本文已被:浏览 1526次 下载 4745次
投稿时间:2019-02-26 修订日期:2019-06-10
投稿时间:2019-02-26 修订日期:2019-06-10
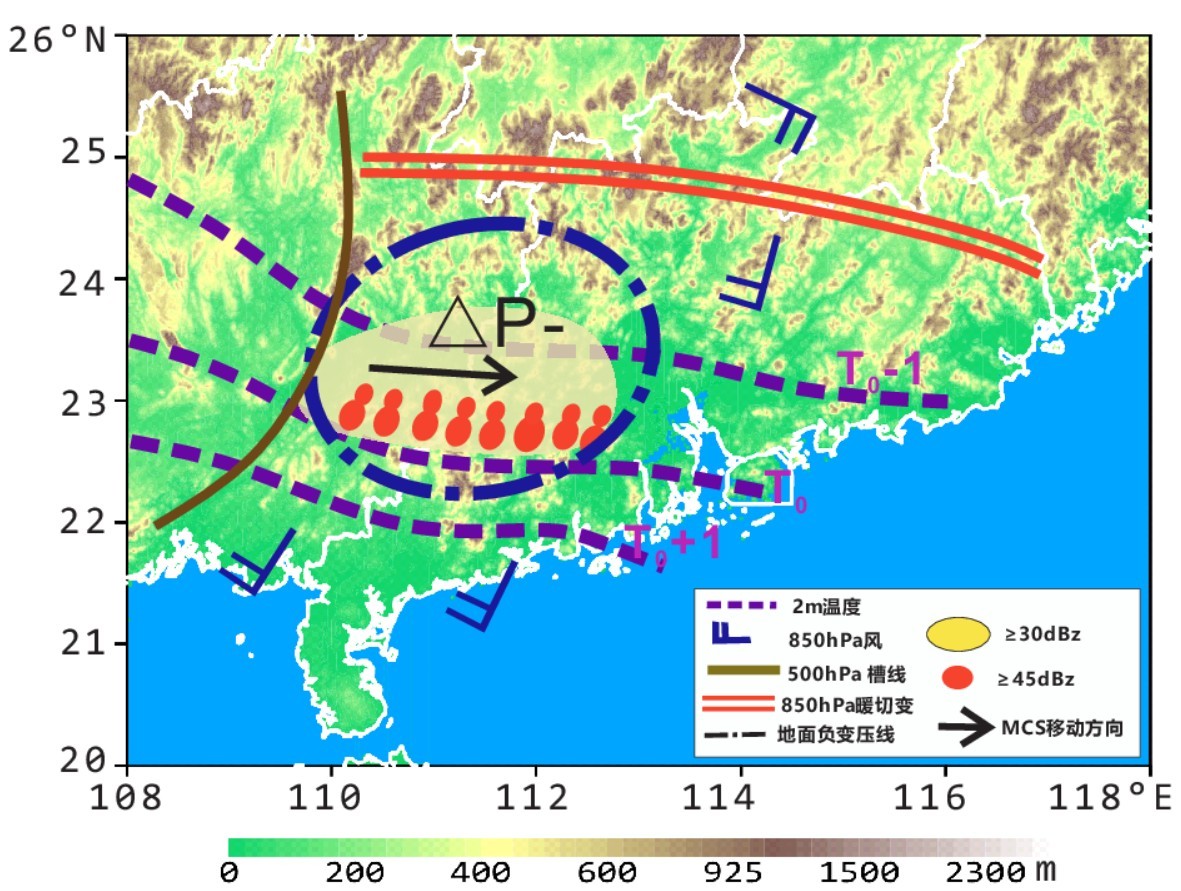
中文摘要: 2014年5月8日上午至9日白天,广东中南部珠江口地区连续受MCS A1、MCS A2两个长生命史中尺度对流系统影响,形成长时间强降水。其中5月8日午后华南内陆地区MCS A1逐步增强,从广西东部向广东珠江口方向移动,陆上活动时间超过11 h; MCS A2从9日凌晨至上午持续影响珠江口沿海地区,维持时间超过9 h,导致珠江口沿海地区出现400 mm 以上单站降水量。过程发生前,8日早上华南南部地区具有弱地面温度梯度,中午MCS A1对流触发与广西南部地面南风增强、华南南部云开大山—云雾山中尺度地形抬升有紧密关系;在弱斜压环境条件下,MCS A1从层云伴随线状对流结构演变为中尺度涡旋组织结构。8日夜间MCS S1入海后,与陆上遗留冷池相关的地面温度边界稳定在珠江口西侧沿海地区;9日凌晨西南低空急流增强后,MCS A2在珠江口沿海残留冷池边界附近开始发展,在向上游迎风方向传播的过程中,逐步形成多条平行β中尺度线状对流组织结构,对流系统整体移动缓慢,造成珠江口沿海地区出现较高的总降水量。计算表明MCS A2冷池边界扩张速度与低层垂直切变相对平衡,有利于形成较为直立的对流单体,增强的边界层水汽输送、更高的对流单体高度有利于产生较高的降水强度。通过总结这两个华南地区长生命史MCS发生发展过程,表明通过分析对流反馈造成的边界层/近地面层热动力特征变化,对于分析MCS发展特征、提高华南前汛期中尺度暴雨预报能力具有重要意义。
中文关键词: 华南前汛期,中尺度对流系统,暴雨,冷池,线状对流
Abstract:Two successive long lived mesoscale convective systems (MCS A1, MCS A2) struck Pearl River Estuary of South China during 8-9 May 2014, and induced extreme precipitation over the region. From noon of 8 May MCS A1 sustained over than 11 h on land of South China, with slowly moving towards southeast from east of Guangxi to Pearl River Estuary in Guangdong. The successive MCS A2 sustained more than 9 h, inducing rainfall of more than 400 mm along the coast of the Pearl River Estuary from early morning to noon of 9 May. Weak cold surface layer sustained in the south of South China with weak surface temperature gradience on the morning of 8 May before the convection burst. The initialization of convection was connected with strengthening of surface south 〖JP2〗wind and topographic lifting near noon of 8 May. MCS A1 evolved from〖JP〗 training line/adjoining stratiform (TL/AS) to mesoscale vortex in convective organization under weak baroclinic environment. With propagation of surface cool pool due to MCS A1’s precipitation in the early night of 8 May, surface temperature boundary and wind convergence zone was pushed to the southwest coast of Guangdong. In the late night of 8 May MCS A1 moved out of land, then MCS A2 was developing adjointly to the remnant cool pool boundary induced by MCS A1 with low level southwest wind enhancing in the early morning of 9 May. MCS A2 was composed by multiple parallel meso β scale line type convective systems, the extreme rainfall was related with quasi stationary cool pool boundary, train moving cells in meso β scale line type convective systems with high precipitation efficiency. From late night of 8 May to morning of 9 May, the balance between cool pool outflow and low level vertical shear could sustain upright convective cells of MCS A2. In conclusion, with carefully researching on convective feedback to boundary and surface layer, the forecast skills could be improved for heavy rainfall events in weak synoptic forcing environment during the pre rainy season in South China.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家重点研发计划(2017YFC1502103)和中国气象局暴雨专家创新团队专项(CMACXTD002-3)共同资助
引用文本:
陈涛,张芳华,符娇兰,于超,2020.2014年5月8—9日引发珠江口区域强降水的两个长生命史MCS特征分析[J].气象,46(4):449-461.
CHEN Tao,ZHANG Fanghua,FU Jiaolan,YU Chao,2020.Analysis of Two Successive Rainstorm Induced Long Lived Mesoscale Convective Systems Struck Pearl River Estuary During 8-9 May 2014[J].Meteor Mon,46(4):449-461.
陈涛,张芳华,符娇兰,于超,2020.2014年5月8—9日引发珠江口区域强降水的两个长生命史MCS特征分析[J].气象,46(4):449-461.
CHEN Tao,ZHANG Fanghua,FU Jiaolan,YU Chao,2020.Analysis of Two Successive Rainstorm Induced Long Lived Mesoscale Convective Systems Struck Pearl River Estuary During 8-9 May 2014[J].Meteor Mon,46(4):449-461.