本文已被:浏览 792次 下载 3934次
投稿时间:2018-12-09 修订日期:2020-02-25
投稿时间:2018-12-09 修订日期:2020-02-25
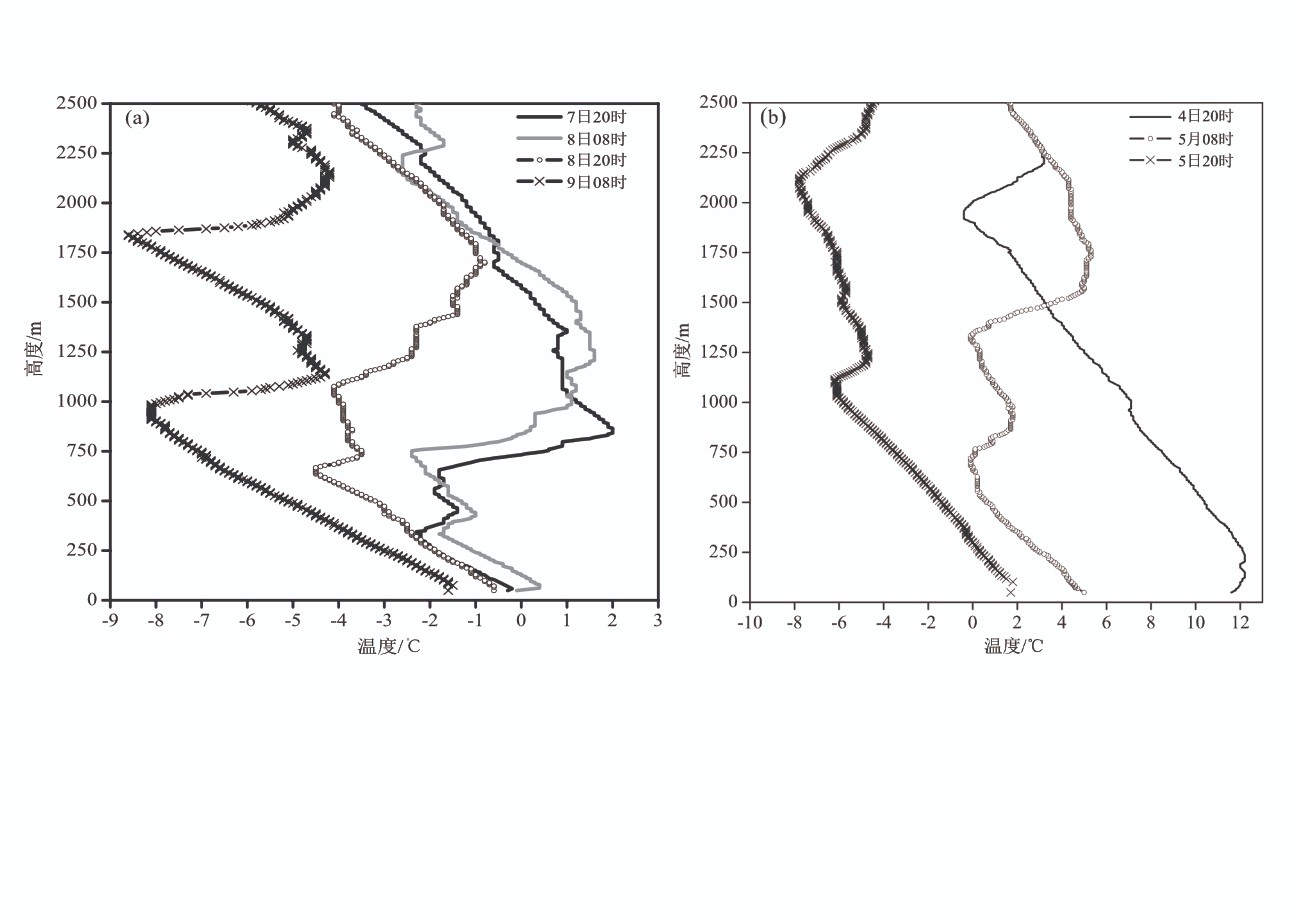
中文摘要: 利用环境监测站大气污染物数据、地面自动气象站观测资料、L波段加密探空资料和0.125°×0.125°的EC再分析资料,结合MODIS遥感火点监测和HYSPLIT4后向轨迹模拟结果,对比分析了2015年11月8日和2016年11月5日的两次由于东北地区秸秆焚烧导致辽宁重污染天气过程的大气边界层特征、气象扩散条件和大气污染物输送来源等。结果表明:两次过程地面PM2.5浓度均出现快速上升和下降,其中2015年11月8日重污染过程的污染强度较2016年11月5日强,且持续时间更长。2015年11月8日重污染过程的混合层高度较低,其上层的中性层结转变为逆温层结,抑制混合层高度的发展。同时低层冷平流不断侵入到暖平流下方,使得大气层结稳定性增强,维持时间较2016年11月5日重污染过程更长,低层下沉运动和黑龙江西南部、吉林西部污染物的远距离输送增强使得辽宁地面污染物浓度快速累积。而2016年11月5日重污染天气过程主要受深厚冷空气影响,东北地区西部污染物的区域输送和地面风场辐合是地面污染物浓度快速上升的主要原因。
中文关键词: 重污染,混合层高度,大气层结,区域输送
Abstract:Based on pollutantion data from environmental monitoring stations, observation data from surface automatic weather stations, L-band dense sounding data and EC 0.125°×0.125° reanalysis data, and combined with fire point data from satellite remote sensing and simulation results of HYSPLIT4 backward trajectory, this paper analyzes the atmospheric boundary layer features, diffusion and transport meteorological conditions of two serious pollution events in Liaoning Province caused by crop residue burning of Northeast China on 8 November 2015 and 5 November 2016. The result shows that PM2.5 concentrations increased and decreased rapidly during the two pollution 〖JP2〗events. The serious pollution event on 8 November 2015 had stronger intensity and longer duration than the event on 5 November 2016. In the 8 November 2015 event, the mixing layer height was lower, on which neutral layer changed into inversion layer restraining the development of mixing layer height. At the same time, the cold advection in lower layer invaded below warm advection in higher layer, making the atmosphere more stable and lasting longer. The enhanced vertical subsidence motion and long-distance horizontal regional transportation of pollutants in southwestern Heilongjiang and western Jilin provinces resulted in rapid accumulation of pollutants on the surface in Liaoning. Due to stronger cold air, regional transportation in west of Northeast China and surface wind convergence strengthened are the main reason for the rapid increase of pollutant concentration in the event on 5 November 2016.
keywords: serious pollution event, mixing layer height, atmospheric stratification, regional transportation
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所项目(2016SYIAEZD3)、辽宁省气象局重点科研项目(201805)、国家自然科学基金项目(41705094)和辽宁省重点研发指导计划(2019JH8/10200022)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 田莉 | 中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所,沈阳 110166 辽宁省气象台,沈阳 110166 |
| 李得勤 | 辽宁省气象台,沈阳 110166 |
| 王扬锋 | 中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所,沈阳 110166 |
| 段云霞 | 辽宁省沈阳市气象台,沈阳 110168 |
| 刘硕 | 辽宁省气象台,沈阳 110166 |
| Author Name | Affiliation |
| 田莉' target='_blank'>TIAN Li | Institute of Atmospheric Environment, CMA, Shenyang 110166 Liaoning Meteorological Observatory, Shenyang 110166 |
| 李得勤' target='_blank'>LI Deqin | Liaoning Meteorological Observatory, Shenyang 110166 |
| 王扬锋' target='_blank'>WANG Yangfeng | Institute of Atmospheric Environment, CMA, Shenyang 110166 |
| 段云霞' target='_blank'>DUAN Yunxia | Shenyang Meteorological Observatory of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110168 |
| 刘硕' target='_blank'>LIU Shuo | Liaoning Meteorological Observatory, Shenyang 110166 |
引用文本:
田莉,李得勤,王扬锋,段云霞,刘硕,2020.两次秸秆焚烧导致辽宁重污染过程的气象条件对比分析[J].气象,46(6):837-849.
TIAN Li,LI Deqin,WANG Yangfeng,DUAN Yunxia,LIU Shuo,2020.Comparative Analysis on Meteorological Condition for Two Serious Pollution Events in Liaoning Province Caused by Crop Residue Burning[J].Meteor Mon,46(6):837-849.
田莉,李得勤,王扬锋,段云霞,刘硕,2020.两次秸秆焚烧导致辽宁重污染过程的气象条件对比分析[J].气象,46(6):837-849.
TIAN Li,LI Deqin,WANG Yangfeng,DUAN Yunxia,LIU Shuo,2020.Comparative Analysis on Meteorological Condition for Two Serious Pollution Events in Liaoning Province Caused by Crop Residue Burning[J].Meteor Mon,46(6):837-849.