本文已被:浏览 795次 下载 3952次
投稿时间:2021-09-29 修订日期:2021-12-02
投稿时间:2021-09-29 修订日期:2021-12-02
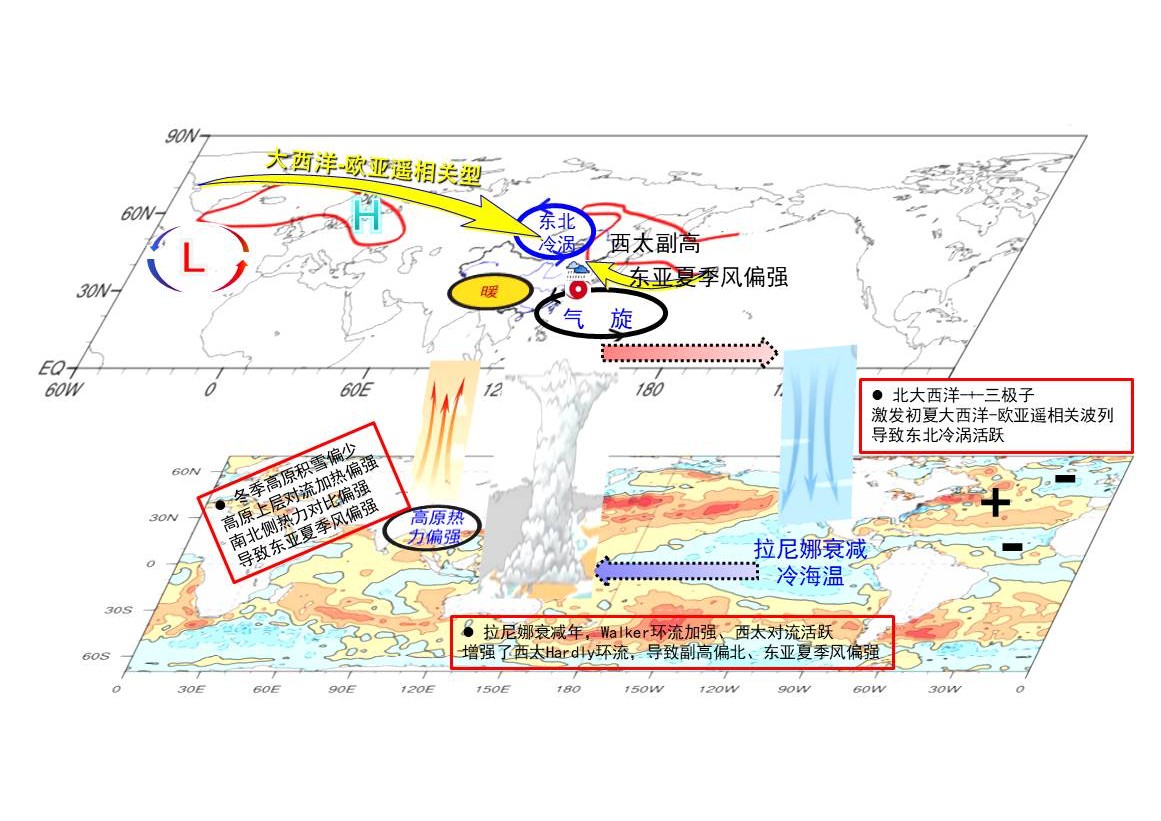
中文摘要: 2021年夏季我国天气气候异常特征突出,极端天气气候事件多,东部主要多雨区在我国北方,降水的季节内变化显著,华南前汛期开始偏晚、江淮流域梅雨和华北雨季开始偏早。东亚大气环流季节内变化对降水异常的空间分布影响较大。6月,东北冷涡活动频繁,导致东北及邻近区域降水异常偏多,黑龙江、嫩江流域发生严重汛情;东北冷涡的异常活跃可能受到前期北大西洋三极子海温持续正位相的影响。7月,长江下游至内蒙古东部的经向型多雨带及河南特大暴雨,主要受到台风烟花长时间维持和北上、偏强的大陆高压和偏东偏北的西太平洋副热带高压的综合影响;副热带大气环流表现出对前期La Ni〖AKn~D〗a事件衰减的滞后响应可能是重要原因。8月,副热带高压异常偏强、偏南,水汽输送异常辐合区位于我国长江流域,导致持续时间长的“倒黄梅”天气;8月热带大气低频振荡处于印度洋达22 d,平均强度偏强,可能是导致副热带大气环流季节内转折的重要原因。
Abstract:The anomaly characteristics of the weather and climate in China were outstanding in the summer of 2021. During this summer, many extreme weather and climate events tookplace with much more precipi- tation in North China. The intraseasonal variation of summer climate was significant. The pre-monsoonal rainfall season in South China started later, and the Meiyu in Yangtze-Huaihe River Valley and the North China rainy season started earlier than normal. The spatial distribution of monthly precipitation anomaly and its possible causes varied greatly in the summer of 2021. In June, the Northeast China cold vortex activity was very frequent, bringing more precipitation in North China and Northeast China. Severe floods occurred in Heilongjiang and Nenjiang River basins. The anomalous activity of the Northeast China cold vortex was mainly influenced by the positive phase of the North Atlantic triple from spring to June 2021. In July, the longitudinal rainy belt from the lower reaches of the Yangtze River to the eastern part of Inner Mongolia and the extremely severe rainfall in Henan were mainly affected by the long-term activity of the strong Typhoon In-Fa, the strong continental high and the Western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH). La Ni〖AKn~D〗a was an important external forcing factor for the above circulation anomalies. In August, the WPSH was much stronger and more southward. The associated anomalous low-level northwestern Pacific anticyclone resulted in anomalous convergence of moisture flux over the Yangtze River and “reoccurrence of Meiyu” weather. Further analysis indicates that the unusually active Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) in August was the critical cause for the significant turning of the tropical and subtropical circulations. MJO located in the Indian Ocean (Phase 2) lasted for 22 days with stronger average intensity, which was rare in history.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0606301)、国家自然科学基金项目(42075017、41875093、42175047、41975098)和2021年中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2021Z011、CXFZ2021J028)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 赵俊虎 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 |
| 陈丽娟 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,南京 210044 |
| 章大全 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 赵俊虎' target='_blank'>ZHAO Junhu | Laboratory of Climate Studies, National Climate Centre, CMA, Beijing 100081 |
| 陈丽娟' target='_blank'>CHEN Lijuan | Laboratory of Climate Studies, National Climate Centre, CMA, Beijing 100081 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044 |
| 章大全' target='_blank'>ZHANG Daquan | Laboratory of Climate Studies, National Climate Centre, CMA, Beijing 100081 |
引用文本:
赵俊虎,陈丽娟,章大全,2022.2021年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,48(1):107-121.
ZHAO Junhu,CHEN Lijuan,ZHANG Daquan,2022.Characteristics and Causes for the Climate Anomalies over China in Summer 2021[J].Meteor Mon,48(1):107-121.
赵俊虎,陈丽娟,章大全,2022.2021年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,48(1):107-121.
ZHAO Junhu,CHEN Lijuan,ZHANG Daquan,2022.Characteristics and Causes for the Climate Anomalies over China in Summer 2021[J].Meteor Mon,48(1):107-121.