本文已被:浏览 583次 下载 3212次
投稿时间:2021-04-08 修订日期:2022-05-11
投稿时间:2021-04-08 修订日期:2022-05-11
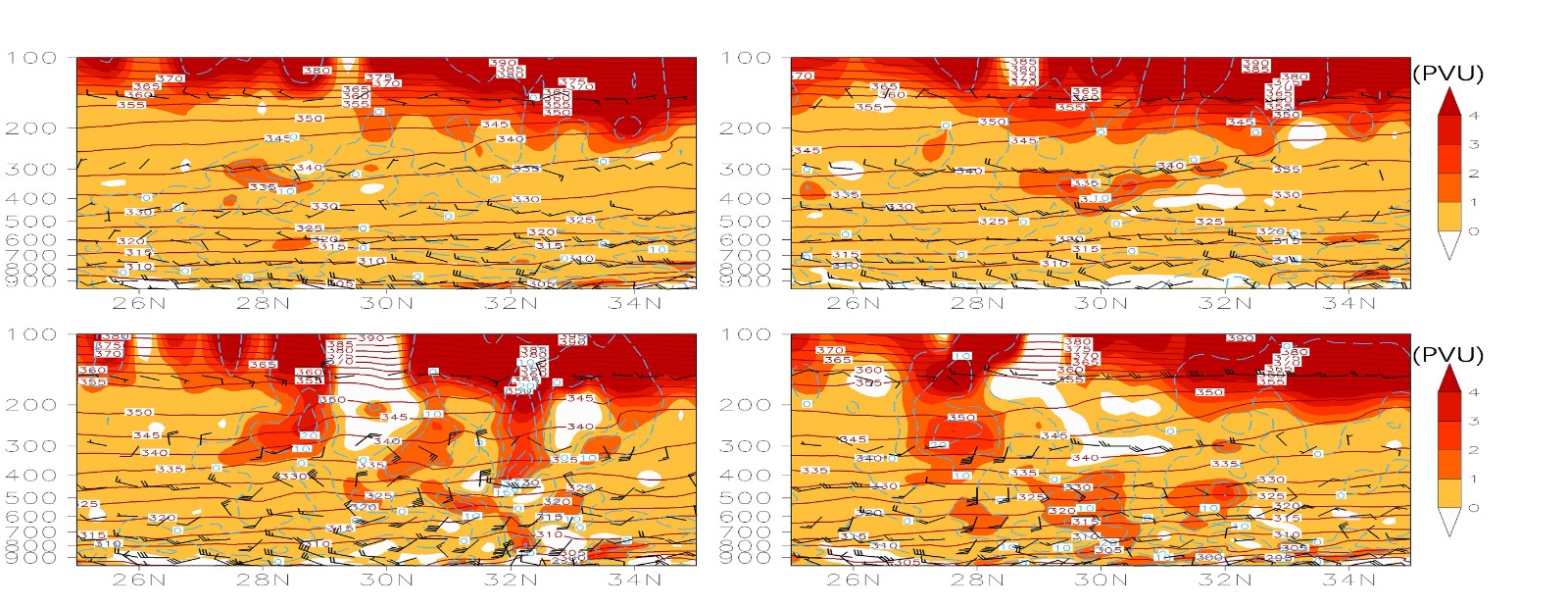
中文摘要: 基于常规高空、地面观测资料、NCEP/NCAR再分析资料以及雷达数据对2020年5月4日冷空气影响环流背景下,湖北随州和荆州地区强对流触发机制及演变特征进行分析,并揭示冷空气对强对流触发的作用,结果表明:此次随州地区强对流有3次触发过程,触发机制分别为暖区辐合线触发、冷锋触发以及低空急流触发。同时随州特殊地形对强对流维持起了重要作用。冷锋触发强对流条件与冷空气厚度和自由对流高度有关。当冷空气与暖湿气流辐合层高于自由对流高度,且辐合有一定垂直厚度时,更易触发对流。随州地区冷空气强度较强,对流层低层锋区明显,正位涡异常中东部上升气流较强,更易触发对流。荆州地区对流层底层锋区减弱,冷空气较弱,上升气流偏弱,导致荆州南部地区无对流触发。
中文关键词: 对流触发,位涡,冷空气,地形
Abstract:Based on the conventional high-altitude and surface observation data, NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data and radar data, this paper analyzes the mechanism and evolution characteristics of convection initiation under the influence of cold air in Suizhou and Jingzhou areas of Hubei Province on 4 May 2020. The results show that there were three initiation processes of severe convection in Suizhou Area, including warm sector convergence process, cold front process and low-level jet process. At the same time, the special topography of Suizhou played an important role in the maintenance of severe convection. The condition of convective initiation under the influence of cold air was related to the thickness of cold air and the level of free convection. When the convergence level of cold air and warm moisture flow was higher than the free convection level and the convergence had a certain vertical thickness, convection initiation was more likely to occur. The cold air intensity in Suizhou was stronger than that in Jingzhou, and the front at lower tropospheric level was strong, the updraft in the middle and east area of the positive potential vorticity anomaly was strong, which favored convection initiation. However, there was no convective initiation in Jingzhou, because the lower tropospheric front was weakened, and the cold air and updraft were also weaker.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41975058)和湖北省气象局科技发展基金项目(2022Z01、2022Y25、2022Z02)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 许冠宇 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 黄龙飞 | 江西省景德镇市气象局,景德镇 333000 |
| 吴涛 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
| 杨浩 | 中国气象局武汉暴雨研究所,武汉 430205 |
| 钟敏 | 武汉中心气象台,武汉 430074 |
引用文本:
许冠宇,黄龙飞,吴涛,杨浩,钟敏,2022.华中地区春季一次强对流触发的多尺度影响机制分析[J].气象,48(8):979-992.
XU Guanyu,HUANG Longfei,WU Tao,YANG Hao,ZHONG Min,2022.Analysis of Multi-Scale Influence Mechanism of a Severe Convection Initiation in Spring in Central China[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):979-992.
许冠宇,黄龙飞,吴涛,杨浩,钟敏,2022.华中地区春季一次强对流触发的多尺度影响机制分析[J].气象,48(8):979-992.
XU Guanyu,HUANG Longfei,WU Tao,YANG Hao,ZHONG Min,2022.Analysis of Multi-Scale Influence Mechanism of a Severe Convection Initiation in Spring in Central China[J].Meteor Mon,48(8):979-992.