本文已被:浏览 170次 下载 1687次
投稿时间:2024-04-30 修订日期:2025-01-10
投稿时间:2024-04-30 修订日期:2025-01-10
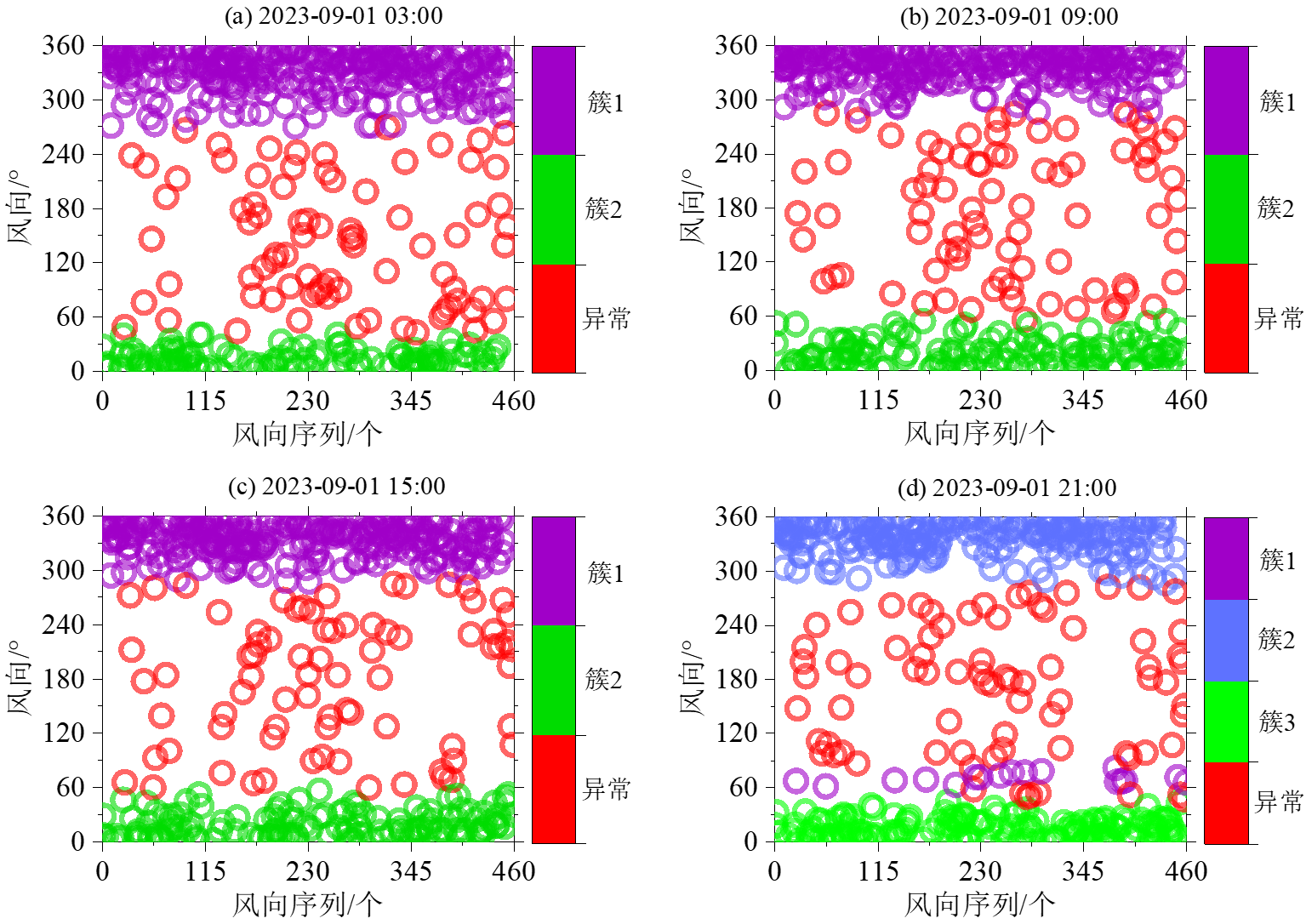
中文摘要: 针对自动气象观测站资料存在高隐蔽度的异常风向问题,基于DBSCAN算法建立自动气象观测站风向异常识别方法。选取2016—2022年影响广州的寒潮、冷空气、台风等16个天气过程个例的自动气象观测站历史风向数据和第2309号台风苏拉影响广州期间的自动气象观测站实时风向数据进行风向异常识别检测。分析结果表明,历史个例的风向可疑站点比例介于0.46%~5.56%,风向错误的站点比例介于0.25%~2.05%;在“苏拉”实时个例中识别出与地面主导风向存在显著偏离的异常风向站点有13个,造成风向异常的原因为风向传感器故障和站点观测环境影响。与传统方法相比,该方法的风向错误识别准确率提高了20.32百分点,为自动气象观测站历史风向数据质量控制提供了新思路,同时也为自动气象观测站设备运行监控及现场核查提供了有力的参考依据。
Abstract:To address the issue of high-concealed abnormal wind directions in automatic weather station (AWS) data, this study establishes an abnormal wind direction identification method based on the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) clustering algorithm. Historical wind direction data from 16 weather events affecting Guangzhou between 2016 and 2022, including cold waves, cold air masses, and typhoons, as well as observed wind direction data from AWSs during the impact of Typhoon Saola (No.2309), are used to detect abnormal wind directions. The analysis results reveal that the proportion of AWSs with suspicious wind directions in historical cases ranges from 0.46% to 5.56%, while the proportion of AWSs with erroneous wind directions varies from 0.25% to 2.05%. During the case of Typhoon Saola, the method identifies 13 AWSs with significantly deviating wind directions from the dominant surface wind direction, which is primarily due to wind direction sensor malfunctions and environmental impacts on AWS observations. Compared to that by the traditional method, the accuracy of wind direction error identification has improved by 20.32 percentage point. The new method provides a novel approach for the quality control of historical wind direction data from AWSs and offers an effective reference for the operational monitoring and on-site verification of AWS equipment.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:广州市科技重点研发计划(2023B04J0704、2023B04J0667)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 张志坚 | 广州市突发事件预警信息发布中心,广州 511430 |
| 张静 | 广州市气象台,广州 511430 |
| 伍光胜 | 广州市突发事件预警信息发布中心,广州 511430; 广州市粤港澳大湾区气象智能装备研究中心,广州 511430; 粤港澳大湾区气象研究院,广州 510641 |
引用文本:
张志坚,张静,伍光胜,2025.一种基于机器学习的自动气象观测站风向异常识别方法[J].气象,51(4):460-472.
ZHANG Zhijian,ZHANG Jing,WU Guangsheng,2025.A Method for Identifying Abnormal Wind Direction at Automatic Weather Stations Based on Machine Learning[J].Meteor Mon,51(4):460-472.
张志坚,张静,伍光胜,2025.一种基于机器学习的自动气象观测站风向异常识别方法[J].气象,51(4):460-472.
ZHANG Zhijian,ZHANG Jing,WU Guangsheng,2025.A Method for Identifying Abnormal Wind Direction at Automatic Weather Stations Based on Machine Learning[J].Meteor Mon,51(4):460-472.