本文已被:浏览 585次 下载 3042次
投稿时间:2021-03-09 修订日期:2022-04-11
投稿时间:2021-03-09 修订日期:2022-04-11
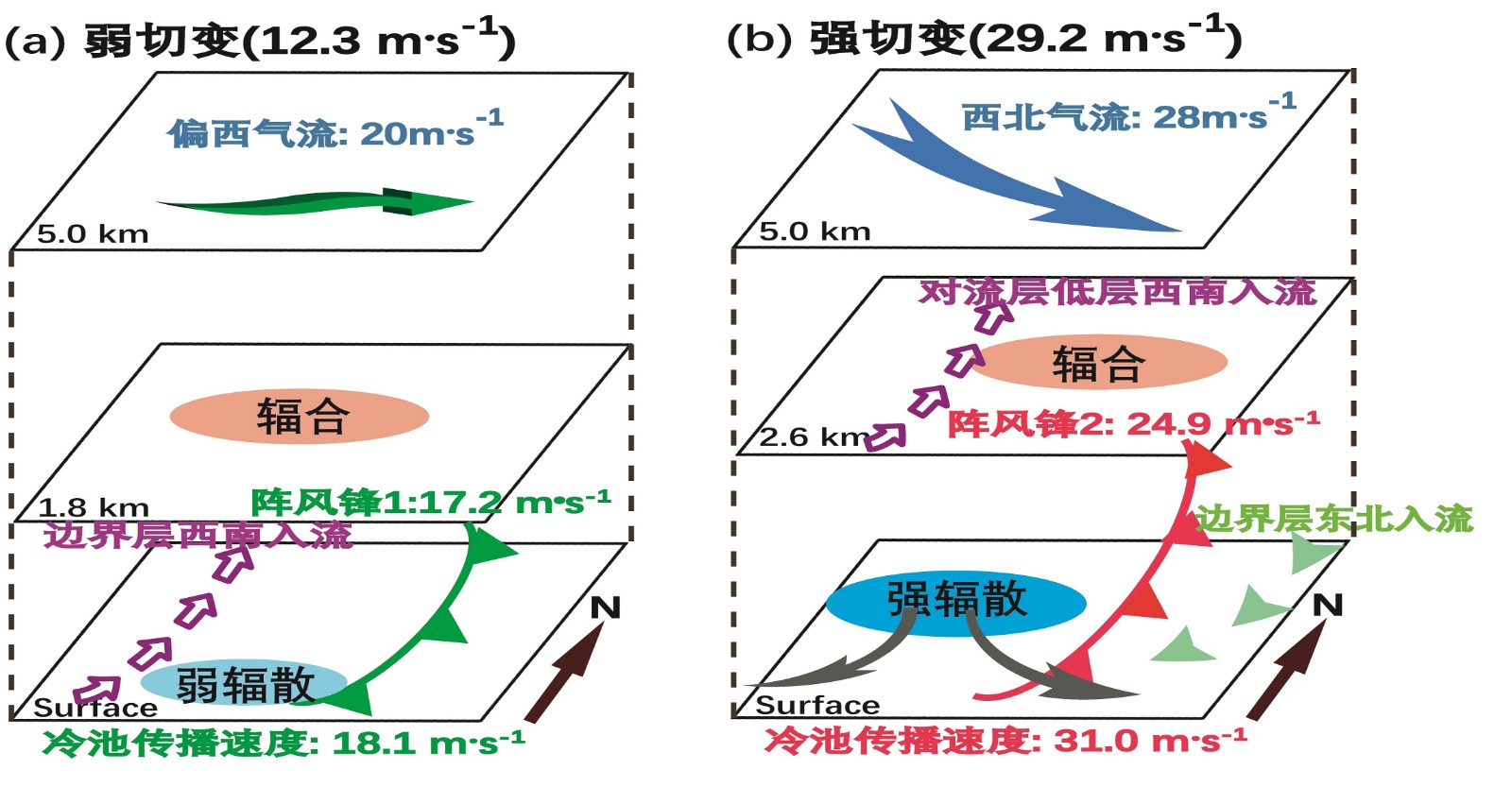
中文摘要: 为加深对雷暴阵风锋多样性的认识,利用多普勒天气雷达、风廓线雷达、边界层气象铁塔、地面加密自动观测资料结合VDRAS系统分析场资料,对比分析了2016年6月10日渤海湾连续出现的两条阵风锋的差异及相互联系。结果表明:两条阵风锋的结构存在明显差异,阵风锋1前沿强切变位置形成近地层γ中尺度涡旋,边界层和对流层低层的西南暖湿气流沿阵风锋1输送到雷暴母体;阵风锋2呈现两支强入流的典型动力结构,一支位于其后侧边界层内呈强东北入流,另一支位于前侧对流层低层呈强西南入流,两支入流分别构成阵风锋前侧反环流和后侧正环流圈。冷池与低层垂直风切变的配置对阵风锋的发展维持起到重要作用。阵风锋1后部冷池强度相对较弱,低层垂直风切变强于冷池传播速度,雷暴单体具有向冷区倾斜的层云结构,不利于系统的发展加强;阵风锋2后部冷池发展强盛,冷池传播速度强于低层垂直风切变,雷暴单体内的上升气流更加竖直,从而促进雷暴单体加强发展。阵风锋前沿γ中尺度涡旋和后部冷池存在相互影响及内在关联,近地层γ中尺度涡旋的碰撞,增强了两条阵风锋之间的辐合抬升,同时配合冷池的合并增强,加剧了低层不稳定,有利于维持上下层旋转,形成较强的水平涡度,从而导致对流风暴快速加强发展并演变为弓形回波。
中文关键词: 阵风锋,冷池,低层垂直风切变,γ中尺度涡旋
Abstract:To understand more about the diversities of thunderstorm gust fronts, based on Doppler radar data from Tianjin and Cangzhou, wind profiler radar data from Xiqing and Huanghua, Tianjin Meteorological Tower, surface observations data, as well as VDRAS data, this paper comparatively analyzes the causes and correlation of two consecutive gust fronts that occurred in the Bohai Sea Bay on 10 June 2016. The results show that the structures are quite different between these two gust fronts. For the first gust front (GFⅠ), the near-surface meso-γ scale vortices tended to appear along the leading of GFⅠ, and the strong southwesterly warm-humid air flows from boundary layer and lower-level were transported to the thunderstorm along GFⅠ. For the second gust front (GF Ⅱ), dynamic structure was characterized by two strong inflows. One was boundary layer rear northeast inflow at 150-750 m height, another strong southwest inflow was at 990-2 190 m height. The two inflows induced two separated vertical clockwise circulations at the front and rear of GF Ⅱ. The configuration of cold pool and low-level vertical wind shear played an important role in formation and maintenance of these two gust fronts. The strength of cold pool at the rear of GFⅠ is relatively weak, and the 0-3 km vertical wind shear was stronger than the propagation speed of cold pool. The thunderstorm inclined to a stratiform cloud structure, which was not conducive to further development. Comparatively, for GF Ⅱ, the cold pool developed stronger, the propagation of cold pool was more than the 0-3 km vertical wind shear, thus the updraft in the thunderstorm was more vertical, resulting in intensified storm. Meanwhile, the interaction and inherent correlation between meso-γ scale vortex and cold pool were also obvious. Due to the collision of meso-γ scale vortices, strong low-level convergence and updraft occurred between the two front gusts. Moreover, the consolidation of the two cold pools aggravated low-layer instability, which increased the rotation of the upper and lower layers, and formed strong horizontal vorticity, finally leading to the rapid strengthening of convective storm and evolution into bow echo.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:天津市自然科学基金项目(18JCQNJC09400)和天津市海洋气象重点实验室开放基金项目(2020TKLOMYB02)共同资助
引用文本:
许长义,卜清军,黄安宁,2022.环渤海湾连续两条阵风锋的关联与成因分析[J].气象,48(6):729-745.
XU Changyi,BU Qingjun,HUANG Anning,2022.Analyses on Correlation and Causes for the Consecutive Thunderstorm Gust Fronts over the Bohai Sea Bay[J].Meteor Mon,48(6):729-745.
许长义,卜清军,黄安宁,2022.环渤海湾连续两条阵风锋的关联与成因分析[J].气象,48(6):729-745.
XU Changyi,BU Qingjun,HUANG Anning,2022.Analyses on Correlation and Causes for the Consecutive Thunderstorm Gust Fronts over the Bohai Sea Bay[J].Meteor Mon,48(6):729-745.