本文已被:浏览 239次 下载 2410次
投稿时间:2022-10-08 修订日期:2022-11-25
投稿时间:2022-10-08 修订日期:2022-11-25
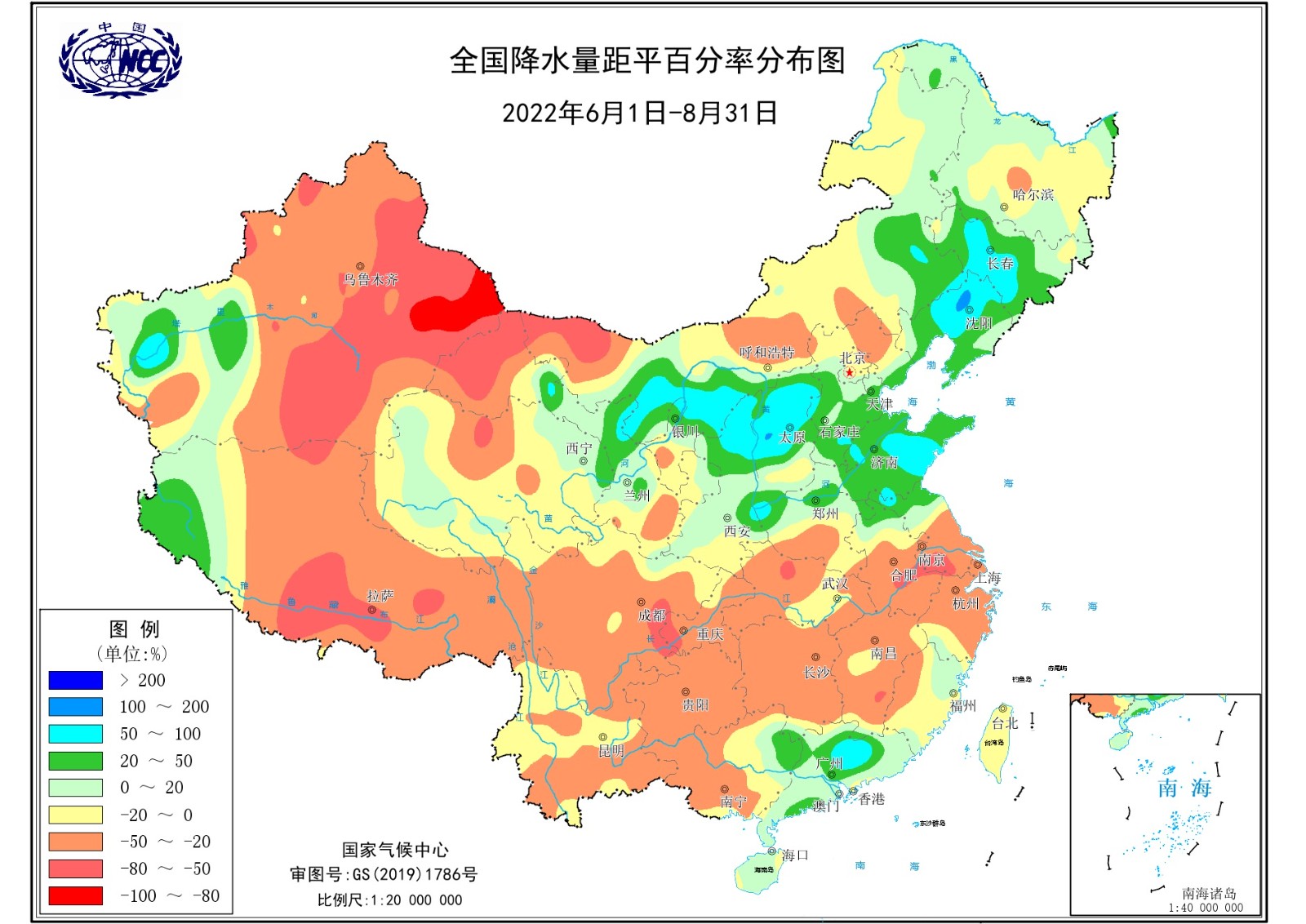
中文摘要: 2022年夏季我国气候异常特征突出,区域性、阶段性旱涝灾害明显,降水空间差异显著。利用观测资料和再分析数据,基于合成和相关分析等方法,总结和探讨东亚夏季风和我国气候异常特征及可能成因。结果表明:2022年东亚夏季风季节进程总体提前,南海夏季风爆发偏早,华南前汛期、西南雨季、江南和长江中下游梅雨、华北和东北雨季开始均较常年偏早。2022年夏季我国气候总体温高雨少,全国平均气温为1961年以来历史同期最高,全国平均降水量为历史同期第二少,盛夏长江流域发生破纪录的高温伏旱。夏季降水异常的阶段性特征显著,6月上中旬主雨带位于华南,6月下旬至8月,随西太平洋副热带高压明显北跳,多雨区北移至华北、黄淮、东北、西北地区东部等地,我国东部地区降水呈“北多南少”分布。2022年夏季气候异常与海温等外强迫因子密切相关。La Ni〖AKn~D〗a事件在春季再次发展,赤道中太平洋冷海温加强和海洋性大陆上空对流活跃,热带印度洋偶极子负位相异常偏强,黑潮及延伸区海温偏暖,导致西太平洋副热带高压加强西伸和北抬,对夏季主雨带位置偏北和长江流域持续性异常高温天气起到重要作用。
Abstract:The climate over China in summer 2022 was extremely abnormal, with significant regional floods and droughts and spatial difference in rainfall distribution. Based on observational and reanalysis dataset, the characteristics and possible causes of East Asia summer monsoon (EASM) and climate anomalies over China was summarized and investigated through correlation and composite analysis. It has been found that the seasonal march of EASM was ahead of climatological mean in general. The onset date of South China Sea monsoon, and the start dates of pre Meiyu rainy season in South China, rainy season in Southwest China, Meiyu in Jiangnan and the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, rainy season in North China and Northeast China were all earlier than in normal years. The average surface temperature over China in summer 2022 ranked the highest since 1961, while the average precipitation across the whole China was the second lowest compared with the rainfall in the same period in history. The Yangtze River Basin experienced record breaking high temperatures and drought in midsummer. The distribution of precipitation also showed significant intraseasonal variability. In early and middle 〖JP2〗June, the main rain belt was in South China. 〖JP〗From late June through August, the western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) shifted northward bringing the main rain belt to shift to North China, Northeast China, Huanghuai Region and eastern Northwest China, and the precipitation in the eastern part of China was “more in the north and less in the south”. The heat wave and drought persisted in the Yangtze River Valley throughout the summer. The abnormal climate in summer 2022 was closely related to the oceanic external forcing. The reinforcement of La Ni〖AKn~D〗a in spring and intensified negative SST anomalies in central Pacific, active convection over maritime continent, developing negative phase of Indian Ocean dipole mode, the Kuroshio and its warm extension area all contributed to the intensification and northwestward extension of WPSH, the northward location of the summer main rain belt and the record breaking heat wave in the Yangtze River Valley.
文章编号: 中图分类号:P461 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金委员会-云南省人民政府联合基金项目(U1902209)、国家自然科学基金项目(41730964、41975091、42175047、41605078)和中国长江三峡集团有限公司项目(0704181)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 章大全 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081; 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,南京 210044 |
| 袁媛 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 |
| 韩荣青 | 国家气候中心,中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 |
引用文本:
章大全,袁媛,韩荣青,2023.2022年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,49(1):110-121.
ZHANG Daquan,YUAN Yuan,HAN Rongqing,2023.Characteristics and Possible Causes of the Climate Anomalies over China in Summer 2022[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):110-121.
章大全,袁媛,韩荣青,2023.2022年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,49(1):110-121.
ZHANG Daquan,YUAN Yuan,HAN Rongqing,2023.Characteristics and Possible Causes of the Climate Anomalies over China in Summer 2022[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):110-121.