本文已被:浏览 397次 下载 2736次
投稿时间:2021-09-26 修订日期:2022-03-25
投稿时间:2021-09-26 修订日期:2022-03-25
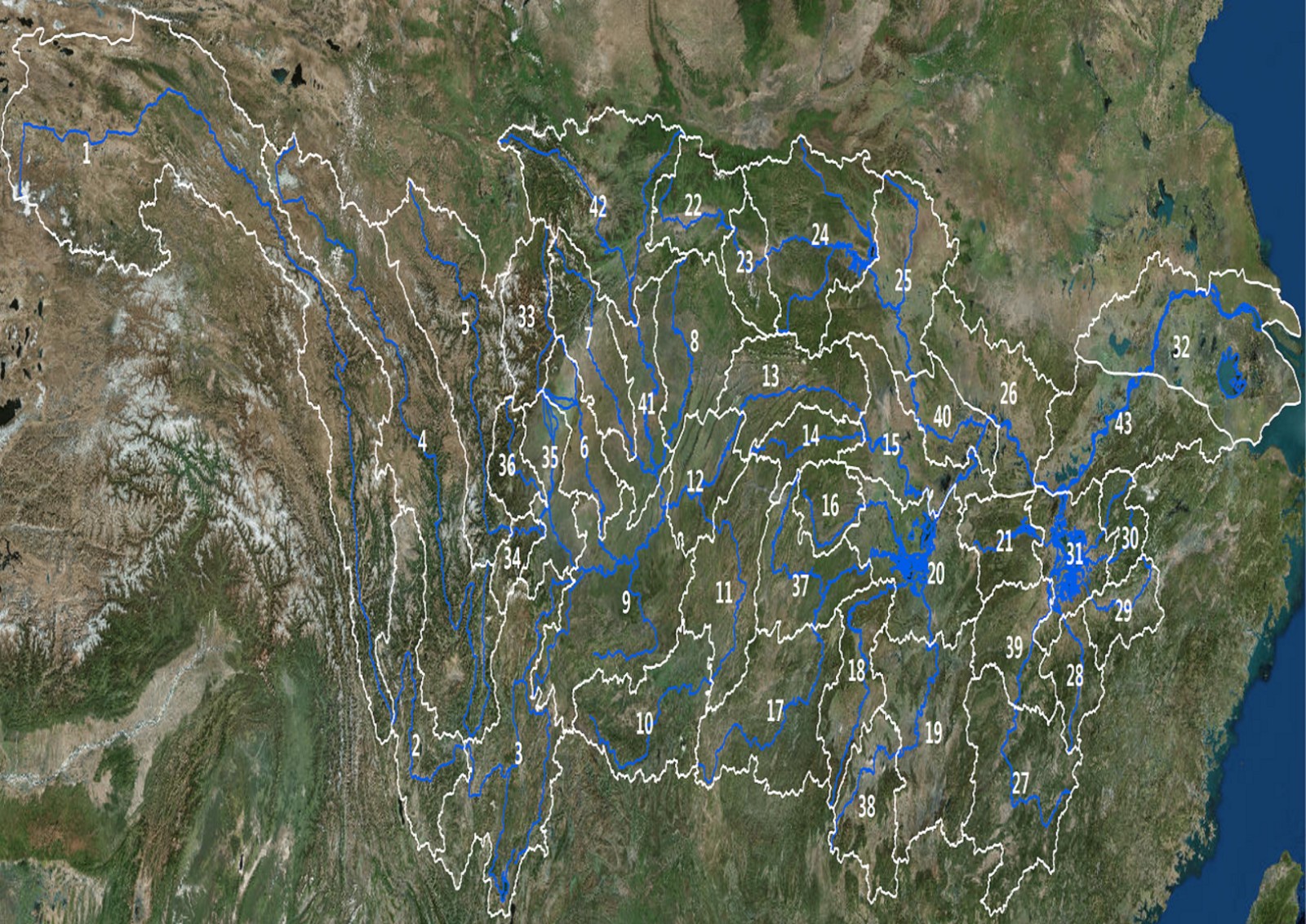
中文摘要: 将长江流域进行精细分区,基于ECMWF、NCEP、CMA-GFS、GERMAN、CMA-MESO、CMA-SH9等多模式降水预报产品,开展各模式在滑动训练期分区、分时效、分量级的动态TS检验,获取各模式降水预报性能动态序列,再经客观识别降水类型,调整不同天气尺度模式排序,对大雨及以上量级采用“邻域择优法”,对中雨及以下量级采用“点对点择优法”,利用集合预报概率产品和模式统计分析结果对强降水和小雨进行消空,最终得到多模式动态集成降水产品(MDI)。采用14、21、28和35 d滑动训练期,分别输出MDI-14、MDI-21、MDI-28和MDI-35。应用分析表明:MDI在各量级降水预报优势明显,其中MDI-28预报大雨及以上的降水效果最好,24 h时效TS评分较其他模式高0.051~0.141;MDI-35预报中雨及以下的降水效果最好,24 h时效TS评分较其他模式高0.006~0.117,空、漏报也有很好的控制。对比24 h时效MDI与ECMWF的站点检验结果空间分布情况发现:前者TS评分在长江流域大部地区高于后者,特别是大雨及以上量级降水评分在长江上游东部、中下游沿江及以北地区高出0.05~0.26。
中文关键词: 精细分区,性能排序,邻域择优法,点对点择优法,动态集成
Abstract:With finely zoning of the Yangtze River Basin and based on ECMWF, NCEP, CMA-GFS, GERMAN,CMA-MESO and CMA-SH9 precipitation forecast products, the rolling tests of finely zoning, time division and precipitation classification are carried out to obtain the corresponding model performance ranking. The “neighborhood optimization method” is used for heavy rain and above, and the “point-to-point optimization method” is used for moderate rain and below to establish the optimal integration scheme. The ensemble forecast and statistical analysis results are used to reduce the empty forecast rate of heavy rainfall and light rain. Finally, the multi-model dynamic integrated precipitation products (MDI) are obtained. MDI-14, MDI-21, MDI-28 and MDI-35 are produced during the 14 d, 21 d, 28 d and 35 d sliding training periods respectively. The application analysis shows that MDI have obvious advantages in precipitation forecasts, among which MDI-28 has the best effect in predicting heavy rain and above, and especially, its 24 h TS-score is 0.051-0.141 higher than that of the others; MDI-35 has the best effect in predicting moderate rain and below, with the 24 h TS-score being 0.006-0.117 higher than that of the others, and empty and missing forecast rate are also controlled well. Comparing the spatial distribution of TS scores of 24 h precipitation forecasts between MDI and ECMWF, we find that the former is higher than that of the latter in most areas of the Yangtze River Basin. Especially, for heavy rain and above, it is 0.05-0.26 higher in the east regions of the upper reaches of Yangtze River as well as in the middle and northern regions of the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFE0196000)、中国长江电力股份有限公司项目(2418020001和2421020002)和湖北省气象局科技发展基金重点项目(2018Z01和2020Z03)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 王海燕 | 湖北省黄石市气象局,黄石 435002 |
| 孟英杰 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 程昌玉 | 湖北省气象信息与技术保障中心,武汉 430074 |
| 陈良华 | 三峡水利枢纽梯级调度通信中心,湖北 宜昌 443000 |
| 李波 | 三峡水利枢纽梯级调度通信中心,湖北 宜昌 443000 |
| 王晓玲 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 王海燕' target='_blank'>WANG Haiyan | Huangshi Meteorological Office of Hubei Province, Huangshi 435002 |
| 孟英杰' target='_blank'>MENG Yingjie | Wuhan Central Meteorological Observatory, Wuhan 430074 |
| 程昌玉' target='_blank'>CHENG Changyu | Hubei Meteorological Information and Technology Support Centre, Wuhan 430074 |
| 陈良华' target='_blank'>CHEN Lianghua | Three Gorges Cascade Dispatch and Communication Center of Hubei Province, Yichang 443000 |
| 李波' target='_blank'>LI Bo | Three Gorges Cascade Dispatch and Communication Center of Hubei Province, Yichang 443000 |
| 王晓玲' target='_blank'>WANG Xiaoling | Wuhan Central Meteorological Observatory, Wuhan 430074 |
引用文本:
王海燕,孟英杰,程昌玉,陈良华,李波,王晓玲,2022.长江流域多模式动态集成降水预报方法及应用评估[J].气象,48(8):1043-1052.
WANG Haiyan,MENG Yingjie,CHENG Changyu,CHEN Lianghua,LI Bo,WANG Xiaoling,2022.Precipitation Forecasting Method and Application Evaluation Based on Multi-Model Dynamic Integration for the Yangtze River Basin[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):1043-1052.
王海燕,孟英杰,程昌玉,陈良华,李波,王晓玲,2022.长江流域多模式动态集成降水预报方法及应用评估[J].气象,48(8):1043-1052.
WANG Haiyan,MENG Yingjie,CHENG Changyu,CHEN Lianghua,LI Bo,WANG Xiaoling,2022.Precipitation Forecasting Method and Application Evaluation Based on Multi-Model Dynamic Integration for the Yangtze River Basin[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):1043-1052.