These results suggest that the ability of machine deep learning to predict the movement of radar echo is better than that of semi-Lagrangian optical flow, indicating its possible wide prospect for operational application.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:
引用文本:
袁凯,李武阶,李明,庞晶,2022.四种机器深度学习算法对武汉地区雷达回波临近预报的检验和评估[J].气象,48(4):428-441.
YUAN Kai,LI Wujie,LI Ming,PANG Jing,2022.Examination and Evaluation of four Machine Deep Learning Algorithms for Radar Echo Nowcasting in Wuhan Region[J].Meteor Mon,48(4):428-441.
袁凯,李武阶,李明,庞晶,2022.四种机器深度学习算法对武汉地区雷达回波临近预报的检验和评估[J].气象,48(4):428-441.
YUAN Kai,LI Wujie,LI Ming,PANG Jing,2022.Examination and Evaluation of four Machine Deep Learning Algorithms for Radar Echo Nowcasting in Wuhan Region[J].Meteor Mon,48(4):428-441.