本文已被:浏览 561次 下载 3884次
投稿时间:2019-11-10 修订日期:2020-08-03
投稿时间:2019-11-10 修订日期:2020-08-03
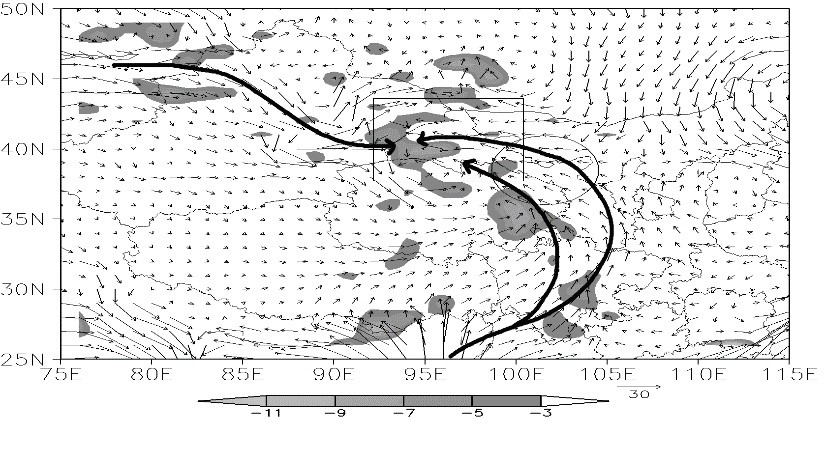
中文摘要: 利用高空、地面观测资料、加密区域站雨量资料、FY-2D云图、NCEP 1°×1°再分析资料,使用物理量诊断、后向轨迹模型等方法分析了2011年6月15—16日河西走廊西部干旱区一次极端暴雨天气的环流形势、中尺度系统、水汽输送和收支特征。结果表明:河西走廊西部受内蒙古西部到河套地区西北—东南向暖性高压脊西部形成的高原低涡中心影响,200~400 km 的低涡中心稳定维持在暴雨区上空超过12 h,形成了良好的动力条件;对流层低层湿度增大气温降低,中层冷空气从低涡南部侵入,大气处于弱不稳定状态,地面风速辐合、地形抬升进一步增强了低涡中心的上升运动,触发局地对流。主要存在随西风气流的西路和绕高原的东路两条水汽输送通道,以绕高原的东路水汽输送为主,其在暴雨期间的贡献率高达84.6%,以对流层中层输入最为显著。甘肃中部500和700 hPa异常偏东气流对东路水汽输送通道的形成十分重要,其能将已到达西北地区东部的暖湿空气继续向西北方向输送从而到达河西走廊西部。暴雨时段内水汽平均净输入强度是前期的2.73 倍,对流层中层高原低涡中心、对流层低层风速风向辐合和地形辐合造成暴雨区550、700和800 hPa三层200~400 km的水汽辐合中心,大气可降水量高达34 mm,是夏季平均值的2倍多。
Abstract:Based on station observations (surface observations and upper-air soundings at weather stations and precipitation observations at regional stations), FY-2D infrared images, water vapor images and NCEP reanalysis data with the resolution of 1°×1°, combined with water vapor flux diagnosis and a backward trajectory model, an extreme rainstorm process which occurred in the arid region of western Hexi Corridor during 15-16 June 2011 was analyzed to study the transport mechanism of water vapor and its budget in the process. The results are as follows. The western Hexi Corridor was affected by the plateau vortex center formed from the western part of warm high-pressure ridge which ran northwest-southeast from western Inner Mongolia to Hetao Area. The plateau vortex center with 200-400 km scale remained stable over the rainstorm area for more than 12 hours, forming good dynamic conditions. The humidity increased and the temperature decreased in the lower troposphere. The cold air invaded from the southern plateau vortex in middle layer. The atmosphere was in a weakly unstable state. The convergence of surface wind speed and the effect of terrain upwind slope triggered local convective weather. The water vapor needed by rainstorm was mainly from the west wind flow and the east wind flow bypassed the plateau, and the latter brought the most water vapor with its contribution rate during rainstorm as high as 84.6%. Further more, the water vapor from two channels were both the most pronounced in the middle and low layer of the tro-posphere. The formation of anomalous easterly airflow in central Gansu at 500 hPa and 700 hPa was important for water vapor transport and convergence in the rainstorm area. The average net input intensity of water vapor during the rainstorm period was 2.73 times of that the pre-rainstorm period. The low vortex center in the middle troposphere, the convergence of wind speed and direction in the lower troposphere, and the convergence of terrain caused the 550 hPa, 700 hPa, and 800 hPa three-layer water vapor convergence center with 200-400 km scale. The atmospheric precipitable water in the rainstorm center was as high as 34 mm, which was more than 2 times the summer average.
keywords: arid region rainstorm, plateau vortex, water vapor transport, water vapor budget, HYSPLIT model
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:甘肃省气象局创新团队(GSQXCXTD-2020-01)、中国气象局预报员专项(CMAYBY2019-121)和甘肃省气象局气象科研项目(Zd2021-01)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 孔祥伟 | 兰州中心气象台,兰州 730020; 兰州大学大气科学学院/兰州天气气候联合研究与实训中心,兰州 730000 |
| 杨建才 | 兰州中心气象台,兰州 730020 |
| 李红 | 中国气象局兰州干旱研究所/甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,兰州 730020 |
| 傅朝 | 兰州中心气象台,兰州 730020 |
引用文本:
孔祥伟,杨建才,李红,傅朝,2021.河西走廊西部干旱区一次极端暴雨天气的水汽特征分析[J].气象,47(4):412-423.
KONG Xiangwei,YANG Jiancai,LI Hong,FU Zhao,2021.Analysis on Water Vapor Characteristics of an Extreme Rainstorm in the Arid Region of Western Hexi Corridor[J].Meteor Mon,47(4):412-423.
孔祥伟,杨建才,李红,傅朝,2021.河西走廊西部干旱区一次极端暴雨天气的水汽特征分析[J].气象,47(4):412-423.
KONG Xiangwei,YANG Jiancai,LI Hong,FU Zhao,2021.Analysis on Water Vapor Characteristics of an Extreme Rainstorm in the Arid Region of Western Hexi Corridor[J].Meteor Mon,47(4):412-423.