本文已被:浏览 1次 下载 0次
投稿时间:2024-05-20 修订日期:2025-07-24
投稿时间:2024-05-20 修订日期:2025-07-24
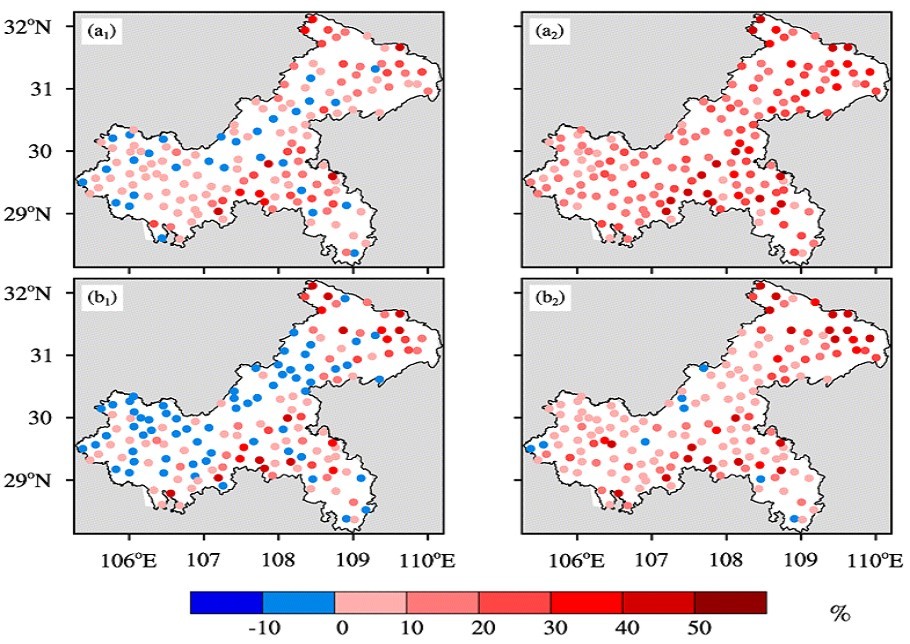
中文摘要: 综合考虑模式气温预报、模式地形和实况气温、真实地形之间的相互关系,设计了随时空演变的动态近似垂直变率2 m气温订正方法,开展2023年重庆地区订正试验。ECMWF模式预报的评估结果表明:2 m最高和最低气温预报性能的空间分布相似,最高气温预报性能明显弱于最低气温,且预报性能随预报时效延长而降低;模式地形高度偏差与气温预报偏差关系密切,在模式地形高度偏差较小的地区,气温预报性能较高,反之亦然。对比研究发现:基于动态近似垂直变率的订正方案,订正能力显著优于基于固定垂直变率的订正方案,二者都能改善ECMWF模式气温预报,对最高气温的订正效果优于最低气温。与ECMWF模式预报相比,基于动态近似垂直变率的订正结果,10 d平均的最高、最低气温预报准确率分别提高了12.71%、8.30%,平均绝对误差分别降低了0.68℃、0.30℃;月平均的24 h预报时效最高、最低气温预报准确率分别提高了20.34%、14.44%,订正后的气温预报性能更加稳定。基于动态近似垂直变率的订正方案,能有效降低气温预报偏差;模式地形高度偏差越大,天气过程波动幅度越小,订正效果越明显。
Abstract:Taking into account the relationships between model temperature forecasts, model topography, observed temperatures and actual topography, this paper designs a dynamically approximated vertical rate correction method for the 2 m temperature that evolves over space and time. A correction test is conducted for Chongqing in 2023. The evaluation results of ECMWF model forecasts show that the spatial distribution of forecast skill for maximum and minimum 2 m temperatures is similar, but forecast skill for maximum temperature is significantly weaker than for minimum temperature, and deteriorates with increasing forecast lead time. A close correlation is found between model topographic elevation bias and temperature forecast bias. Areas with smaller elevation bias tend to exhibit better forecast skill, and vice versa. Comparative research reveals that the correction scheme based on dynamically approximated vertical rate signifi-cantly outperforms the scheme based on the constant vertical rate. Both schemes can improve the ECMWF model temperature forecasts, with better correction performance for maximum temperatures than for minimum temperatures. Compared to the raw model forecasts, the corrected results based on dynamically approximated vertical rate have increased the 10 d average forecast accuracy of maximum and minimum temperatures by 12.71% and 8.30%, respectively, and reduced the mean absolute error by 0.68℃ and 0.30℃, respectively. The monthly average forecast accuracy of the maximum temperature for 24 h forecast lead time has increased by 20.34% and the minimum temperature has increased by 14.44%. Overall, the corrected temperature forecasts are more stable. The correction scheme based on dynamically approximated vertical rate can effectively reduce the temperature forecast bias. The greater the model topographic elevation bias, the smaller the amplitude of weather process fluctuation, and the more obvious the correction performance.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:中国气象局青年创新团队项目(CMA2024QN04)、中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2023J001)、重庆市气象部门业务技术攻关项目(YWJSGG-202302)和重庆市自然科学基金面上项目(cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0057)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 吴胜刚 | 中国气象局气候资源经济转化重点开放实验室,重庆 401147 重庆市气象台,重庆 401147 |
| 赵声蓉 | 国家气象中心,北京 100081 |
| 王玉 | 国家气象中心,北京 100081 |
| 张焱 | 中国气象局气候资源经济转化重点开放实验室,重庆 401147 重庆市气象台,重庆 401147 |
引用文本:
吴胜刚,赵声蓉,王玉,张焱,2025.基于动态近似垂直变率的ECMWF模式2 m气温订正方法研究[J].气象,51(10):1237-1248.
WU Shenggang,ZHAO Shengrong,WANG Yu,ZHANG Yan,2025.Study on ECMWF 2 m Temperature Bias Correction Based on Dynamically Approximated Vertical Change Rate[J].Meteor Mon,51(10):1237-1248.
吴胜刚,赵声蓉,王玉,张焱,2025.基于动态近似垂直变率的ECMWF模式2 m气温订正方法研究[J].气象,51(10):1237-1248.
WU Shenggang,ZHAO Shengrong,WANG Yu,ZHANG Yan,2025.Study on ECMWF 2 m Temperature Bias Correction Based on Dynamically Approximated Vertical Change Rate[J].Meteor Mon,51(10):1237-1248.