本文已被:浏览 583次 下载 2173次
投稿时间:2022-10-15 修订日期:2023-09-12
投稿时间:2022-10-15 修订日期:2023-09-12
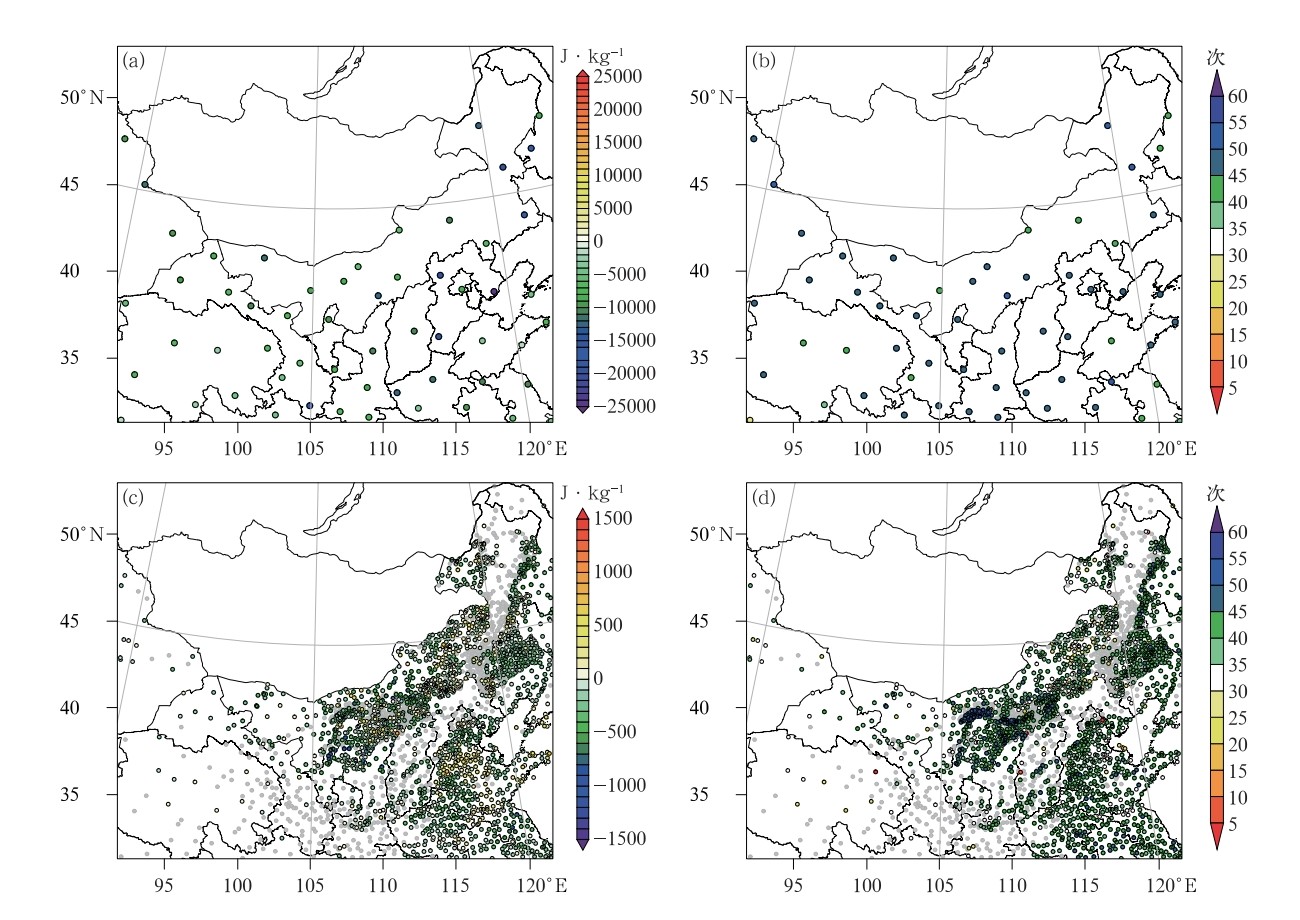
中文摘要: 基于内蒙古睿图预报系统的低分辨率版本和WRFDA-FSO诊断工具,评估2021年7月现有探空和地面观测对内蒙古睿图预报系统预报的影响。该方法计算代价相对低廉,并允许根据观测变量、观测类型、气压层次、地理区域等观测的子集对观测影响进行划分。代价函数为以干总能量为度量的背景场和分析场的预报误差之间的差异。结果表明:观测影响的总体总和为负,观测对预报起正贡献作用。对12h预报误差减小贡献最大的观测来自探空观测的动力变量(U、V风分量)。而单时次单位数量平均观测影响,探空观测的贡献约为地面观测的1/2。探空观测对12h预报误差减小从近地面层至模式层顶均保持正贡献作用,并在对流层中低层和对流层高空急流层存在两个极大值区域;地面观测在850hPa以下低层正贡献占比明显。探空观测在被同化系统同化时均总体具有有利的影响,也反映出探空观测数据稳定、质量较高的特征;地面观测对12h预报误差减小起正贡献作用次数最多的区域在河套地区尤为显著。同时,探讨了需进一步提高地面观测资料同化率的问题。
Abstract:Based on the low resolution version of RMAPS-NM forecast system and WRFDA-FSO diagnostic tool, this paper evaluates the impact of existing radiosonde and surface observation on RMAPS-NM forecast system in July 2021. This method is relatively cheap in computation, and allows the observation impact to be divided to the subset of observation according to observation variables, observation types, barometric levels, geographical regions, etc. The cost function is the difference between the prediction error of the background field and the analysis field measured by the total dry energy. The results show that the total sum of observation impact is negative, and observation plays a positive role in prediction. The observation that contributes most to the reduction of 12 h prediction error comes from the dynamic variables (U, V wind components) of radiosonde observation. However, the contribution of radiosonde observation to the average observation impact per unit quantity of a single time is about 1/2 of that of surface observation. The radiosonde observation has a positive contribution to the reduction of 12 h prediction error from the near surface layer to the top of model layer, and there are two maximum zones in the middle and lower troposphere and in the troposphere upper jet layer. The positive contribution of surface observation is obvious in the lower layer below 850 hPa. The radiosonde observation, when assimilated by the assimilation system, has a favorable influence overall, which also reflects the characteristics of stable and high-quality characteristics to radiosonde observation. The zone with the most times of positive contribution for surface observation to the reduction of 12 h prediction error is particularly significant in the Hetao Region. At the same time, the problem that the assimilation rate of surface observation data should be further improved is discussed.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(42030604)、中国科学院科技服务网络计划项目(KFJ-STS-QYZD-2021-01-001)和内蒙古自治区科技成果转化专项资金项目(2021CG0047)共同资助
引用文本:
姚乐宝,沈丹,孟雪峰,孙鑫,孟智勇,黄晓璐,叶飞,刘林春,孙永刚,2024.内蒙古区域数值预报对探空和地面观测资料的敏感性试验研究[J].气象,50(2):144-158.
YAO Lebao,SHEN Dan,MENG Xuefeng,SUN Xin,MENG Zhiyong,HUANG Xiaolu,YE Fei,LIU Linchun,SUN Yonggang,2024.Experimental Study on Regional Numerical Forecast Sensitivity to Radiosonde and Surface Observation in Inner Mongolia[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):144-158.
姚乐宝,沈丹,孟雪峰,孙鑫,孟智勇,黄晓璐,叶飞,刘林春,孙永刚,2024.内蒙古区域数值预报对探空和地面观测资料的敏感性试验研究[J].气象,50(2):144-158.
YAO Lebao,SHEN Dan,MENG Xuefeng,SUN Xin,MENG Zhiyong,HUANG Xiaolu,YE Fei,LIU Linchun,SUN Yonggang,2024.Experimental Study on Regional Numerical Forecast Sensitivity to Radiosonde and Surface Observation in Inner Mongolia[J].Meteor Mon,50(2):144-158.