本文已被:浏览 687次 下载 3618次
投稿时间:2019-08-23 修订日期:2020-08-27
投稿时间:2019-08-23 修订日期:2020-08-27
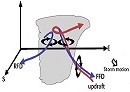
中文摘要: 通过研究大冰雹超级单体风暴的偏振特征、动力及云物理结构的演变,可了解大冰雹形成的物理过程,并获得与大冰雹形成、生长相关的相关征兆偏振特征,进而提升对大冰雹超级单体的预警能力。利用厦门S波段双偏振雷达资料,结合双雷达风场反演和粒子相态识别算法对2019年4月22日发生在闽南地区一次导致大冰雹的超级单体进行了分析。研究表明:差分反射率因子(Zdr)大值区位于三体散射(TBSS)的起始位置及反射率因子(Zh)强中心的远端。同时,TBSS中的相关系数(CC)较低,TBSS的偏振特征有助于识别高空中的大冰雹。大冰雹区表现出高Zh和低Zdr的偏振特点,随着大冰雹降落融化,其表面存在外包水膜现象使得大冰雹周围的Zdr增大,CC减小。在超级单体低层的Zh强中心内存在一个差分相位常数(Kdp)增大的区域,被称为Kdp足。Kdp对大冰雹较不敏感,是冰雹融化的较好指标。因此,Kdp足可用于指示由冰雹融化导致的下沉气流区。在水平风场上存在明显的双涡旋结构。双涡旋结构有助于超级单体的发展及大冰雹的循环增长。在中气旋的东北侧,存在一个中等强度Zh、低Zdr、高CC的区域,被称为霰带。粒子相态识别算法显示霰带中主要的水凝物为霰。由于靠近中气旋,部分霰作为雹胚被卷入上升气流中。基于上述分析给出大冰雹超级单体的偏振特征和三维风场结构示意图。
Abstract:Investigating the evolution of the polarimetric signatures, dynamical and microphysical characteristics in the heavy hail supercell are beneficial to understanding the physical processes that lead to heavy hail formation, determining possible precursive signatures associated with heavy hail formation and growth, and improving warnings for heavy hail supercell. A supercell accompanied by heavy hail in southern Fujian on 22 April 2019 which was detected by the Xiamen S-band dual-polarization radar was analyzed using the dual-Doppler radars wind field retrieval and hydrometeor classification algorithm. The study reveals that the differential reflectivity (Zdr) at the beginning portion of the three-body scatter signature (TBSS) was very high, located radially behind the horizontal reflectivity (Zh) core. It was also found that the cross-correlation coefficient (CC) is very low in the TBSS. Polarimetric signatures associated with TBSS are good indicators of heavy hail aloft. The polarimetric signatures of the heavy hail region manifested as high values of Zh collocated with near-zero value of Zdr. However, during the heavy hail descent, Zdr increased and CC decreased on the periphery of the hail core. The increased Zdr and decreased CC due to the increasing presence of water coating on the melting hailstones. At low level, an area of enhanced specific differential phase (Kdp) was observed within the Zh core of supercell, which was called the Kdp foot. Kdp was less sensitive to heavy hail and thus was a better indicator of melting hail. Therefore, the Kdp foot may be a favorable index of the downdraft zone which was driven by melting of hail. The horizontal wind field showed a distinct double vortex developing in the supercell. The double vortex structure contributed to the development of supercell and the circulation growth of heavy hail. On the northeast of the mesocyclone, a zone of modest Zh, low Zdr, and high CC were observed, called the graupel belt. The hydrometeor classification algorithm suggests that graupel is the dominant hydrometeor type. Because of the proximity to the mesocyclone, some of the graupel were entrained into the updraft, serving as hail embryos. The schematic diagrams of polarimetric signatures and three-dimensional wind field structure of the heavy hail supercell are given based on these analyses.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41675029)、福建省自然科学基金项目(2018J01060)和福建省气象局基层科技专项(2019J06)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 潘佳文 | 厦门市气象局,海峡气象开放实验室,厦门 361012 |
| 魏鸣 | 南京信息工程大学,气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,南京 210044 |
| 郭丽君 | 中国气象科学研究院云雾物理环境重点实验室,北京 100081 |
| 阮悦 | 福建省气象台,福州 350001 |
| 罗昌荣 | 厦门市气象局,海峡气象开放实验室,厦门 361012 |
| 巫凌寒 | 厦门市气象局,海峡气象开放实验室,厦门 361012 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 潘佳文' target='_blank'>PAN Jiawen | Laboratory of Straits Meteorology, Xiamen Meteorological Bureau, Xiamen 361012 |
| 魏鸣' target='_blank'>WEI Ming | Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044 |
| 郭丽君' target='_blank'>GUO Lijun | Key Laboratory for Cloud Physics, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081 |
| 阮悦' target='_blank'>RUAN Yue | Fujian Meteorological Observatory, Fuzhou 350001 |
| 罗昌荣' target='_blank'>LUO Changrong | Laboratory of Straits Meteorology, Xiamen Meteorological Bureau, Xiamen 361012 |
| 巫凌寒' target='_blank'>WU Linghan | Laboratory of Straits Meteorology, Xiamen Meteorological Bureau, Xiamen 361012 |
引用文本:
潘佳文,魏鸣,郭丽君,阮悦,罗昌荣,巫凌寒,2020.闽南地区大冰雹超级单体演变的双偏振特征分析[J].气象,46(12):1608-1620.
PAN Jiawen,WEI Ming,GUO Lijun,RUAN Yue,LUO Changrong,WU Linghan,2020.Dual-Polarization Radar Characteristic Analysis of the Evolution of Heavy Hail Supercell in Southern Fujian[J].Meteor Mon,46(12):1608-1620.
潘佳文,魏鸣,郭丽君,阮悦,罗昌荣,巫凌寒,2020.闽南地区大冰雹超级单体演变的双偏振特征分析[J].气象,46(12):1608-1620.
PAN Jiawen,WEI Ming,GUO Lijun,RUAN Yue,LUO Changrong,WU Linghan,2020.Dual-Polarization Radar Characteristic Analysis of the Evolution of Heavy Hail Supercell in Southern Fujian[J].Meteor Mon,46(12):1608-1620.