本文已被:浏览 491次 下载 2683次
投稿时间:2023-02-03 修订日期:2023-03-22
投稿时间:2023-02-03 修订日期:2023-03-22
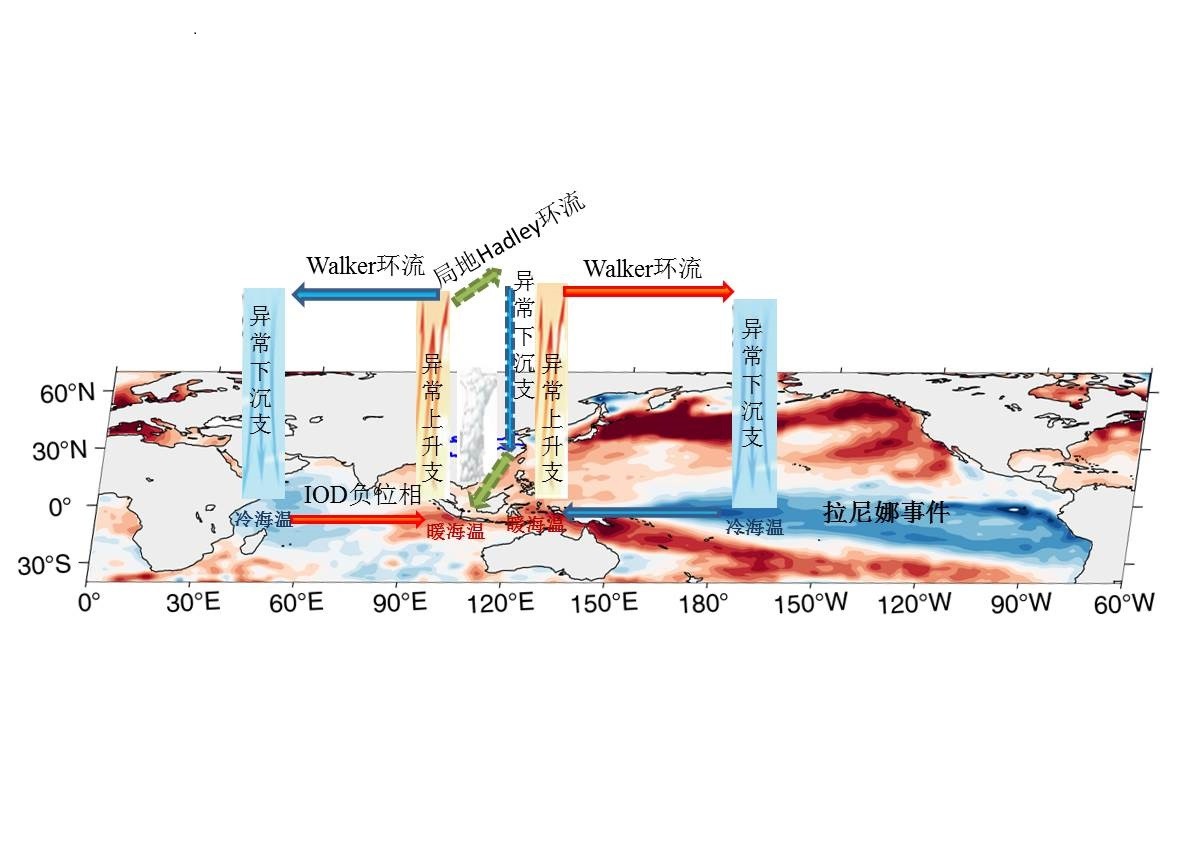
中文摘要: 2022年秋季,全国气候总体呈现暖干的特征,其中南方大部出现持续高温干旱。秋季平均气温为1961年以来历史同期最高。秋季降水季节内变率大,9月全国大部降水偏少,10月降水总体呈现南北少、中间多,11月我国中东部大部降水偏多而西部大部降水偏少。9—10月环流异常特征显示我国南方上空为偏北风距平,来自南海和西北太平洋的水汽输送条件极差,西北太平洋副热带高压偏强偏西,我国南方受下沉运动控制,有利于大部地区降水偏少、气温偏高,出现持续干旱。海温外强迫影响分析显示,2022年秋季印度 太平洋暖池异常偏暖,热带太平洋中东部偏冷,赤道印度洋西部偏冷,对应赤道印度洋上空纬向季风环流和太平洋上空Walker环流之间为显著的耦合特征。热带印度洋偶极子(TIOD)显著影响区域为江南西部和西南地区东南部,厄尔尼诺 南方涛动显著影响区域是江南大部和华南北部。即2022年秋季我国南方降水异常偏少受到TIOD负位相和拉尼娜状态的协同影响。
Abstract:In boreal autumn (September-October-November, SON) of 2022, the climate of China is characterised as “warmer and drier” than normal, and most of southern part has experienced persistent high temperature and drought. The average autumn temperature in China is ranked the highest since 1961. And the intraseasonal variability of precipitation is significant, with less rainfall in most of China in September, less in the south and north of China and more in Central China in October, more in central-eastern China and less in the west of China in November. From September to October, the northerly wind anomaly is strong over southern China with worse than normal moisture transport from South China Sea and Northwesten Pacific. The West Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) is stronger, larger and more westward than normal. Descending motion is dominant over southern China leading to less rainfall and high temperature, and thus drought condition. The influence of tropical sea surface temperature (SST) forcing shows that the warmer warm-pool in Indo-Pacific, colder SST in tropical East-Central Pacific and west equatorial Indian, correspond to the significant coupling characteristics between the zonal monsoon circulation over the equatorial Indian Ocean and the Walker circulation over the Pacific Ocean, which further play important roles in modulating drought over most of southern China. The SST anomalies in equatorial Indian and Pacific are coupled with the air-sea gearing between Indian summer monsoon and Walker circulation in Pacific. The tropical Indian Ocean dipole (TIOD) has significant influence of precipitation over the western part of Jiangnan and the southeastern part of Southwest China, while El Ni〖AKn~D〗o-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) mainly affects most of Jiangnan and northern South China. Therefore, the heavy drought over southern China in autumn 2022 is modulated by both the TIOD negative mode and La Ni〖AKn~D〗a state.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(U2242206、41975088、42275030)、国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1506006)、国家重点基础研究发展计划(973计划)(2015CB453203)和中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022J009)共同资助
引用文本:
洪洁莉,陈丽娟,王悦颖,章大全,2023.2022年秋季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,49(4):495-505.
HONG Jieli,CHEN Lijuan,WANG Yueying,ZHANG Daquan,2023.Features and Possible Causes of Abnormal Climate over China in Autumn 2022[J].Meteor Mon,49(4):495-505.
洪洁莉,陈丽娟,王悦颖,章大全,2023.2022年秋季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J].气象,49(4):495-505.
HONG Jieli,CHEN Lijuan,WANG Yueying,ZHANG Daquan,2023.Features and Possible Causes of Abnormal Climate over China in Autumn 2022[J].Meteor Mon,49(4):495-505.