本文已被:浏览 0次 下载 0次
投稿时间:2024-07-23 修订日期:2025-04-03
投稿时间:2024-07-23 修订日期:2025-04-03
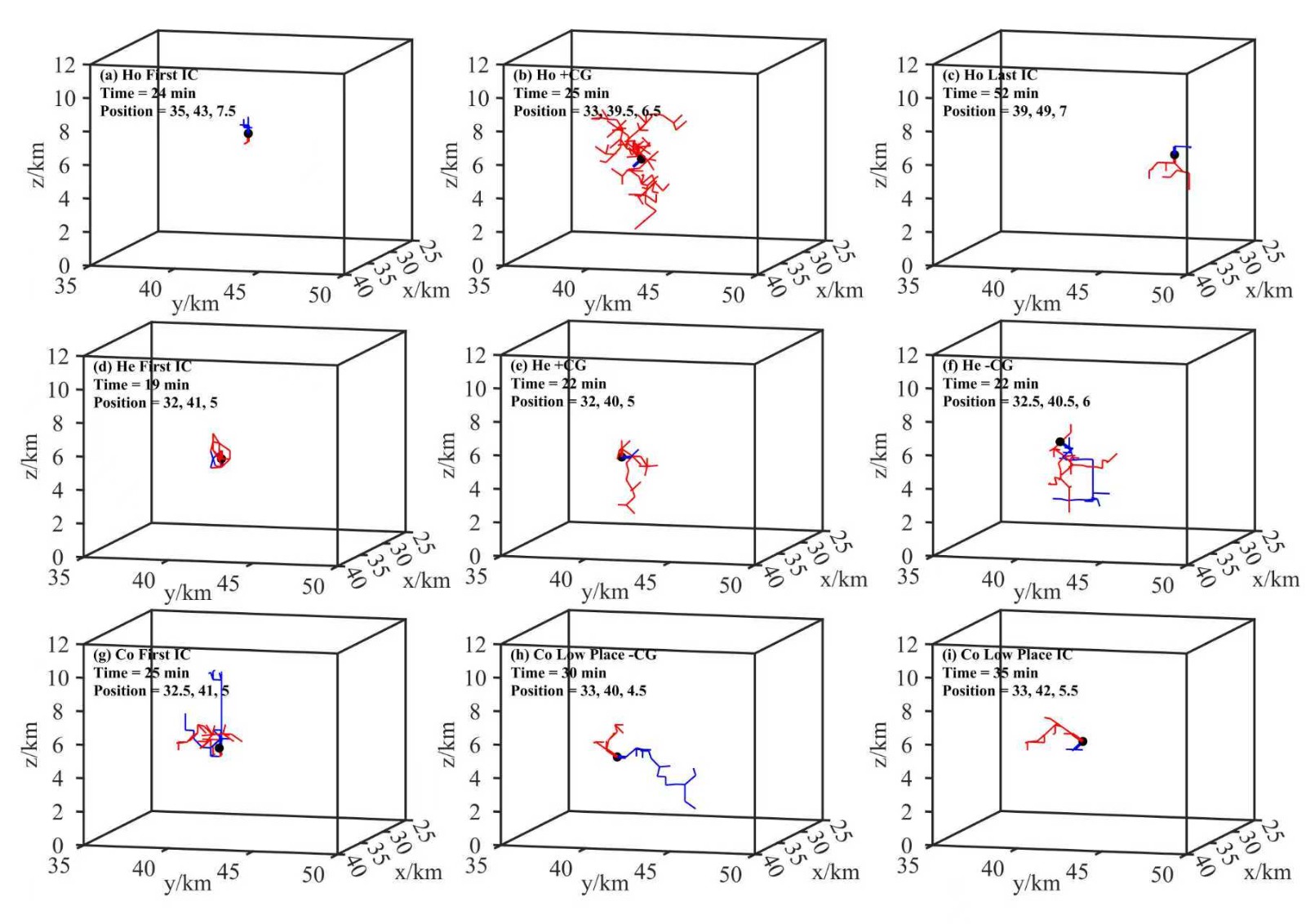
中文摘要: 近年来,气溶胶与雷暴云电学活动的相互作用关系已成为学术界关注的重点之一。可溶气溶胶液滴的同质核化和冰核异质核化是冰晶粒子形成的两种来源,而雷暴云中冰晶粒子大小和浓度对电荷的产生及其分层状况有一定影响,是导致闪电发生的重要因素。文中利用三维雷暴云模式,选取一次山地弱雷暴个例,研究了三种冰晶核化方案对雷暴云放电特征的影响。结果表明:同质核化在云顶低温区形成大量冰晶粒子,雷暴云中放电持续时间长,电荷结构以偶极性为主,闪电频次较低,产生的闪电以云闪为主,其触发点高度高。异质核化在高温区形成冰晶,导致雷暴云中出现更早的起电过程,高温区冰晶易满足电荷反转条件,显著增加了负非感应起电率,雷暴云电荷结构易形成三极型。此背景下,闪电发生时间提前且触发点相对较低,即异质核化促进了闪电的发生。同质核化和异质核化同时发生时,雷暴起电过程强,闪电频次高。此外,两种核化过程造成闪电首次发生时间提前,闪电的触发点高度分布范围大,三极型电荷结构促进了更多负地闪的发生。
中文关键词: 核化过程,同质核化,异质核化,闪电频次,数值模拟
Abstract:In recent years, the interaction between aerosols and thunderstorm electrification has emerged as a focal point in academic research. Homogeneous nucleation of soluble aerosol droplets and heterogeneous nucleation of ice nuclei are two primary sources for ice crystal formation. The size and concentration of ice crystals in thunderstorms significantly influence charge generation and distribution, and are critical factors in lightning events. This paper employs a three-dimensional thunderstorm model to investigate the impact of three distinct ice nucleation schemes on lightning discharge characteristics, focusing on a mountain weak thunderstorm case. The results demonstrate that homogeneous nucleation generates a substantial number of ice crystals in the low-temperature zones at the cloud top, resulting in prolonged discharge duration within the thunderstorm. The charge structure is predominantly dipolar, with a lower lightning frequency, primarily consisting of cloud flashes originating from higher altitudes. In contrast, heterogeneous nucleation forms ice crystals in high-temperature zones, leading to an earlier charging process in thunderstorms. Ice crystals in these zones readily meet charge reversal conditions, significantly increasing the negative non-inductive charging rate and favoring the formation of tripolar charge structures. Under these conditions, lightning occurs earlier and initiates from relatively lower altitudes, with heterogeneous nucleation facilitating lightning occurrence. When both homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation processes occur simultaneously, the thunderstorm charging process intensifies, resulting in a high lightning frequency. Furthermore, both nucleation processes advance the initial lightning occurrence time and expand the height range of the initial lightning trigger points. The tripolar charge structure promotes the occurrence of a substantial number of negative cloud-to-ground flashes.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点项目(42030606)、中国气象局雷电重点开放实验室开放课题(2024KELL-A004)和浙江省自然科学基金联合基金项目(LZJMZ24D050009)共同资助
引用文本:
师正,陈浩琛,樊艳峰,曲凯悦,崔雪东,陈家豪,王玉莹,2025.不同核化过程对雷暴云放电过程影响的数值模拟研究[J].气象,51(10):1215-1225.
SHI Zheng,CHEN Haochen,FAN Yanfeng,QU Kaiyue,CUI Xuedong,CHEN Jiahao,WANG Yuying,2025.Numerical Simulation Study on Effects of Different Nucleation Parameterizations on Electrification in Thunderstorms[J].Meteor Mon,51(10):1215-1225.
师正,陈浩琛,樊艳峰,曲凯悦,崔雪东,陈家豪,王玉莹,2025.不同核化过程对雷暴云放电过程影响的数值模拟研究[J].气象,51(10):1215-1225.
SHI Zheng,CHEN Haochen,FAN Yanfeng,QU Kaiyue,CUI Xuedong,CHEN Jiahao,WANG Yuying,2025.Numerical Simulation Study on Effects of Different Nucleation Parameterizations on Electrification in Thunderstorms[J].Meteor Mon,51(10):1215-1225.