本文已被:浏览 577次 下载 4264次
投稿时间:2022-07-22 修订日期:2022-11-18
投稿时间:2022-07-22 修订日期:2022-11-18
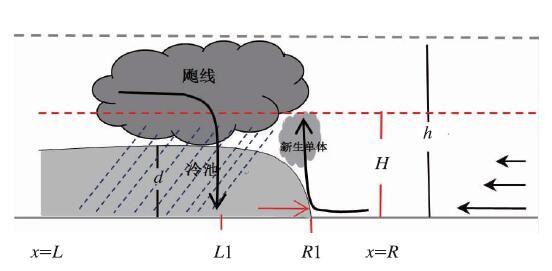
中文摘要: 从预报预警业务的视角,重点讨论了直线型对流大风形成机理与对流风暴形态结构演变、风暴内部热动力学与云-水微物理过程之间的科学逻辑关系,以及它们在现代业务观测体系中的“显性表征”,对一些存在不同观点或解释的科学问题进行了探讨,以期帮助相关人员科学理解“观测现象”背后的物理逻辑、提高科学预警能力。主要结论:对流风暴引发的直线型地面强风,直接驱动因子来自于风暴内部的垂直运动,而垂直运动的主要贡献来自于“热力学作用造成的扰动气压垂直变化”和对流冷池效应强迫,它们又与风暴内部的蒸发(凝结)、融化(凝华)等云-水微物理过程直接相关;这些热动力学和云-水微物理过程的演变可以通过一系列的“观测现象”表征出来,例如雷达观测到的弱回波槽口、后侧入流急流、中层径向强辐合、中气旋、阵风锋等,以及地面气象要素随时间的剧烈变化。线型风暴系统的形态变化特征是由于风暴系统内部的动力学过程或者风暴系统与环境大气相互作用导致的,并不是所有的线型风暴系统都会演变为弓状回波特征的飑线;RKW理论本质上解释了整体飑线系统与环境风垂直切变之间的相互作用问题,实质上环境风场更多是在主导飑线移动和传播,而飑线的发展、维持可能主要是由风暴内部的热动力学过程控制的。
Abstract:In order to help weather forecasters understand the physical mechanisms concealed among observational phenomena and scientifically improve their warning skills, from the operational point of view on weather forecasting and warning, this paper emphatically discusses the scientific relationships between the mechanisms triggering linear convective gales and the structure evolution, thermodynamic and dynamic processes of convective storms and the cloud-water macrophysical processes, and also explains their “dominant characters” in the contemporary operational observation system. Besides, some scientific problems with different views or interpretations are discussed as well. The major results are as follows. The surface linear gales incurred by convective storms are directly derived from the internal vertical movement of storms, while major compositions of the vertical velocity are contributed by the cold pool forcing and the downward vertical gradient of the disturbed pressure for thermodynamic effect. The thermodynamic effect and cold pool effect are directly related to cloud-water macrophysical processes within storms, such as evaporation (condensation), melting (sublimation), and their evolutions can be demonstrated by a series of observed phenomena, such as weak echo slot, descending rear inflow jet, MARC (mid-altitude radial convergence), mesocyclone, gust front and the acute variations of meteorological elements on surface. The pattern variations of linear convective storms are induced by the inner dynamic processes of storm systems or by the interaction between storm systems and ambient atmosphere. It can not be definitely considered that all linear convective storms should develop into squall lines with bow echoes. The RKW theory can essentially interpret the interaction between the integrated squall line and the vertical shear of ambient wind. Virtually, the ambient wind performs the principal function of leading the movement and propagation of squall line, and the development or maintenance of squall line is possibly controlled by its inner thermodynamic and dynamic processes.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金气象联合基金项目(U2142203)资助
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| SUN Jisong | State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081 Nanjing Joint Institute for Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing 210041 |
引用文本:
孙继松,2023.与直线型对流大风相关的强风暴形态结构和热动力学过程[J].气象,49(1):1-11.
SUN Jisong,2023.The Pattern Structure and Thermodynamic and Dynamic Processes of Severe Storms Associated with Linear Convective Gales[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):1-11.
孙继松,2023.与直线型对流大风相关的强风暴形态结构和热动力学过程[J].气象,49(1):1-11.
SUN Jisong,2023.The Pattern Structure and Thermodynamic and Dynamic Processes of Severe Storms Associated with Linear Convective Gales[J].Meteor Mon,49(1):1-11.