本文已被:浏览 582次 下载 3536次
投稿时间:2019-12-23 修订日期:2020-08-28
投稿时间:2019-12-23 修订日期:2020-08-28
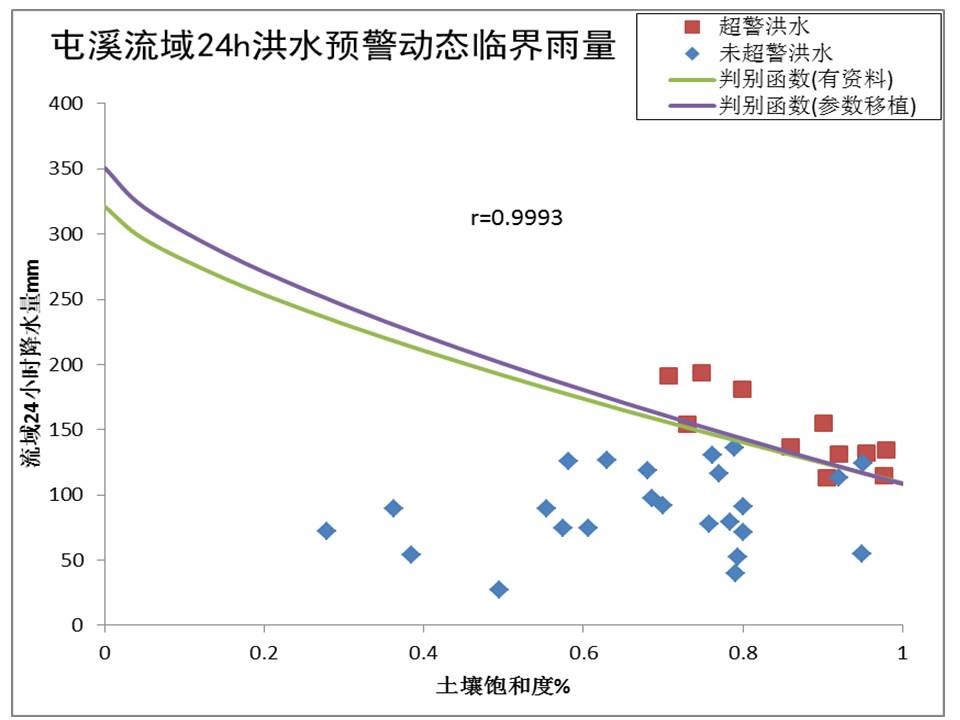
中文摘要: 构建基于流域下垫面地形地貌的中小河流致洪动态临界面雨量阈值移植技术,旨在提出一种解决无资料中小流域洪水预警方法。选取影响中小河流致洪的四个流域特征信息:面积、河道坡度、土地利用类型和土壤类型,建立基于流域土壤饱和度的致洪动态临界面雨量阈值与四个流域特征数据之间的指数模型;将指数模型移植至无资料或缺资料中小流域,根据待求的四个流域特征确定致洪动态临界面雨量阈值。选取我国东部亚热带季风气候区的淮河潢川流域、钱塘江屯溪与渔梁流域、太湖西苕溪与南苕溪流域五个中小流域为试验流域,以警戒洪水为例,结合流域长序列水文气象资料,基于GMKHM分布式水文模型分别推求出潢川、渔梁、西苕溪与南苕溪流域致洪动态临界面雨量阈值;依据建立的指数模型,推求确定屯溪流域致洪动态临界面雨量阈值,并与基于长序列水文气象资料反演出的动态临界面雨量阈值在屯溪流域35场典型洪水预警中的效果对比验证。结果表明,本研究构建的中小河流洪水致洪动态临界面雨量阈值模型与基于长序列水文气象资料的动态临界面雨量阈值反演模型在屯溪流域洪水预警效果相近,命中率为91.4%,对无资料中小河流洪水预报预警与山洪灾害预警均有一定的借鉴意义。
Abstract:A topography-based dynamic critical arearainfall threshold model was developed for solving flood warning of the ungauged and small to middle-sized basin in this paper. The exponential equation model between dynamic critical arearainfall threshold and four main characteristic factors was established. The four main characteristic factors include basin area, channel slope, land use and soil type, which affect the flood generation processes primarily in small to middle-sized basins. Dynamic critical arearainfall threshold in the ungauged basin is calculated with the developed exponential equation model of the gauged basins and four main characteristic factors of the ungauged basin. Five small to middle sized basins in the subtropical monsoon climate region of eastern China were selected as the test basins, 〖JP2〗including Huangchuan Basin of Huaihe River, Tunxi and Yuliang basins of Qiantang River, Xitiaoxi and Nantiaoxi basins of Taihu Lake. Taking the warning flood as an example, dynamic critical arearainfall thresholds of Huangchuan, Yuliang, Xitiaoxi and Nantiaoxi basins were inversed with the long-term hydrological and meteorological data by the GMKHM hydrological distributed model. According to the developed critical threshold model, dynamic critical arearainfall threshold of Tunxi Basin was calculated 〖JP2〗based on the developed exponential equation model.〖JP〗 The topography-based dynamic critical arearainfall threshold was applied to flood warning verification of 35 representative flood events in Tunxi Basin. The results show that flood warning hit rate based on the topography-based dynamic critical arearainfall threshold is 91.4%, which is close to that on the basis of dynamic critical arearainfall threshold calculated with long-term hydrological and meteorological data in Tunxi Basin. The developed topography-based dynamic critical arearainfall threshold model has certain reference significance for similar flood warning of ungauged basins and flash flood warning.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1508102、2018YFC1507205、2016YFC0402702)、国家自然科学基金项目(41775111、41875131)、国家气象中心2019年现代化项目(1-13)、2020年青年基金项目(Q202004,Q202006)和2020年科技成果转化基金项目(K202004)共同资助
引用文本:
包红军,林建,曹爽,王蒙,2020.基于流域地貌的中小河流致洪动态临界面雨量阈值研究[J].气象,46(11):1495-1507.
BAO Hongjun,LIN Jian,CAO Shuang,WANG Meng,2020.Topography-Based Dynamic Critical Arearainfall Threshold for Small to Middle-Sized River Flood Warning[J].Meteor Mon,46(11):1495-1507.
包红军,林建,曹爽,王蒙,2020.基于流域地貌的中小河流致洪动态临界面雨量阈值研究[J].气象,46(11):1495-1507.
BAO Hongjun,LIN Jian,CAO Shuang,WANG Meng,2020.Topography-Based Dynamic Critical Arearainfall Threshold for Small to Middle-Sized River Flood Warning[J].Meteor Mon,46(11):1495-1507.