本文已被:浏览 547次 下载 2665次
投稿时间:2021-09-13 修订日期:2022-08-10
投稿时间:2021-09-13 修订日期:2022-08-10
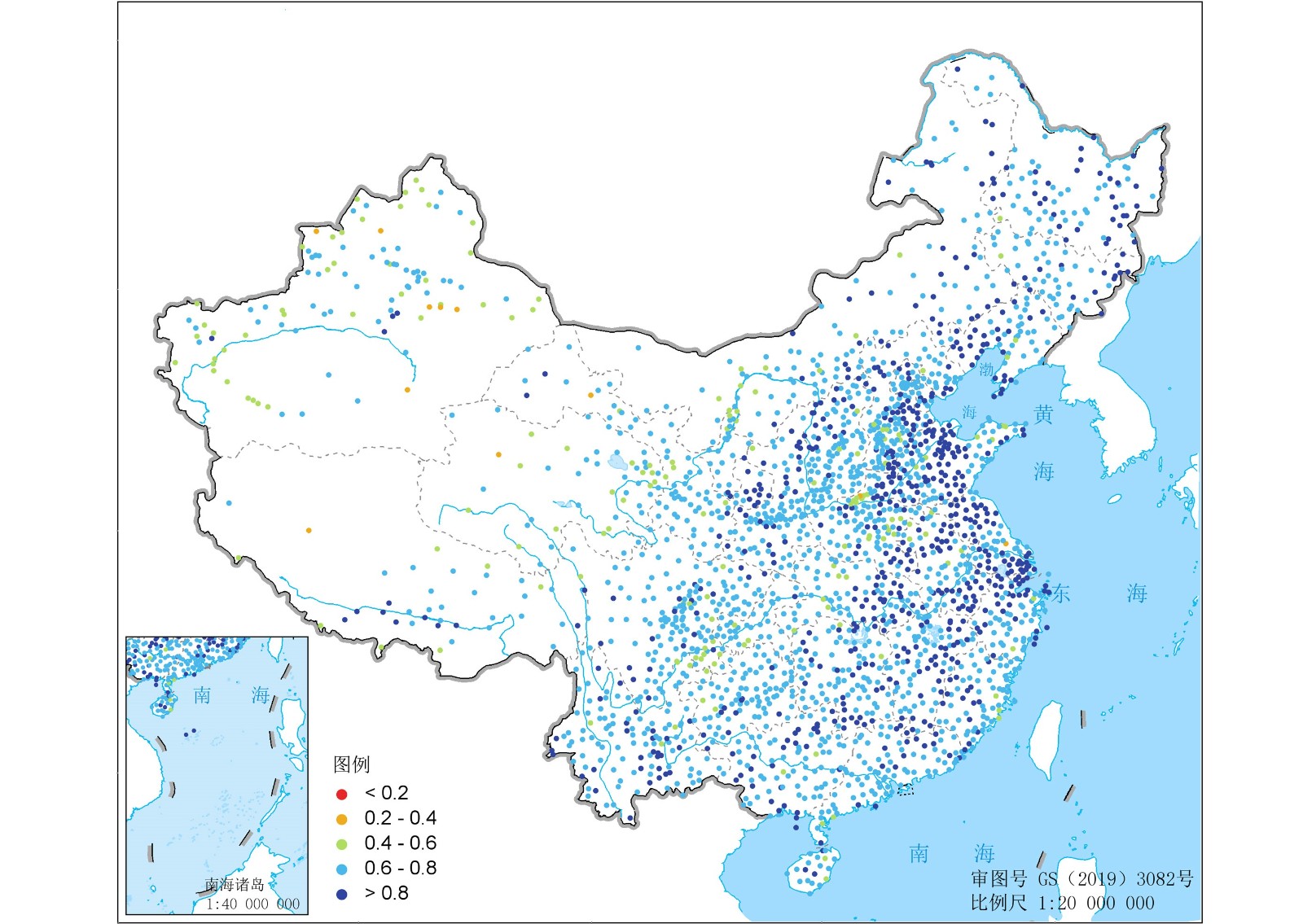
中文摘要: 以中国2423个地面气象站点的降水传感器观测数据为基准,采用定量统计指标(相关系数R、均方根误差RMSE、平均绝对误差MAE、相对误差RE)以及分类统计指标(探测率POD、误报率FAR、虚报漏报率Bias、风险评分ETS),从不同空间尺度、不同时间尺度和不同降水强度三个维度,分析了GPM降水产品的观测准确性,以探究GPM卫星降水产品在中国大陆的适用性。结果表明:从不同空间尺度特征看,GPM降水在全国范围均呈现较高的观测准确性,72%的站点R值超过0.7,在华东地区最好,西北区相对较差;全国大部分区域都为正的相对误差,各区RE集中分布在0~20%。不同高程带内的准确性显示,GPM产品对降水的高估情况在低海拔(<2000 m)、高海拔(>4000 m)地区较为明显,在中海拔地区(2000~4000 m)GPM降水数据适用性相对较好。从不同时间尺度特征看,GPM降水产品与降水传感器实测降水年总量分布上较为一致,两者的R为0.75,但在量值上存在一定程度的偏差,RMSE为6.15 mm·d-1。从逐月结果看,GPM降水产品与地面降水传感器的一致性在1—10月表现较好,R均在0.7以上,11、12月略低,夏季误差值比冬季大。从不同降水强度特征看,POD随着降水强度的增加而降低,GPM降水产品对“中雨”强度降水事件的整体探测能力较优,而在“小雨”和“暴雨”的探测能力稍弱。
中文关键词: GPM,降水量,准确性分析,分类统计指标
Abstract:Based on the gauges data of 2423 meteorological stations in China, continuous statistical metrics (correlation coefficient: R, root mean squared error: RMSE, mean absolute error: MAE, relative error: RE) and classified statistical metrics (probability of detection: POD, false alarm ratio: FAR, bias score: Bias, equitable threat score: ETS) are used to analyze the accuracy of Global Prediction Measurement (GPM) precipitation products from three dimensions including different spatial scales, different time scales and different precipitation intensity so as to explore the applicability of GPM satellite precipitation products over mainland China. The main results show that from different spatial scales, GPM precipitation has high observation accuracy in all regions, and the correlation coefficient (R) values of 72% stations exceede 0.7, with the best in East China and relatively poor in Northwest China. RE is concentrated in 0-20%. The accuracy of different altitude-zone elevations show that the overestimation of GPM is more obvious in low altitude (< 2000 m) and high altitude (> 4000 m) regions, and the applicability of GPM data is relatively good in mid-altitude regions (2000-4000 m). In terms of different temporal scales, the total annual precipitation of GPM is consistent with that of rain gauges, and the R is 0.75, but there is a certain deviation in the amount of precipitation, with RMSE being 6.15 mm·d-1. The consistency between GPM precipitation products and rain gauges is better from January to October, with the R above 0.7, slightly lower in November and December. The error value in summer is higher than that in winter, and the RE is positive mostly. In addition, the accuracy results of different precipitation intensity suggests that POD decreases with the increase〖JP2〗 of precipitation intensity. GPM precipitation products have a better detection ability for “moderate rain” intensity, while the detection ability for “light rain” and “heavy rain” is slightly weaker. 〖JP〗
keywords: GPM (Global Prediction Measurement), precipitation, accuracy analysis, category statistical metric
文章编号: 中图分类号:P414 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1507502)和中国沙漠气象科学研究基金(Sqj2019007)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 施丽娟 | 中国气象局气象探测中心,北京 100081 |
| 冯婉悦 | 新疆维吾尔自治区气象技术装备保障中心,乌鲁木齐 830002 |
| 雷勇 | 中国气象局气象探测中心,北京 100081 |
| 王智敏 | 新疆维吾尔自治区人工影响天气办公室,乌鲁木齐 830002 |
| 郑清 | 中国气象局气象探测中心,北京 100081 |
引用文本:
施丽娟,冯婉悦,雷勇,王智敏,郑清,2022.GPM日降水产品在中国大陆的准确性评估[J].气象,48(11):1428-1438.
SHI Lijuan,FENG Wanyue,LEI Yong,WANG Zhimin,ZHENG Qing,2022.Accuracy Evaluation of Daily GPM Precipitation Product over Mainland China[J].Meteor Mon,48(11):1428-1438.
施丽娟,冯婉悦,雷勇,王智敏,郑清,2022.GPM日降水产品在中国大陆的准确性评估[J].气象,48(11):1428-1438.
SHI Lijuan,FENG Wanyue,LEI Yong,WANG Zhimin,ZHENG Qing,2022.Accuracy Evaluation of Daily GPM Precipitation Product over Mainland China[J].Meteor Mon,48(11):1428-1438.