本文已被:浏览 643次 下载 4078次
投稿时间:2020-09-06 修订日期:2021-04-15
投稿时间:2020-09-06 修订日期:2021-04-15
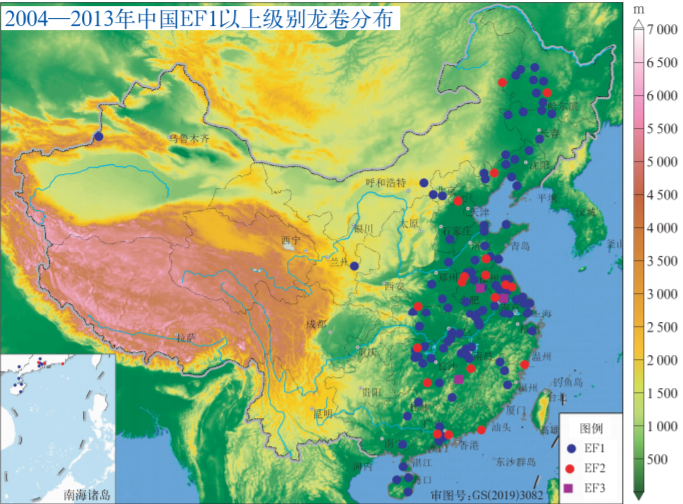
中文摘要: 近年来,中国几个EF3级以上强龙卷导致了严重人员伤亡和重大经济损失。龙卷尺度非常小,发生频率非常低。中国虽然目前尚不具备业务预报龙卷能力,但随着新一代天气雷达及自动气象站的观测网、现场调查和数值模式的发展,龙卷研究取得了显著进展,对中国龙卷时空分布气候特征和有利的天气背景以及环境条件已有较为全面的了解,也认识到不同天气背景下有利于龙卷产生的环境条件不尽相同。龙卷风灾现场调查流程和分析技术已经较为完备, 2016年江苏阜宁EF4级龙卷等多个强龙卷都得到了详细规范的现场调查和分析,为减灾防灾提供了重要数据。对孕生龙卷的超级单体风暴中小尺度特征取得了较为深入的认识,如不太强的地面冷池、中气旋底高通常低于1 km、强度与龙卷强度正相关、倾斜、龙卷碎片特征、下沉反射率因子核和部分龙卷的多涡旋特征等。使用精细云模式成功对江苏阜宁和北京通州龙卷分别进行了理想模拟,且使用WRF(Weather Research and Forecasting)模式成功模拟出了2005年台风麦莎对流眼墙中的龙卷尺度涡旋和2016年阜宁龙卷的多涡旋结构。未来,仍然需要在龙卷探测技术、龙卷对流风暴精细地面要素分布和结构特征、龙卷涡旋和闪电活动特征等方面进行深入研究,更需要通过更高时空分辨率观测资料分析和极高分辨率的数值模拟获取龙卷发展的关键因素和机理,从而为提升龙卷的预报预警能力提供更为坚实的科学基础。
中文关键词: 龙卷,气候,环境条件,现场调查,中小尺度,数值模拟
Abstract:Several intense tornadoes (≥EF3) in China in recent years resulted in heavy casualties and serious economic losses. Tornado has a very small scale, and its occurrence frequency in China is extremely low. At present, China still does not have the operational capability of forecasting tornadoes. However, with the development of observation networks of new-generation weather radar and surface automatic weather stations, damage survey and numerical weather prediction model, remarkable progress in tornado research in China has been made. The spatio-temporal and climatological characteristics, favorable synoptic backgrounds and environmental conditions for tornado in China have been understood more comprehensively, and it has also been found that the favorable environmental conditions for tornado in different synoptic backgrounds are somewhat different. The damage survey process and analysis technology of tornado disaster have been developed. The damage surveys and analyses of several intense tornadoes, such as the 2016 Funing, Jiangsu Province EF4 tornado, have been made in detail, which provide indispensable data for disaster prevention and mitigation. More understandings of meso- and micro-scale characteristics of tor-nadic convective storms have been got, including the findings of the storm cold pool with appropriate intensity, the bottom of the mesocyclone generally lower than the height of 1 km, the positive intensity correlation between tornado and its parent mesocyclone, slantwise mesocyclone, tornadic debris signature, descending reflectivity core, and multi-vortex structure of some tornadoes. Two tornadoes have successfully been ideally simulated using a fine-resolution cloud model, and the tornado-scale vortices in the convective eye wall of 2005 Typhoon Matsa and the multiple vortices of the 2016 Funing Tornado have been successfully simulated by the WRF (Weather Research and Forecasting) model. In future, we still need to further develop tornado detection technology, and to study fine surface meteorological element distribution and structure features, tornado vortex and lightning activity of tornadic convective storms. What’s more, researches on the development mechanisms of tornado are more needed through finer-resolution observation data and higher-resolution numerical weather simulation so as to provide more scientific foundations for promoting the tornado forecasting and warning capability in China.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1507504和2017YFC1502003)、国家自然科学基金面上项目(41375051)共同资助
引用文本:
郑永光,刘菲凡,张恒进,2021.中国龙卷研究进展[J].气象,47(11):1319-1335.
ZHENG Yongguang,LIU Feifan,ZHANG Hengjin,2021.Advances in Tornado Research in China[J].Meteor Mon,47(11):1319-1335.
郑永光,刘菲凡,张恒进,2021.中国龙卷研究进展[J].气象,47(11):1319-1335.
ZHENG Yongguang,LIU Feifan,ZHANG Hengjin,2021.Advances in Tornado Research in China[J].Meteor Mon,47(11):1319-1335.