本文已被:浏览 1074次 下载 3878次
投稿时间:2018-01-18 修订日期:2018-06-14
投稿时间:2018-01-18 修订日期:2018-06-14
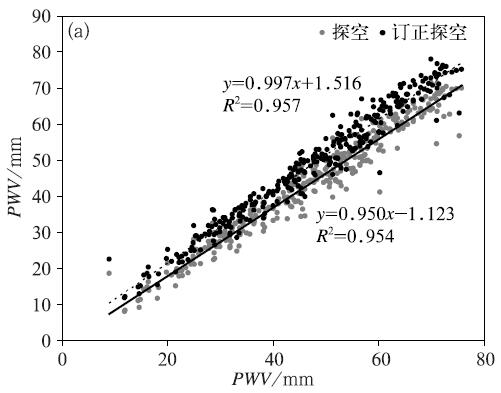
中文摘要: 为了探讨探空观测的水汽可降水量资料的可靠性,本文以GNSS/MET遥感的大气可降水量为参照标准,对广东汕头站2013年以及西藏那曲站2016年6月至2017年5月的两种可降水量观测结果进行对比分析和偏差订正。经过研究分析表明:两个站探空可降水量相比地基GNSS可降水量偏干,偏差分别为7.4%和9.8%。探空可降水量的偏差显示具有季节变化和日变化的特征,其中夏季偏差较明显,00时比12时明显。太阳辐射加热引起的地面气温的日变化和季节变化是造成偏差的重要原因。本文根据太阳辐射偏差订正经验公式,对两个站的探空可降水量进行偏差订正,订正后偏差明显减少。
Abstract:In order to investigate the reliability of total atmospheric water vapor data from L-band radiosonde observations (RS PW), the atmospheric water vapor of GNSS/MET remote sensing (GNSS PW) is taken as the reference standard in this paper to comparatively analyze and correct the observed RS PW at Shantou Station in 2013 and Nagqu Station from June 2016 to May 2017. Research and analysis show that RS PWs at the two stations are obviously smaller than GNSS PW, and the deviations are 7.4% and 9.8%, respectively. The deviation has obvious seasonal and diurnal variation characteristics. In summer it is most obvious, and is more obvious at 0000 UTC than at 1200 UTC. Solar radiation heating and air temperature changes in the daily and seasonal variations are important reasons for the deviation. According to solar radiation bias correction formula, the L bias correction algorithm is proposed and used for correction. Then the deviation is reduced obviously after correction.
keywords: L-band radiosonde, precipitable water vapor, ground-base GNSS, systematic error calibration
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:中国气象局气象探测中心青年基金项目(MOCQNJJ201404)资助
引用文本:
胡姮,曹云昌,梁宏,2019.L波段探空观测偏差分析及订正算法研究[J].气象,45(4):511-521.
HU Heng,CAO Yunchang,LIANG Hong,2019.Systematic Errors and Their Calibrations for Precipitable Water Vapor of L-Band Radiosonde[J].Meteor Mon,45(4):511-521.
胡姮,曹云昌,梁宏,2019.L波段探空观测偏差分析及订正算法研究[J].气象,45(4):511-521.
HU Heng,CAO Yunchang,LIANG Hong,2019.Systematic Errors and Their Calibrations for Precipitable Water Vapor of L-Band Radiosonde[J].Meteor Mon,45(4):511-521.