本文已被:浏览 1263次 下载 4078次
投稿时间:2018-11-16 修订日期:2019-05-06
投稿时间:2018-11-16 修订日期:2019-05-06
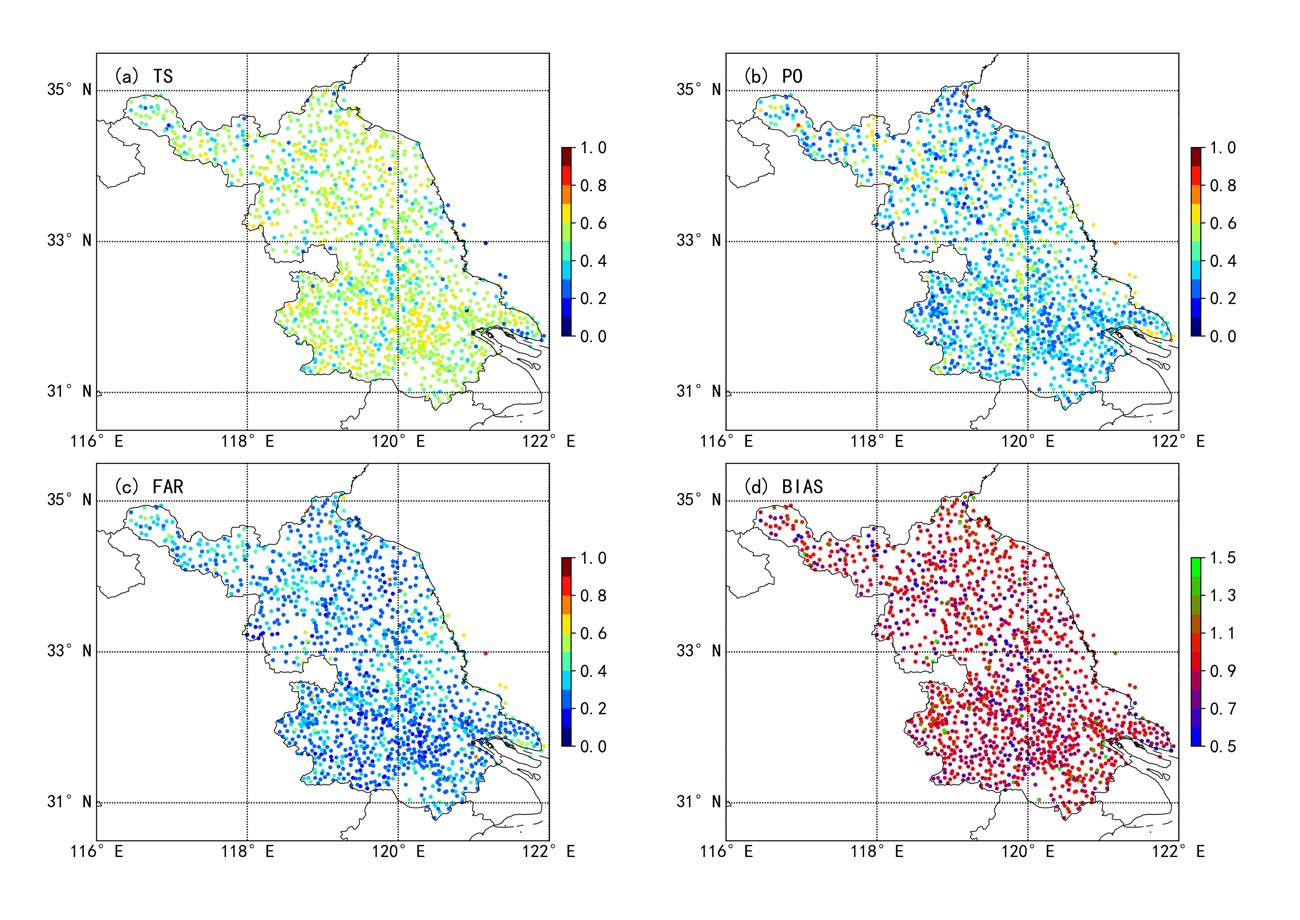
中文摘要: 利用国家级格点实况分析资料与地面气象站实况数据,采用误差分析、技巧评分等方法评估了2017年7月至2018年6月逐时的格点实况产品在江苏地区的地面2 m气温、2 m相对湿度、10 m风和降水要素的一致性和准确性,同时采用MODE检验方法对格点降水产品空间分布偏差进行了分析。结果表明:2 m气温格点实况与自动站观测基本一致,平均绝对误差在0.5~0.8℃,均方根误差在0.8℃左右,其中日最高气温误差较小。格点实况和自动站2 m相对湿度之间的平均绝对误差在5%左右,均方根误差在6%~7%,表现出较高的准确性和稳定性。格点实况10 m风向准确率达到70%左右,而风速准确率仅为56%,与气象站点观测相比有明显差异。格点降水产品的全年有无降水准确率为90%~98%,对于晴雨检验存在带来较大影响的可能。格点实况产品对小雨级别降水的准确率最高,随着降水量级增大,格点实况降水场相比站点观测存在较多的降水漏报,因此,对于降水分量级检验还不适合用格点实况场来替代气象站点观测。设计了一种基于空间形态的降水准确率评分方法对降水空间落区进行检验,格点实况降水场的空间形态准确率评分在0.9左右,较准确地反映了实际降水空间分布。因而,格点实况数据在江苏平原地区都有较高的精度,误差在可接受的范围内,基本可以代替自动站观测作为预报和模式检验的真实实况场,但也存在以下几个方面的问题:(1)格点2 m气温、2 m相对湿度产品在江苏的丘陵地带误差较大,降水产品在海岛气象站准确性较低;(2)格点降水产品一定程度地弱化了大雨以上量级降水强度;(3)格点实况风速产品误差较大,与业务服务需求有一定差距。
中文关键词: 格点实况产品,准确性检验,技巧评分
Abstract:Based on the National Gridded Real-time Observation Datasets covering Jiangsu Province released by the National Meteorological Information Centre of CMA and observations of automatic stations, the consistency and accuracy of hourly 2 m temperature, 2 m relative humidity, 10 m wind and precipitation from July 2017 to June 2018 were evaluated in details by the error statistical analysis, skill score and other methods. The MODE method was applied to reveal the spatial deviation of precipitation between gridded products and observed rainfall records. The results indicate that the mean absolute error of 2 m temperature is between 0.5 and 0.8℃, the root mean square error is around 0.8℃ and the 2 m maximum temperature exhibits a better accuracy than the minimum temperature. The root mean square error range of 2 m relative humidity is 6%-7%, which means that the gridded 2 m temperature and 2 m relative humidity data are well consistent with observation. The accuracy of gridded 10 m wind direction is about 70% while that of wind speed is only 56%, showing a big difference from observation. The verification results of precipitation show that the gridded data with accuracy 90%-98% performs well in forecasting rain or no-rain. Nonetheless, it may still have a great impact on the precipitation frequency evaluation. TS score of light rain is higher than those in other classes, but it declines sharply when rainfall magnitude increases. Moderate rain or above has a relatively higher probability of detection, which means that the precipitation event is less detected than observed. Therefore, for the quantitative precipitation verification, it is not suitable to replace the observation data by the gridded data. Further study on 24 h accumulated rainfall bias between gridded data and observation indicates that the spatial structure of precipitation can be well described by gridded data. The spatial scores of precipitation designed in this article is above 0.9, which reflects the spatial distribution of actual precipitation. Generally, the gridded data in Jiangsu Plain Region can basically replace the automatic stations as the real-time meteorological field for forecast and model verification. However, there are still some problems as follows: (1) the 2 m temperature and 2 m relative humidity have large errors in the hilly areas of Jiangsu Province, and precipitation product from island stations has a lower accuracy; (2) the intensity of precipitation above heavy rain is weakened by the gridded data; (3) the wind speed value is lower than the observation, leaving a gap with the requirement of forecasting operation.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:江苏省气象局预报员专项(JSYBY201802)资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 俞剑蔚 | 江苏省气象台,南京 210008 |
| 李聪 | 南京市气象台,南京 210019 |
| 蔡凝昊 | 江苏省气象台,南京 210008 |
| 刘梅 | 江苏省气象台,南京 210008 |
| 赵启航 | 江苏省气象局,南京 210008 |
引用文本:
俞剑蔚,李聪,蔡凝昊,刘梅,赵启航,2019.国家级格点实况分析产品在江苏地区的适用性评估分析[J].气象,45(9):1288-1298.
YU Jianwei,LI Cong,CAI Ninghao,LIU Mei,ZHAO Qihang,2019.Applicability Evaluation of the National Gridded Real-Time Observation Datasets in Jiangsu Province[J].Meteor Mon,45(9):1288-1298.
俞剑蔚,李聪,蔡凝昊,刘梅,赵启航,2019.国家级格点实况分析产品在江苏地区的适用性评估分析[J].气象,45(9):1288-1298.
YU Jianwei,LI Cong,CAI Ninghao,LIU Mei,ZHAO Qihang,2019.Applicability Evaluation of the National Gridded Real-Time Observation Datasets in Jiangsu Province[J].Meteor Mon,45(9):1288-1298.