本文已被:浏览 643次 下载 2420次
投稿时间:2021-06-07 修订日期:2022-06-21
投稿时间:2021-06-07 修订日期:2022-06-21
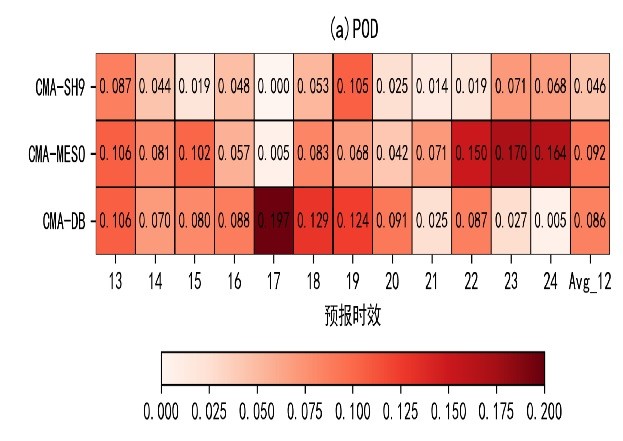
中文摘要: 利用气象大数据云平台中逐小时降水资料,基于目标对象检验法和邻域法,评估2019—2020年辽宁主汛期降水过程中中国气象局上海数值预报模式系统(CMA-SH9)、中国气象局中尺度天气数值预报系统(CMA-MESO)、中国气象局睿图东北数值预报模式系统(CMA-DB)的预报性能。结果表明:千米尺度或接近千米尺度的上述三个模式,在36 h时效内,对于累积强降水(12 h 降水量≥50 mm)落区形态预报与实况有相似性,落区质心预报偏差一般在20 km左右。然而,预报落区与实况重叠的面积一般都在10%以下,个别情形下(如CMA-MESO对于气旋型降水过程)累积强降水落区预报与实况重叠度能够接近20%;位置偏离的直接结果是导致漏报率高(一般在75%左右,CMA-MESO模式漏报率略低,为10%~20%),其中高压后部型降水过程中累积强降水的漏报率超过80%,位置偏离也造成较高空报率。对于短时强降水(1 h降水量≥20 mm)预报,在方圆40 km内不计偏差情况下,各模式预报命中率平均在10%以下(最大值为9.2%),空报率平均为58.7%;三种降水类型中,模式对台风型降水过程的短时强降水预报性能最低。
中文关键词: 多区域模式,空间检验,目标对象检验法,邻域法,降水分型
Abstract:In this study, based on the methods for object-based vertification and neighborhood, the hourly precipitation data from the CMADaas (China Meteorological Administration Data as a server), the forecast performances of three numerical models during the main flood seasons from 2019 to 2020 in Liaoning Province are investigated. The three models are the Shanghai Numerical Prediction Model of China Meteorological Administration (CMA-SH9), the Mesoscale Weather Numerical Prediction System of China Meteorological Administration (CMA-MESO) and the Rapid-Refresh Multi-Scale Analysis and Prediction System-Northeast China Model of China Meteorological Administration (CMA-DB). The results show that even for the kilometer-scale or near-kilometer-scale models, there are still obvious deviations in the forecast of the heavy rainfall area (12 h cumulative rainfall ≥ 50 mm) within the 36 h lead time. The ratio of overlapping area between the forecasted and observed heavy rainfall areas is generally less than 10% of the total area, and in individual cases the value is close to 20%, such as the forecast of CMA-MESO on cyclone-type precipitation processes. The deviation of rainfall area results in a high missing alarm rate (MAR) (generally around 75%, and the MAR of the CMA-MESO is 10%-20% lower than that). The MAR of heavy precipitation forecast for the rear of high-pressure type precipitation exceeds 80%. Besides, the deviation of heavy rainfall area also results in a higher false alarm rate (FAR). For the forecast of short-term heavy rainfall (1 h rainfall ≥ 20 mm), by analyzing the mean values of the statistical indexes within 12 h forecast lead time, we find that the average percentage of detection is below 10%, with the maximum value being only 9.2%. The average FAR is 58.7%. Among the three types of rainfall processes, the model has the poorest performance in the forecast of short-term heavy rainfall in typhoon-type rainfall processes.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:中国气象局预报员专项(CMAYBY2019-025)、中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所和东北冷涡研究重点开放实验室联合开放基金课题(2020SYIAE05)、中国气象局数值预报发展专项“2020年多模式降水及雷达回波检验评估”和“2021年短时强降雨和雷暴大风检验评估”共同资助
引用文本:
刘静,任川,赵梓淇,陈传雷,王瀛,才奎志,2022.多区域高分辨率模式强降水预报检验分析[J].气象,48(10):1292-1302.
LIU Jing,REN Chuan,ZHAO Ziqi,CHEN Chuanlei,WANG Ying,CAI Kuizhi,2022.Comparative Analysis on Verification of Heavy Rainfall Forecasts in Different Regional Models[J].Meteor Mon,48(10):1292-1302.
刘静,任川,赵梓淇,陈传雷,王瀛,才奎志,2022.多区域高分辨率模式强降水预报检验分析[J].气象,48(10):1292-1302.
LIU Jing,REN Chuan,ZHAO Ziqi,CHEN Chuanlei,WANG Ying,CAI Kuizhi,2022.Comparative Analysis on Verification of Heavy Rainfall Forecasts in Different Regional Models[J].Meteor Mon,48(10):1292-1302.