本文已被:浏览 414次 下载 2072次
投稿时间:2023-02-14 修订日期:2023-09-04
投稿时间:2023-02-14 修订日期:2023-09-04
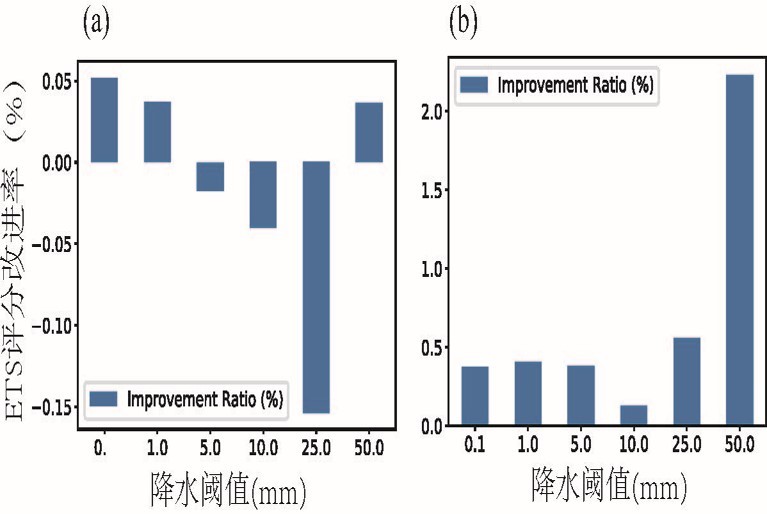
中文摘要: 往返平飘式探空通过一次探空气球施放实现“上升段-平飘段-下降段”三段观测,其下降段能实现在06时(世界时,下同)和18时自动垂直加密观测大气,具备提升区域高分辨率快速同化循环预报系统在06时和18时的预报技巧潜力。为了实现往返平飘式探空在区域高分辨率模式中的同化,分析其对预报的影响,初步提出了“选取模式层最接近观测”的垂直稀疏化方法来预处理资料,深入分析了稀疏化对同化效果的影响,论证了资料垂直稀疏化对于同化应用的必要性;在此基础上,开展了为期1个月的批量同化影响试验,着重分析了往返平飘式探空在长江中下游区域的组网观测对CMA-MESO模式预报技巧的影响。稀疏化敏感性试验结果表明,同化不稀疏化的往返平飘式探空相比同化传统业务探空,分析和预报误差显著增加,降水预报评分也显著降低,相反,“选取最接近模式层”数据的垂直稀疏化方案能提高模式的分析和预报技巧,表明往返平飘式探空同化前必须进行垂直稀疏化。批量同化试验结果表明,在冷启动时刻(00时和12时,为常规探空释放时刻),同化往返平飘式探空(上升段)相对同化传统业务探空,分析误差和预报误差变化较小。但在暖启动时刻(03、06、09、15、18、21时,无常规探空释放时刻),增加往返平飘式探空下降段数据,相比控制试验,分析场精度提高了约0.4%。此外,0~12h 累计降水预报的ETS评分变化较小,但12~24 h累计降水预报在0.1、1.0、5.0、10.0、25.0mm量级降水ETS评分提高了约0.5%,在50.0mm量级的降水ETS评分提高了约2.3%。总体而言,同化往返平飘式探空对于区域高分辨率快速同化循环预报系统在暖启动时刻的降水预报技巧有正贡献。
Abstract:The round-trip horizontal drift radiosonde can do the three-stage observation of “ascending-drifting-descending stages” by releasing one sounding balloon at only one time. In particular, in the descending stage the radiosonde can increase the vertical observation of the atmosphere at 06 UTC and 18 UTC respectively, and it has the potential to significantly improve the prediction skills of the regional high-resolution rapid assimilation cycle prediction system at 06 UTC and 18 UTC. In order to achieve the assimilation of the round-trip horizontal drift sounding in the high-resolution regional model and analyze its impacts on the forecast, one vertical thinning method by “selecting the closest observation according to the model layer” for assimilation is preliminarily proposed, and the influence of this thinning method on model analysis is deeply analyzed. On this basis, a one-month batch assimilation impact experiment was carried out by using the networked observations in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, and the impacts on model forecasts are investigated in detail in this paper. The results of the thinning sensitivity tests show that, compared with the assimilation of traditional operational soundings, the analysis and prediction root mean square errors (RMSE) of the assimilation of non-thinning round-trip horizontal drift radiosonde observations are significantly increased, while the precipitation prediction scores are significantly reduced. On the contrary, the model performances in analysis and prediction fields are improved by assimilating the data after vertical thinning, which indicates that the vertical thinning of round-trip horizontal drift radiosonde observations must be carried out before assimilation. The results of batch experiments show that at the cold start time (00 UTC and 12 UTC, time with conventional radiosonde), the assimilation of round-trip horizontal drift sounding (ascending stage) observations has smaller changes in analysis error and prediction error relative to assimilation of traditional operational radiosonde data. At the warm start time (03 UTC, 06 UTC, 09 UTC, 15 UTC, 18 UTC, 21 UTC, time without conventional radiosonde), however, compared with the control experiment, the accuracy of the analysis field is improved by about 0.4% by assimilating the data of descending section of the horizontal drift sounding. The ETS scores of the 0-12 h accumulated precipitation forecast change less, but the ETS scores of the 12-24 h accumulated precipitation forecast at 0.1, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 25.0 mm thresholds increase by about 0.5%. Moreover, the ETS score at 50.0 mm threshold increases by about 2.3%. All above results show that the round-trip horizontal drift sounding must be thinned before assimilation, and the assimilation of the round-trip horizontal drift sounding can improve the precipitation forecast skill of the regional high-resolution rapid assimilation cycle forecast system at the warm start time.
keywords: round-trip horizontal drift radiosonde, CMA-MESO, vertical thinning scheme, 3DVar, data assimilation
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1506205、2022YFC3004002)共同资助
引用文本:
王金成,王丹,王瑞文,谭娟,容娜,2024.往返平飘式探空在CMA-MESO三维变分中的同化及对模式预报的影响[J].气象,50(2):159-169.
WANG Jincheng,WANG Dan,WANG Ruiwen,TAN Juan,RONG Na,2024.Assimilation of Round-Trip Horizontal Drift Radiosonde Data in CMA-MESO 3DVar and Its Impact on Model Forecast[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):159-169.
王金成,王丹,王瑞文,谭娟,容娜,2024.往返平飘式探空在CMA-MESO三维变分中的同化及对模式预报的影响[J].气象,50(2):159-169.
WANG Jincheng,WANG Dan,WANG Ruiwen,TAN Juan,RONG Na,2024.Assimilation of Round-Trip Horizontal Drift Radiosonde Data in CMA-MESO 3DVar and Its Impact on Model Forecast[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):159-169.