本文已被:浏览 1004次 下载 3826次
投稿时间:2018-09-17 修订日期:2019-01-15
投稿时间:2018-09-17 修订日期:2019-01-15
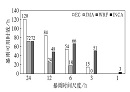
中文摘要: 为了让数值预报产品能够在流域气象业务中达到最佳应用效果,从而为淮河防汛调度提供决策支持,利用2015—2017年6—8月EC、JMA、WRF、INCA四种数值模式降水预报产品,采用TS评分、空估率和漏估率等方法,分别评估四种模式对淮河流域24、12、6、3和1 h时间尺度暴雨的预报性能,并对比分析四种模式对各种时间尺度暴雨预报的可用时效。在此基础上,选取EC的24 h累积降水预报产品驱动分布式水文模型CREST,构建淮河上游的气象水文耦合洪水预报模型,并对2016年6—8月、2017年5—8月的实时运行结果进行评估,探讨了淮河流域洪水的可预报性。主要结论如下:(1)对于24、12 h时间尺度的暴雨,EC预报性能最优、可用时效最长。当暴雨时间尺度缩短到6 h时,WRF的预报性能及可用时效均超越EC,当暴雨发生在3 h内时,WRF的优势更加明显。JMA对各个时间尺度暴雨的预报能力均最差。(2)在0~3 h预报时效内,EC和WRF均存在暴雨漏报率异常偏高、TS异常偏低的现象,其暴雨预报在临近预警中不具备参考价值。INCA则表现出在临近预报中的绝对优势,对 1 h预报时效的暴雨预报TS评分为54%,可用时效为3 h。(3)EC、JMA和WRF对6、3 h时间尺度的暴雨预报性能存在明显的日变化特征。(4)淮河上游洪水预报的可用时效为108 h。
中文关键词: 暴雨,多模式,评估,洪水,可预报性
Abstract:In order to make the numerical forecast products achieve the best application effect in Huaihe River Basin meteorological operation, and to provide decision support for flood control, the forecasting performances of four numerical weather predictions (EC, JMA, WRF and INCA) for 24 h, 12 h, 6 h, 3 h and 1 h time-scale rainstorms in Huaihe River Basin during flood seasons from 2015 to 2017 were evaluated by means of TS score, false alarm rate and missing forecast respectively. The lead time of usable forecast of four models for various time scale rainstorms was compared and analyzed as well. On this basis, EC precipitation forecasting with 24 h time resolution was selected to drive distributed hydrological model CREST and construct a meteorological-hydrological coupling flood forecasting model for the upper reaches of the Huaihe River. Moreover, the real-time operation results of June-August 2016 and May-August 2017 were evaluated, and the predictability of flood in the Huaihe River basin was discussed. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) EC has the best forecasting performance and the longest usable time for 24 h and 12 h rainstorms. When the time scale of rainstorm is 6 h, the WRF’s forecasting performance and usable time are both better than EC. When the rainstorm occurs within 3 h, the advantage of WRF is more obvious. JMA has the worst forecast performance for all time scale rainstorms. (2) EC and WRF show abnormally high missing forecast rate and low TS when the lead time is less than 3 h. So the two NWPs cannot provide valuable reference for rainstorm nowcasting. However, INCA shows perfect performance in rainstorm nowcasting with TS score of 54% in 1 h forecast, and the lead time of usable forecast is 3 h. (3) The performances for 6 h and 3 h time scale rainstorm forecasting of EC, JMA and WRF have obvious features of diurnal variation. (4) The lead time of usable forecast for flood forecasting in the upper reaches of Huaihe River is 108 h.
文章编号: 中图分类号:P456,P641 文献标志码:
基金项目:中国气象局预报员专项(CMAYBY2018-032)和国家自然科学基金青年基金项目(41705029)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 郝莹 | 淮河流域气象中心,合肥 230031 安徽省气象台,合肥 230031 南京大学大气科学学院,南京 210023 |
| 王元 | 南京大学大气科学学院,南京 210023 |
| 王皓 | 安徽省气象台,合肥 230031 |
| 邱学兴 | 安徽省气象台,合肥 230031 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 郝莹' target='_blank'>HAO Ying | Huaihe Basin Meteorological Centre, Hefei 230031 Anhui Meteorological Observatory, Hefei 230031 School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023 |
| 王元' target='_blank'>WANG Yuan | School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023 |
| 王皓' target='_blank'>WANG Hao | Anhui Meteorological Observatory, Hefei 230031 |
| 邱学兴' target='_blank'>QIU Xuexing | Anhui Meteorological Observatory, Hefei 230031 |
引用文本:
郝莹,王元,王皓,邱学兴,2019.淮河流域不同时间尺度暴雨的多模式预报性能评估及洪水可预报性探讨[J].气象,45(7):989-1000.
HAO Ying,WANG Yuan,WANG Hao,QIU Xuexing,2019.Evaluation of Multi-NWPs Rainstorm Forecasting Performance in Different Time Scales in Huaihe River Basin and Discussion on Flood Predictability[J].Meteor Mon,45(7):989-1000.
郝莹,王元,王皓,邱学兴,2019.淮河流域不同时间尺度暴雨的多模式预报性能评估及洪水可预报性探讨[J].气象,45(7):989-1000.
HAO Ying,WANG Yuan,WANG Hao,QIU Xuexing,2019.Evaluation of Multi-NWPs Rainstorm Forecasting Performance in Different Time Scales in Huaihe River Basin and Discussion on Flood Predictability[J].Meteor Mon,45(7):989-1000.