本文已被:浏览 636次 下载 3497次
投稿时间:2021-06-01 修订日期:2022-05-06
投稿时间:2021-06-01 修订日期:2022-05-06
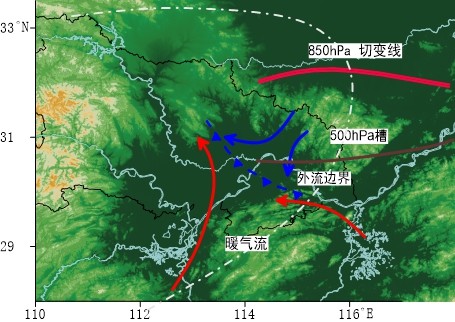
中文摘要: 利用2008—2016年常规观测、地面自动站和NCEP再分析场资料,结合天气雷达和气象卫星等资料,在系统性分析39例梅雨期极端暴雨过程边界层中尺度天气系统动力热力特征的基础上,研究归纳了三种不同天气类型下极端暴雨边界层中尺度天气系统的发展模型。结果表明:在同一类天气类型背景下,对应的极端暴雨中尺度天气系统的发展具有相同的规律,且极端暴雨的产生均与边界层中尺度天气系统的强烈发展有密切关系,而长江中游特殊地形在边界层中尺度系统发生发展中起到重要作用。在有利环流背景和强烈发展边界层中尺度天气系统的触发和组织作用下,中尺度对流系统(MCS)的合并加强、停滞、后向传播以及对流单体列车效应等是极端强降水产生的重要原因。锋面气旋类极端暴雨地面中尺度天气系统有三种,均由冷式切变线、暖区局地中尺度辐合线和大别山西侧MCS出流边界等交汇发展而来。低涡切变极端暴雨的中尺度天气系统主要是边界层新生于武陵山脉东部江汉 洞庭湖平原的局地中尺度涡旋,尺度为150~300 km,其形成伴随显著的边界层多支气流的强烈辐合、局地斜压性的发展过程等;局地中尺度涡旋的形成与西南涡和长江中游特殊地形密切相关,四川盆地西南涡加强,湘鄂西部二级地形区域涡前强降水的形成是其发展的主要诱因,有利于多支气流辐合的长江中游马蹄形地形是其在江汉 洞庭湖平原多发的关键因素。弱强迫梅雨锋暖区极端暴雨中尺度天气系统的形成发展与大别山西侧雷暴冷池逆流和夜间边界层超低空急流的辐合增强、维持有关。
Abstract:By using conventional observation data, automatic meteorological station data and NCEP reanalysis data, as well as the data of CINRAD and meteorological satellite, the mesoscale weather system development models in the boundary layer of extreme rainstorm under three different weather types are summarized, based on the systematic analysis about the dynamic and thermal characteristics of the boundary layer mesoscale weather system in 39 cases of extreme rainstorms. The results show that the mesoscale weather systems in extreme rainstorm share the same regularity under the same weather system. The occurrence of extreme rainstorm is closely related to the strong development of mesoscale weather system in boundary layer. The special topography in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River plays an important role in the occurrence and development of mesoscale weather systems. By the trigger and organization of strong developing mesoscale weather system in boundary layer under the background of favorable circulation, the consolidation strengthening, stagnation, backward propagation of mesoscale convective system (MCS) and convective cell train effect are important reasons for extreme heavy rainfalls. To be specific, there are three paterns of surface mesoscale synoptic systems related to frontal cyclone type, which are all developed from the intersection of cold shear line, warm mesoscale convergence line and the gust front of MCS in the west of Dabie Mountains. The low vortex shear-type mesoscale weather system is mainly a local mesoscale vortex, newly born in boundary layer in Jianghan-Dongting Lake Plain in the eastern Wuling Mountains of Hunan and Hubei and the scale is about 150-300 km. Its formation is accompanied by the strong convergence of multiple flows in the boundary layer and the development of local baroclinicity. The strengthening of the southwest vortex and the formation of heavy precipitation in front of the second-order regional vortex in the west of Hunan and Hubei are the main inducements for the development of local mesoscale vortex in the boundary layer of the eastern plain. The horseshoe-shaped terrain in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, which is conducive to the convergence of multiple air streams, is the key factor for the occurrence of local mesoscale vortex in the eastern plain. The formation and development of the extreme rainstorm mesoscale weather system in the warm sector of the weakly forced Meiyu front is mainly related to the enhanced convergence and maintenance of the thunderstorm cold pool countercurrent on the westside of the Dabie Mountains and the nighttime boundary layer ultra-low-level jet.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(U2142202)、中国气象局气象关键技术集成与应用项目(CMAGJ2015M38)和湖北省气象局科技发展基金项目(2018Z03,2022Y03)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 周金莲 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 张家国 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 吴涛 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 许冠宇 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 刘希文 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 王珏 | 中国气象局武汉暴雨研究所,暴雨监测预警湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430205 |
| 韩芳蓉 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
引用文本:
周金莲,张家国,吴涛,许冠宇,刘希文,王珏,韩芳蓉,2022.长江中游梅雨锋极端暴雨过程中的边界层中尺度系统主要特征[J].气象,48(8):1007-1019.
ZHOU Jinlian,ZHANG Jiaguo,WU Tao,XU Guanyu,LIU Xiwen,WANG Jue,HAN Fangrong,2022.Characteristics of the Mesoscale Weather System Producing Extreme Rainstorm in Boundary Layer During the Meiyu Front over the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):1007-1019.
周金莲,张家国,吴涛,许冠宇,刘希文,王珏,韩芳蓉,2022.长江中游梅雨锋极端暴雨过程中的边界层中尺度系统主要特征[J].气象,48(8):1007-1019.
ZHOU Jinlian,ZHANG Jiaguo,WU Tao,XU Guanyu,LIU Xiwen,WANG Jue,HAN Fangrong,2022.Characteristics of the Mesoscale Weather System Producing Extreme Rainstorm in Boundary Layer During the Meiyu Front over the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):1007-1019.