本文已被:浏览 1421次 下载 3835次
投稿时间:2019-02-02 修订日期:2019-07-09
投稿时间:2019-02-02 修订日期:2019-07-09
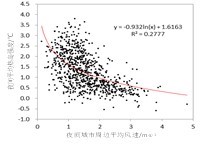
中文摘要: 首先利用上海77个区域站2011—2014年逐时气温和风资料,研究了地面风对上海城市热岛(urban heat island,UHI)的影响及UHI季节性空间分布特征的成因,并从海陆热力差异初步揭示了向岸风对热岛强度(urban heat island intensity,IUHI)的影响。其次利用上海7个国家站1961—2014年逐月气温和风资料,研究了上海各季地面风速与IUHI的年际变化关系。结果表明:(1)UHI中心出现的位置与风向、风速有密切的关系,特别是夜间UHI中心有向城市下风方向漂移的特征,其平均漂移风速阈值为2 m·s-1,UHI区域随风速增大向城市下风方向延伸,IUHI随风速的增大而减小。(2)上海各季夜间UHI特征明显,尤以秋冬季最为明显,春季次之,夏季最弱。春夏季夜间UHI中心出现在城区西北侧,而秋冬季夜间UHI中心稳定在城区,表现为典型UHI。各季白天均表现为下风方大范围增暖现象。季节地面盛行风决定了UHI季节性空间分布特征。(3)白天向岸风具有抑制升温作用(春夏季最为明显),受其影响气温大值区易出现在内陆地区,春夏季城市偏东区IUHI小于偏西区;夜间向岸风具有抑制降温作用(秋冬季最为明显),受其影响秋冬季东部沿海地区出现明显增暖且城市偏东区IUHI大于偏西区。海陆热力差随季节不同和盛行风风速大小决定了向岸风这种作用的大小及影响范围。(4)各季年平均地面风速与IUHI均呈显著负相关,1961—2014年上海各季风速均表现为递减趋势(春冬季最明显),为IUHI增大提供有利条件。21世纪以来各季IUHI均呈现减缓特征(夏秋季最明显),风速并不是导致IUHI减缓的主要因素。
中文关键词: 城市热岛,地面风,上海,向岸风,海陆热力差
Abstract:Using the hourly air temperature and wind data of 77 regional meteorological stations from 2011 to 2014, the influence of surface wind on urban heat island (UHI) in Shanghai and the cause of seasonal spatial distribution of UHI were studied. The influence of onshore wind on urban heat island intensity (IUHI) was preliminarily revealed from sea land thermal difference. Besides, the interannual variation of surface wind speed and IUHI in different seasons in Shanghai was studied based on the monthly air temperature and wind data of seven national meteorological stations from 1961 to 2014. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) The location of UHI center is closely related to wind direction and wind speed. The UHI center at night has the feature of moving to the leeward side of urban area when the average wind speed threshold is 2 m·s-1. With the increase of wind speed, the UHI area extends to the leeward side of city, but the IUHI decreases. (2) UHI characteristics are obvious in Shanghai at night, especially in autumn and winter, followed by spring and summer in order. UHI center appears in the northwest of urban areas at night in spring and summer, while UHI center is stabilized in urban areas at night in autumn and winter, showing typical UHI. In the daytime in each season, there is a large scale warming phenomenon in the downwind area. Seasonal surface prevailing wind determines the seasonal spatial distribution characteristics of UHI. (3) Onshore wind inhibits warming in the daytime, especially obvious in spring and summer. Affected by this phenomenon, the high temperature tends to appear in inland area. The IUHI is larger in the western urban area than in the eastern urban area in spring and summer. Onshore wind inhibits cooling at night, which is the most obvious and caused obvious warming in the eastern coastal areas in autumn and winter. The IUHI is larger in the eastern urban area than that in the western urban area in autumn and winter. Both the land sea thermal difference in different seasons and the prevailing wind speed determine the magnitude and impact scope of the onshore wind. (4) The average annual surface wind speed in each season has a significant negative correlation with the corresponding IUHI. The seasonal wind speed shows a decreasing trend (the most obvious in spring and winter) from 1961 to 2014 in Shanghai, which is good for IUHI increasing. Since the 21st century, the increasing trend of IUHI in all seasons has slowed down (the most obvious in summer and autumn), but wind speed is not the main factor causing the increasing trend of IUHI to slow down.
keywords: urban heat island (UHI), surface wind, Shanghai, onshore wind, land-sea thermal difference
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:华东区域气象科技协同创新基金合作项目(QYHZ201607)资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 徐伟 | 上海市气象局,上海 200030 南京大学,南京 210046 |
| 张蕾 | 上海市气象局,上海 200030 |
| 漆梁波 | 上海市气象局,上海 200030 |
| 刘冬韡 | 上海市气象局,上海 200030 |
| 张仕鹏 | 南京大学,南京 210046 |
| 曹丹萍 | 上海市气象局,上海 200030 |
引用文本:
徐伟,张蕾,漆梁波,刘冬韡,张仕鹏,曹丹萍,2019.地面风对上海城市热岛影响的观测分析[J].气象,45(9):1262-1277.
XU Wei,ZHANG Lei,QI Liangbo,LIU Dongwei,ZHANG Shipeng,CAO Danping,2019.Observation Analysis of the Influence of Surface Wind on Urban Heat Island in Shanghai[J].Meteor Mon,45(9):1262-1277.
徐伟,张蕾,漆梁波,刘冬韡,张仕鹏,曹丹萍,2019.地面风对上海城市热岛影响的观测分析[J].气象,45(9):1262-1277.
XU Wei,ZHANG Lei,QI Liangbo,LIU Dongwei,ZHANG Shipeng,CAO Danping,2019.Observation Analysis of the Influence of Surface Wind on Urban Heat Island in Shanghai[J].Meteor Mon,45(9):1262-1277.