本文已被:浏览 682次 下载 3124次
投稿时间:2021-11-17 修订日期:2022-05-16
投稿时间:2021-11-17 修订日期:2022-05-16
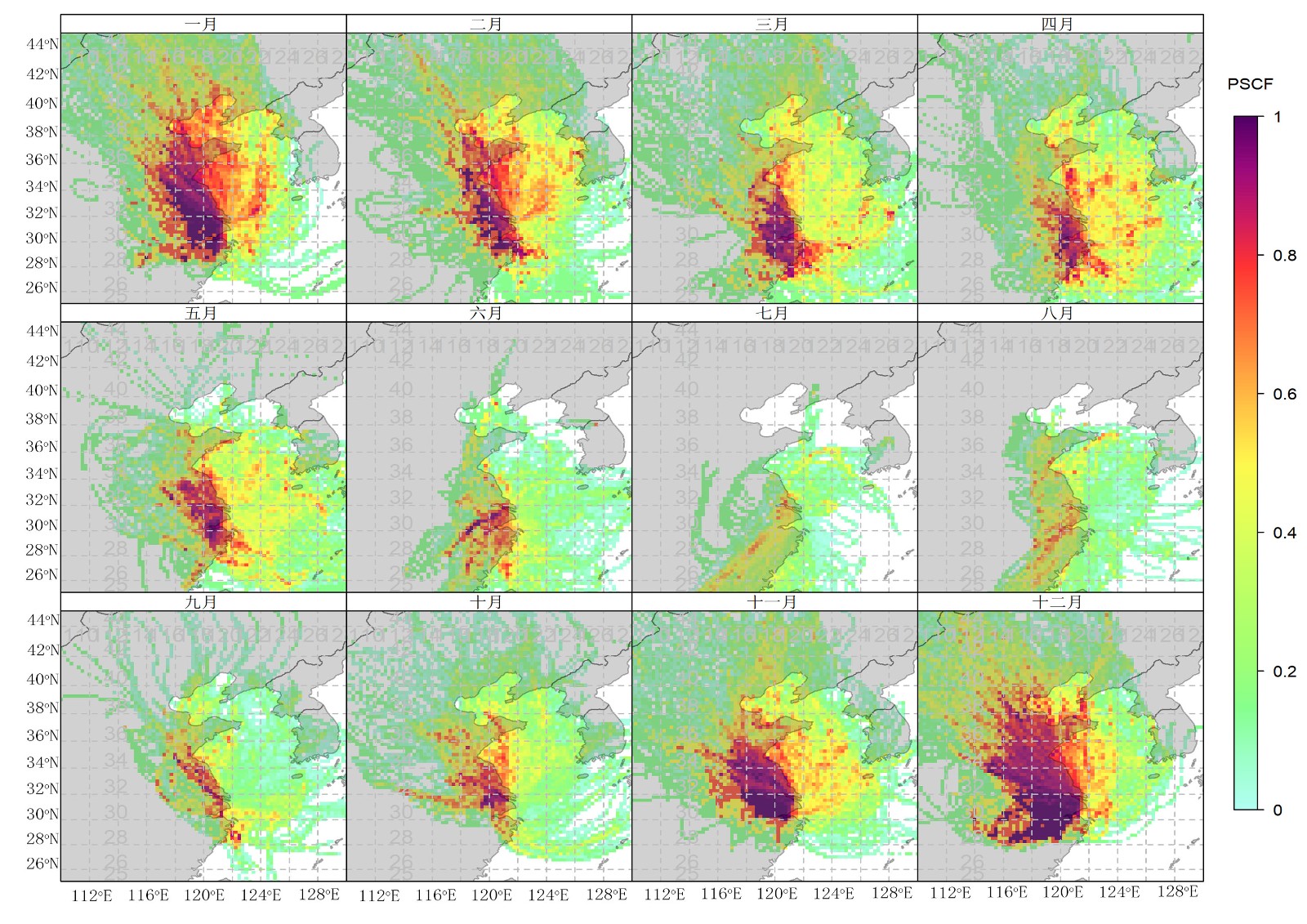
中文摘要: 根据2008—2015年上海崇明东滩大气成分观测站(以下简称东滩站)大气颗粒物(PM)观测数据,分析其浓度水平、变化趋势、影响气团和潜在源区。结果表明,2008—2015年东滩站PM质量浓度的长期变化趋势不显著,但细粒子(PM2.5)比例不断升高。PM2.5/PM10从0.84上升至0.92,表明二次气溶胶占比趋于增加。对8年大样本数据进行后向轨迹聚类,发现东滩站主要受大陆型、海洋型、大陆/海洋混合型气团影响,三者所占比率分别为32.0%、38.8%、29.3%。海洋型气团中PM2.5本底质量浓度为11~15 μg·m-3,而大陆型气团中PM2.5本底质量浓度的季节差异显著,在29~56 μg·m-3波动,对东滩站具有明显的输入效应。东滩站PM2.5的潜在源区随季节变化,秋季和冬季主要受华北、黄淮、苏皖影响,春季收缩至苏皖和浙江北部,夏季则转换至长三角南部的浙江及浙闵沿海。总体而言,上海及周边的苏锡常、杭嘉湖对东滩PM2.5浓度贡献最显著,来自渤海、黄海近海污染回流的贡献也不可忽视。
中文关键词: 东滩,可吸入颗粒物,后向轨迹,潜在源区
Abstract:Based on the particulate matter and meteorological measurements at the Dongtan Atmospheric Composition Observing Station (shortened Dongtan Station) from 2008 to 2015, the arriving air mass is classified, the PM2.5 concentration level and its annual variation are examined, and the potential source of higher level of PM2.5 is also identified in this article. The long-term variation of PM2.5 concentration presents an in-significant trend from 2008 to 2015, but the percentage of fine particles (PM2.5) keeps increasing. The ratio of PM2.5/PM10 increases from 0.84 to 0.92, indicating more and more data of secondary aerosols are observed at Dongtan Station. The air mass of 8-year big sample data at Dongtan Station can be aggregated into 3 types of back trajectories, that is, land, ocean, and land/ocean mixing types, accounting for 32.0%, 38.8% and 29.3% respectively. Among them, the PM2.5 background mass concentration ranges stably within 11-15 μg·m-3 in ocean air mass, 〖JP2〗but 29-56 μg·m-3 in land air mass, showing largely seasonal variability. The potential source of relatively higher PM2.5 observed at Dongtan Station presents clear seasonal transition from areas north to Shanghai including North China and, Huanghuai regions as well as Jiangsu and Anhui provinces in autumn and winter to southern Yangtze River Delta region including northern Zhejiang Province and its seaboard extending to Fujian Province in summer by PSCF analysis. In general, higher PM2.5 loading at Dongtan Station is mostly contributed by air mass from Shanghai and its neighboring city clusters including Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Jiaxing and Huzhou etc. It is noted that air mass recycled from Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea is also an important source area for the elevated PM2.5 observed at Dongtan Station in spring, autumn and winter.
文章编号: 中图分类号:X16,P448 文献标志码:
基金项目:上海市科学技术委员会科研计划(19DZ1205003)、中国气象局风云三号03批气象卫星工程项目[FY-3(03)-AS-12.08]共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 许建明 | 长三角环境气象预报预警中心,上海 200135 |
| 阎凤霞 | 中国民用航空华东地区空中交通管理局气象中心,上海 200335 |
| 潘亮 | 长三角环境气象预报预警中心,上海 200135 |
| 贺芳芳 | 上海市气候中心,上海 200135 |
| 高伟 | 长三角环境气象预报预警中心,上海 200135 |
引用文本:
许建明,阎凤霞,潘亮,贺芳芳,高伟,2023.上海东滩大气颗粒物长期变化及影响源区分析[J].气象,49(1):74-86.
XU Jianming,YAN Fengxia,PAN Liang,HE Fangfang,GAO Wei,2023.Analysis on the Long-Term Variation and Potential Source of the Particulate Matters Observed at Dongtan Station in Shanghai[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):74-86.
许建明,阎凤霞,潘亮,贺芳芳,高伟,2023.上海东滩大气颗粒物长期变化及影响源区分析[J].气象,49(1):74-86.
XU Jianming,YAN Fengxia,PAN Liang,HE Fangfang,GAO Wei,2023.Analysis on the Long-Term Variation and Potential Source of the Particulate Matters Observed at Dongtan Station in Shanghai[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):74-86.