本文已被:浏览 524次 下载 3353次
投稿时间:2021-10-07 修订日期:2022-04-20
投稿时间:2021-10-07 修订日期:2022-04-20
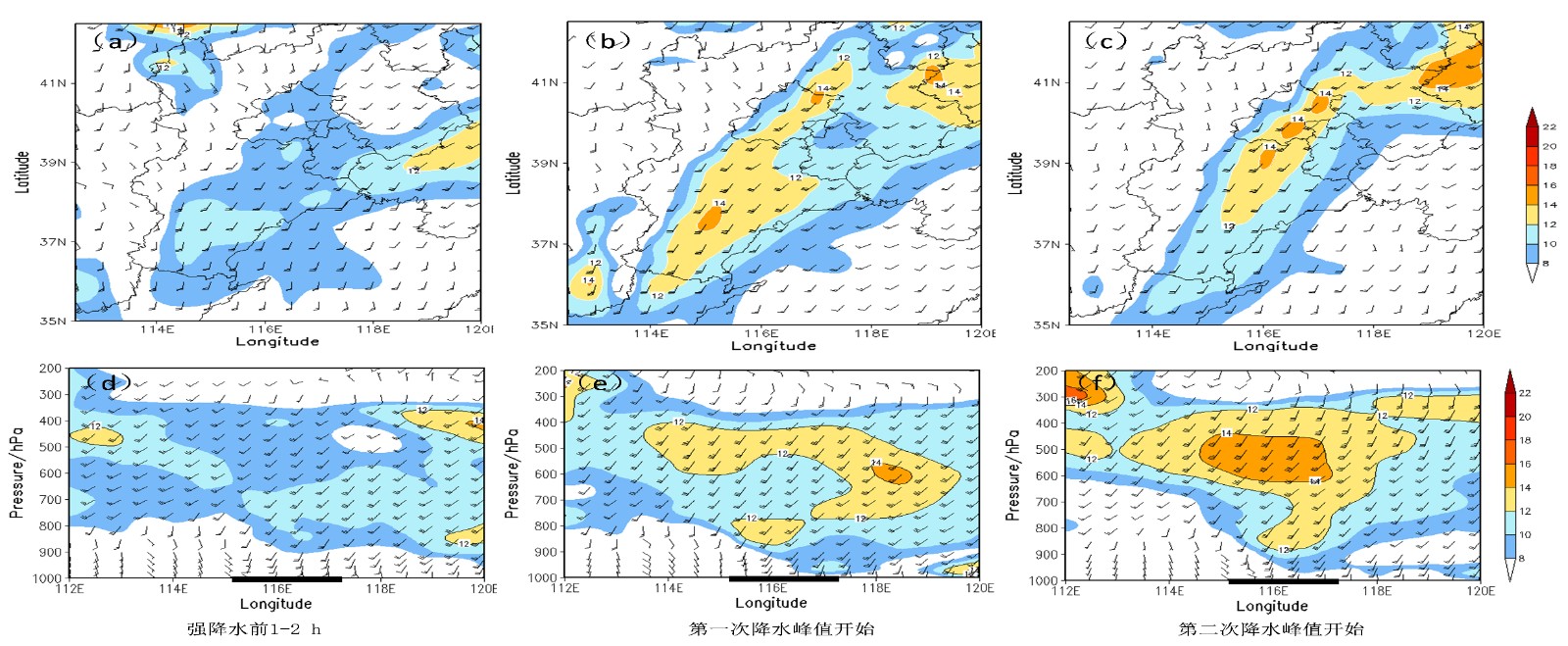
中文摘要: 为了揭示北京地区夏季暴雨形成过程中的低空急流成因、结构特征及其作用,利用风廓线雷达测风数据、NCEP/GFS再分析资料(0.5°×0.5°)、国家级地面气象观测站和区域自动气象站小时降水量观测数据,对两次不同天气系统类型和强度等级的暴雨过程开展对比分析,得到结论如下:2018年7月16日(简称“7·16”)北京特大暴雨是在副热带高压边缘低空西南急流的影响下形成的,低涡低槽东移发展、低空急流不断加强,加之地形辐合线的影响,为大暴雨的发生提供了极为有利的低空水汽输送、辐合和抬升条件。2019年7月22日(简称“7·22”)北京暴雨是在高空槽前低空急流的影响下形成的,低空急流是由高空急流东移、下传所产生,低空水汽输送和辐合作用相对较小。在两次暴雨过程中的强降水发生前3 h,均出现低空急流强度增大、低空急流最低高度下降、低空急流指数激增、1500 m以下出现明显的垂直风切变并且逐渐增大等特征。在“7·16”暴雨过程中,边界层急流遇到山脉地形触发了对流新生,低空急流、地形辐合线共同作用使对流系统不断发展和组织化,是沿山地区极端强降水形成的关键原因。低空急流特征量(低空最大风速、急流最低高度和低空急流指数)和1500 m以下的垂直风切变大小对强降水的发生具有重要的指示意义。
Abstract:In order to reveal the evolution characteristics and effects of low-level jet (LLJ) during the formation of summer rainstorms, comprehensive observational data and reanalysis data are used to compare and analyze the two summer rainstorm cases with different synoptic types and rainstorm intensities in Beijing. The data include the wind profiler radar (WPR), NCEP/GFS reanalysis data (0.5°×0.5°), and hourly precipitation data from automatic weather stations. The results show that the 16 July rainstorm process in 2018 (shortened as “7·16” rainstorm) was formed under the influence of southwest low-level jet (LLJ) at the edge of the subtropical high. The eastward movement of the vortex and trough, the continuously strengthening of the LLJ, and the influence of terrain convergence line provided extremely favorable conditions including low-level water vapor transport, convergence and uplift conditions for the occurrence of extreme rainstorm. The 22 July rainstorm process in 2019 (shortened as “7·22” rainstorm) was formed under the influence of the LLJ in front of the upper-level trough, which was caused by downward propagation of the upper-level jet during its eastward movement. This kind of LLJ has relatively smaller impacts on water vapor transport and convergence in the lower layers. Within 3 hours before the two rainstorms, similar characteristics appeared as follows: the low-level wind speed increased, the minimum height of LLJ decreased, the LLJ index sharply increased, obvious vertical wind shear occurred below 1500 m, and the vertical wind shear gradually〖JP2〗 increased with the approach of rainstorm. During the “7·16”〖JP〗 rainstorm, the occurrence of the convective cells was triggered by the boundary layer jet (BLJ), and the developing convective system was well organized by the joint action of the LLJ and the terrain convergence line. So, these are the key reasons for the formation of extreme heavy rainfall along the mountains. The characteristic parameters of the LLJ (maximum wind speed of LLJ, minimum height of LLJ, LLJ index) and the magnitude of the vertical wind shear below 1500 m are important indicators for the occurrence of rainstorm.
文章编号: 中图分类号:P458 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC3000901、2018YFC1506801)、京津冀协同创新共同体建设专项(19245419D)和北京市自然科学基金(8204061)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 李青春 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
| 程丛兰 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
| 全继萍 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
| 陈敏 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
| 窦有俊 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
| 仲跻芹 | 北京城市气象研究院,北京 100089 |
引用文本:
李青春,程丛兰,全继萍,陈敏,窦有俊,仲跻芹,2022.夏季两次不同强度暴雨过程的低空急流特征及其作用对比分析[J].气象,48(11):1384-1401.
LI Qingchun,CHENG Conglan,QUAN Jiping,CHEN Min,DOU Youjun,ZHONG Jiqin,2022.Comparison of Characteristics and Effects About Low-Level Jet in Two Rainstorm Processes with Different Intensities in Summer[J].Meteor Mon,48(11):1384-1401.
李青春,程丛兰,全继萍,陈敏,窦有俊,仲跻芹,2022.夏季两次不同强度暴雨过程的低空急流特征及其作用对比分析[J].气象,48(11):1384-1401.
LI Qingchun,CHENG Conglan,QUAN Jiping,CHEN Min,DOU Youjun,ZHONG Jiqin,2022.Comparison of Characteristics and Effects About Low-Level Jet in Two Rainstorm Processes with Different Intensities in Summer[J].Meteor Mon,48(11):1384-1401.