本文已被:浏览 1119次 下载 3865次
投稿时间:2017-04-14 修订日期:2018-11-07
投稿时间:2017-04-14 修订日期:2018-11-07
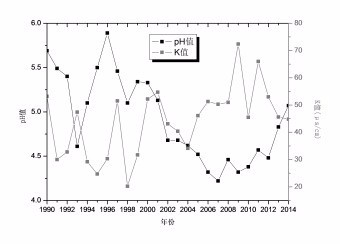
中文摘要: 利用质量控制后1990—2014年酸雨逐日观测数据,分析武汉市酸雨变化特征,并研究酸雨与降水强度、风、气团来源及污染源的关系。结果表明:武汉站年均pH值为4.86,属弱酸雨等级,酸雨强度整体呈增加趋势但2007年后趋于减弱;年均电导率为39.1 μS·cm-1,呈8.8 μS·cm·(10 a)-1的增加趋势。酸雨强度冬强夏弱,发生频率冬多夏少,电导率冬高夏低。武汉市强酸雨pH值和电导率呈显著负相关,非酸雨呈显著正相关。降水强度在酸雨强弱、发生频率演变过程中作用显著,但不同季节各有差异。1500 m高度处风速增大,武汉市酸雨强度减弱、发生频率减少,西南风向下酸雨发生频率高。强酸雨主要受来自南方酸雨重污染区气团影响,外来污染源经大气输送对武汉市强酸雨贡献大。武汉市SO2浓度趋于减少,NO2浓度趋于增加,两者浓度之和自2000年以来呈减少趋势。
中文关键词: 酸雨,pH值,电导率,降水,气团来源
Abstract:Based on the daily observation data of acid rain in Wuhan during 1990-2014, we studied the variation of acid rain and its relationship with rainfall intensity, wind, air mass source and pollutant source. The results indicated that the precipitation in Wuhan shows weak acidity and the annual mean pH is 4.86. The acid rain intensity showed an increasing trend in general but has tended to weaken since 2007. The annual mean electrical conductivity is 50.3 μS·cm-1 with a rise of 8.8 μS·cm-1 per decade. The pH value is lower in winter than in summer while the frequency and electrical conductivity are higher in winter than in summer. The conductivity and pH value of intense acid rain have an obvious negative correlation while a significant positive correlation is for non acid rain. The rainfall intensity is an important factor in the development of acid rain intensity and frequency, showing differences in different seasons. The intensity and the frequency of acid rain decrease when the wind speed at 1500 m height increases. Acid rain occurs more in southwest wind direction. The intense acid rain is mainly affected by acid rain from the south heavy air pollution area, and the external pollution sources by the atmospheric transmission contribute greatly to the intense acid rain in Wuhan. The sulphur dioxide content (SO2) in Wuhan tends to decline while the nitrogen dioxide content (NO2) tends to increase. The total concentrations of the two have presented a decreasing trend since 2000.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:湖北省气象局科技发展基金(2015Y05)和中国气象局气候变化专项(CCSF201620)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 王苗 | 武汉区域气候中心,武汉 430074 |
| 吕桅桅 | 武汉区域气候中心,武汉 430074 |
| 王凯 | 武汉区域气候中心,武汉 430074 |
| 马德栗 | 武汉区域气候中心,武汉 430074 |
| 方思达 | 武汉区域气候中心,武汉 430074 |
引用文本:
王苗,吕桅桅,王凯,马德栗,方思达,2019.武汉市酸雨变化特征及影响因子分析[J].气象,45(2):282-289.
WANG Miao,Lü Weiwei,WANG Kai,MA Deli,FANG Sida,2019.Analysis of Variation Characteristics of Acid Rain in Wuhan and Its Impact Factors[J].Meteor Mon,45(2):282-289.
王苗,吕桅桅,王凯,马德栗,方思达,2019.武汉市酸雨变化特征及影响因子分析[J].气象,45(2):282-289.
WANG Miao,Lü Weiwei,WANG Kai,MA Deli,FANG Sida,2019.Analysis of Variation Characteristics of Acid Rain in Wuhan and Its Impact Factors[J].Meteor Mon,45(2):282-289.