本文已被:浏览 571次 下载 3125次
投稿时间:2020-06-18 修订日期:2021-02-05
投稿时间:2020-06-18 修订日期:2021-02-05
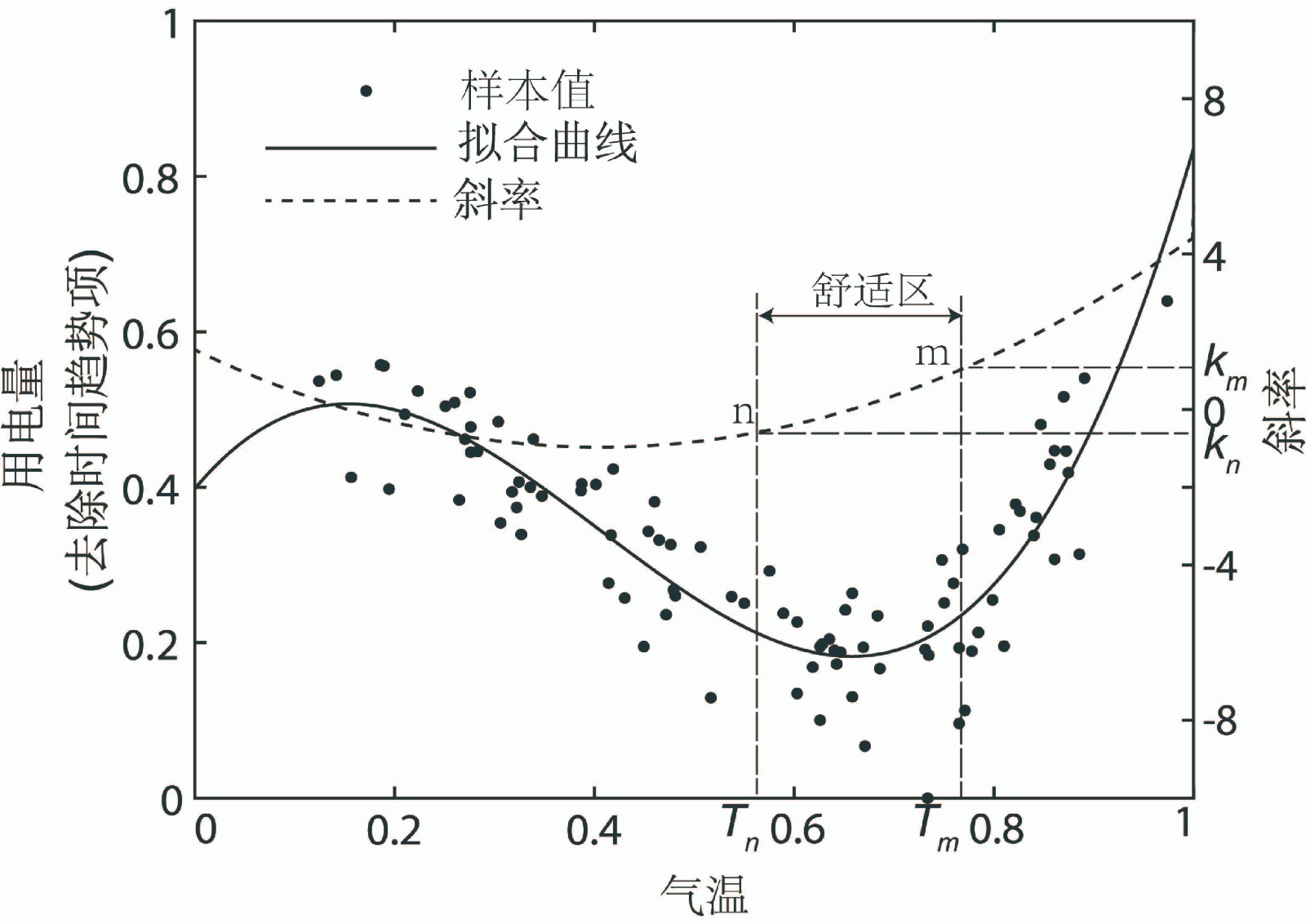
中文摘要: 气象条件是影响电力消耗的主要因素之一,是用电量预测模型的基础要素。利用天津市2014—2018 年日用电量数据和气象观测数据,分析二者之间关系。发现天津地区日用电量与气温和相对湿度呈“U”型的非线性关系,舒适区与冷却区之间的气温阈值随相对湿度增加向低温一侧明显偏移。基于此,在关系模型中引入相对湿度,利用用电量与温湿度之间的非线性拟合曲线斜率确定舒适区的气温阈值,提出基于温湿效应的日用电量分段新方法。对比发现,该方法对用电量的预测效果有明显提升,线性模型中,较“V”型方法,均方根误差(RMSE)和平均绝对百分误差(MAPE)分别减小1.562 GW·h和0.546%;针对舒适区与冷却区的过渡区域(21.1~26.2℃),较传统“U”型方法,RMSE和MAPE分别减小0.759 GW·h和0.215%,非线性模型中则分别减小0.647 GW·h和0.209%,不同模型中预测提升效果稳定。可见,综合温湿度的“U”型分段方法能够有效提升日用电需求预测精准度。
Abstract:Meteorological condition is one of important factors in influencing electricity consumption, and is widely used in electricity load forecasting model. This study uses daily electricity load and meteorological data in Tianjin during 2014-2018 and analyzes the relationship between electricity and meteorological elements. The results show that the relationship between daily electricity load and temperature and relative humidity is nonlinear correlation with “U” shape. With the increasing of relative humidity, the temperature threshold between the comfort zone and the cooling zone is obviously offset to the low temperature side. Thus, the relative humidity is joined into the electricity load relational model. Based on the slope of the non-linear fitting curve between electricity load and temperature and relative humidity, a new method which considered the temperature and humidity effect of electricity consumption segmentation is proposed. It is found that the new method can effectively promote the fitting level of electricity load. In liner model, compared with the “V” segmented method, the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) values decrease by 1.562 GW·h and 0.546%, respectively. For transition area between comfort zone and cooling zone (21.1℃ to 26.2℃), the RMSE and MAPE values decrease by 0.759 GW·h and 0.215% compared with the traditional “U” segmented method, while the RMSE and MAPE values decrease by 0.647 GW·h and 0.209% in the nonlinear model. This shows the stable prediction effect of different models. Thus, this “U” segmented method based on temperature and humidity effect can effectively improve the accuracy of daily electricity load forecasting.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0606300)和天津市气象局科技项目(202135dgxm)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 兰辉 | 天津市气象服务中心,天津 300074 |
| 于佳卉 | 天津市气象服务中心,天津 300074 |
| 曹经福 | 天津市气象科学研究所,天津 300074 |
| 刘玉坤 | 国网天津市电力公司,天津 300010 |
| 孙玫玲 | 天津市气象服务中心,天津 300074 |
| 郭玲 | 天津市气象服务中心,天津 300074 |
| 熊明明 | 天津市气候中心,天津 300074 |
引用文本:
兰辉,于佳卉,曹经福,刘玉坤,孙玫玲,郭玲,熊明明,2021.基于温湿效应的日用电量分段方法与预测效果初探[J].气象,47(7):872-879.
LAN Hui,YU Jiahui,CAO Jingfu,LIU Yukun,SUN Meiling,GUO Ling,XIONG Mingming,2021.Study on Segmental Method and Prediction Effect of Daily Electricity Load Based on Temperature and Humidity[J].Meteor Mon,47(7):872-879.
兰辉,于佳卉,曹经福,刘玉坤,孙玫玲,郭玲,熊明明,2021.基于温湿效应的日用电量分段方法与预测效果初探[J].气象,47(7):872-879.
LAN Hui,YU Jiahui,CAO Jingfu,LIU Yukun,SUN Meiling,GUO Ling,XIONG Mingming,2021.Study on Segmental Method and Prediction Effect of Daily Electricity Load Based on Temperature and Humidity[J].Meteor Mon,47(7):872-879.